Electrolyte water contains essential minerals like sodium, potassium, and magnesium that help maintain hydration and support muscle function. Alkaline water has a higher pH level than regular water, which may help neutralize acid in your body and improve hydration efficiency.
Table of Comparison
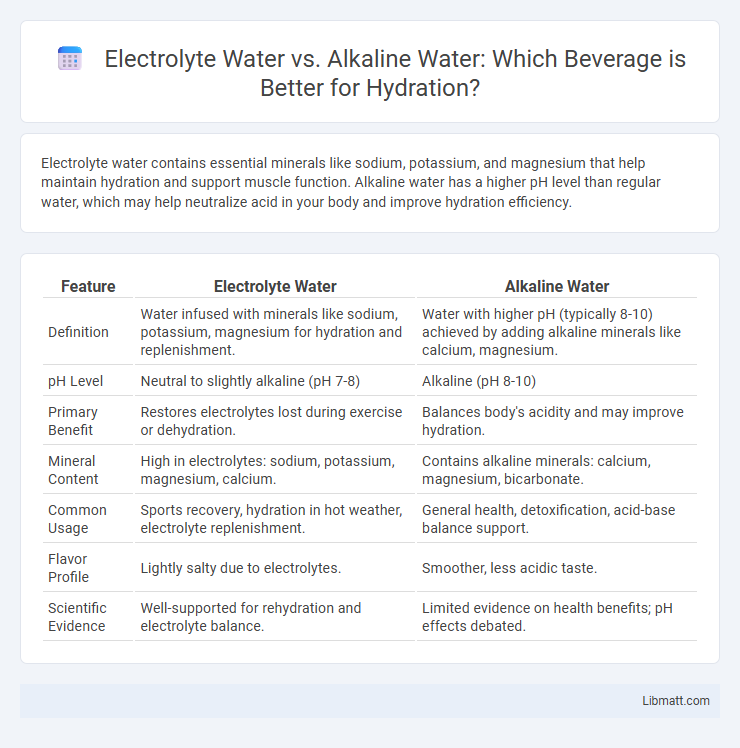
| Feature | Electrolyte Water | Alkaline Water |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Water infused with minerals like sodium, potassium, magnesium for hydration and replenishment. | Water with higher pH (typically 8-10) achieved by adding alkaline minerals like calcium, magnesium. |
| pH Level | Neutral to slightly alkaline (pH 7-8) | Alkaline (pH 8-10) |
| Primary Benefit | Restores electrolytes lost during exercise or dehydration. | Balances body's acidity and may improve hydration. |
| Mineral Content | High in electrolytes: sodium, potassium, magnesium, calcium. | Contains alkaline minerals: calcium, magnesium, bicarbonate. |
| Common Usage | Sports recovery, hydration in hot weather, electrolyte replenishment. | General health, detoxification, acid-base balance support. |
| Flavor Profile | Lightly salty due to electrolytes. | Smoother, less acidic taste. |
| Scientific Evidence | Well-supported for rehydration and electrolyte balance. | Limited evidence on health benefits; pH effects debated. |
Understanding Electrolyte Water
Electrolyte water contains essential minerals such as sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium that help replenish the body's electrolyte balance, which is critical for hydration and muscle function. Unlike alkaline water, which is defined by a higher pH level, electrolyte water emphasizes mineral content to support cellular processes and fluid regulation. Understanding electrolyte water can help you maintain optimal hydration, especially during intense physical activity or heat exposure.
What Is Alkaline Water?
Alkaline water is characterized by a higher pH level, typically around 8 or 9, compared to regular drinking water which has a neutral pH of 7. It contains alkaline minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which contribute to its higher pH and potential health benefits. Alkaline water is often promoted for its ability to neutralize acid in the bloodstream and improve hydration.
Key Differences Between Electrolyte and Alkaline Water
Electrolyte water contains essential minerals such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium that help maintain hydration and balance electrolyte levels in the body. Alkaline water has a higher pH level, typically above 7.5, aimed at neutralizing acid in the bloodstream and improving metabolism. The primary difference lies in electrolyte water's mineral content for hydration support versus alkaline water's emphasis on pH balance and potential antioxidant properties.
Health Benefits of Electrolyte Water
Electrolyte water enhances hydration by replenishing essential minerals like sodium, potassium, and magnesium, which support muscle function and nerve signaling. It helps prevent dehydration during intense physical activity and maintains electrolyte balance critical for optimal cellular function. Consuming electrolyte water can improve endurance, reduce muscle cramps, and accelerate recovery.
Potential Advantages of Alkaline Water
Alkaline water, typically with a pH above 7, may help neutralize acid in the bloodstream, potentially improving hydration and reducing acid reflux symptoms. Rich in essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, alkaline water supports electrolyte balance and bone health. Studies suggest it might enhance antioxidant properties, reducing oxidative stress and promoting overall wellness.
Hydration and Athletic Performance: Which Water Wins?
Electrolyte water enhances hydration by replenishing essential minerals like sodium, potassium, and magnesium lost during intense physical activity, supporting muscle function and reducing cramps. Alkaline water, with a higher pH level, may help neutralize lactic acid buildup and reduce acid reflux, but scientific evidence on its impact on athletic performance remains limited. For athletes seeking rapid rehydration and electrolyte balance, electrolyte water delivers more targeted benefits in maintaining optimal hydration and endurance.
Safety and Side Effects: Electrolyte vs. Alkaline Water
Electrolyte water contains essential minerals like sodium, potassium, and magnesium, which can aid hydration without significant safety concerns when consumed in moderation. Alkaline water, with a higher pH level typically above 8, may cause minor digestive issues or alter stomach acidity if consumed excessively. Both types are generally safe, but individuals with kidney problems or electrolyte imbalances should consult a healthcare professional before regular intake.
How to Choose the Right Water for Your Needs
Choosing the right water for your needs depends on factors such as hydration goals, mineral content, and pH balance. Electrolyte water contains essential minerals like sodium, potassium, and magnesium that support rapid hydration and electrolyte replenishment, ideal after intense physical activity. Alkaline water, with its higher pH level, may help neutralize acidity in the body and support overall wellness, making it suitable for those seeking acid-base balance.
Myths and Misconceptions Debunked
Electrolyte water and alkaline water often face myths such as electrolyte water being only for athletes or alkaline water dramatically altering blood pH; however, electrolyte water primarily replenishes minerals like sodium and potassium lost through sweat, while alkaline water's impact on blood pH is minimal due to the body's natural regulation. Misconceptions also include the belief that alkaline water cures diseases, yet scientific evidence does not support significant health benefits beyond regular hydration. Understanding the distinct functions and realistic effects of both types helps debunk exaggerated claims and promotes informed hydration choices.
Final Verdict: Electrolyte Water or Alkaline Water?
Electrolyte water contains essential minerals like sodium, potassium, and magnesium to help maintain hydration and electrolyte balance during intense physical activity, while alkaline water has a higher pH level that may neutralize acidity but lacks significant scientific evidence supporting major health benefits. Choosing between electrolyte water and alkaline water depends on individual needs: athletes or those with electrolyte imbalances benefit more from electrolyte water, whereas alkaline water is typically used for general hydration with claims of pH balance. For optimal hydration and replenishment after exercise, electrolyte water is the recommended choice.
Electrolyte water vs alkaline water Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com