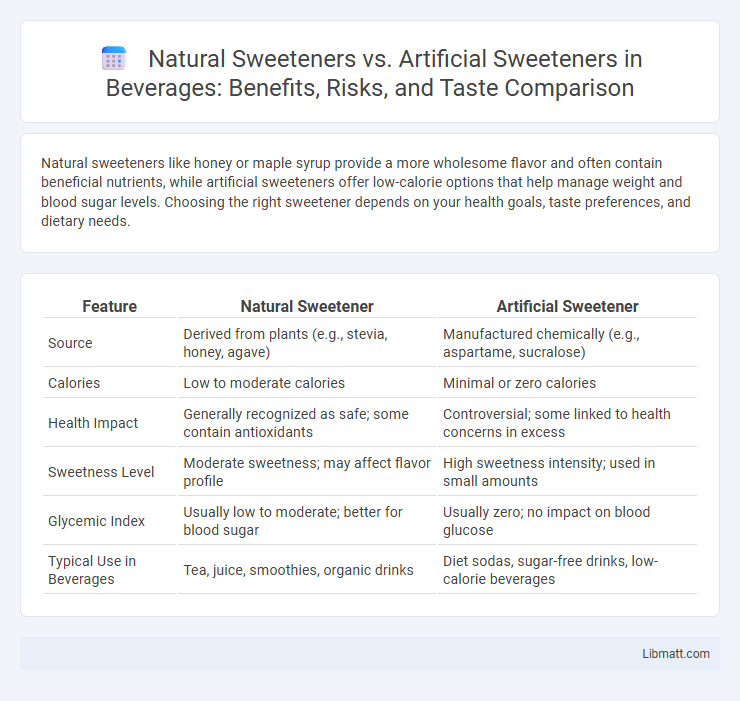
Natural sweeteners like honey or maple syrup provide a more wholesome flavor and often contain beneficial nutrients, while artificial sweeteners offer low-calorie options that help manage weight and blood sugar levels. Choosing the right sweetener depends on your health goals, taste preferences, and dietary needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Natural Sweetener | Artificial Sweetener |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from plants (e.g., stevia, honey, agave) | Manufactured chemically (e.g., aspartame, sucralose) |
| Calories | Low to moderate calories | Minimal or zero calories |
| Health Impact | Generally recognized as safe; some contain antioxidants | Controversial; some linked to health concerns in excess |
| Sweetness Level | Moderate sweetness; may affect flavor profile | High sweetness intensity; used in small amounts |
| Glycemic Index | Usually low to moderate; better for blood sugar | Usually zero; no impact on blood glucose |
| Typical Use in Beverages | Tea, juice, smoothies, organic drinks | Diet sodas, sugar-free drinks, low-calorie beverages |
Introduction to Natural and Artificial Sweeteners
Natural sweeteners, such as honey, maple syrup, and stevia, are derived from plants and contain varying levels of nutrients and antioxidants. Artificial sweeteners like aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin are synthetic compounds designed to provide sweetness with minimal calories and no impact on blood sugar levels. Understanding the differences between these sweeteners can help you make informed choices based on health goals and dietary preferences.
What Are Natural Sweeteners?
Natural sweeteners are substances derived from plants, such as stevia, honey, maple syrup, and agave nectar, valued for their minimal processing and lower glycemic impact compared to refined sugars. These sweeteners contain essential nutrients like antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support your overall health, contrasting sharply with artificial sweeteners that typically offer no nutritional benefits. Choosing natural sweeteners can enhance flavor while providing a more wholesome alternative to synthetic sugar substitutes often linked to metabolic concerns.
Understanding Artificial Sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin, are synthetic sugar substitutes designed to provide sweetness with little to no calories. These compounds are intensely sweet, often hundreds of times sweeter than sugar, which allows their use in smaller amounts while maintaining flavor in foods and beverages. Understanding the metabolic impact and safety profiles of artificial sweeteners can help you make informed choices about their role in your diet compared to natural sweeteners like honey or stevia.
Common Types of Natural Sweeteners
Common types of natural sweeteners include honey, maple syrup, agave nectar, and stevia, each derived from plant sources with varying glycemic indexes. Honey contains antioxidants and trace minerals, while maple syrup provides manganese and zinc, contributing to overall nutritional value. Stevia stands out for its zero-calorie content and ability to maintain blood sugar levels, making it a popular choice for natural, low-calorie sweetening.
Popular Artificial Sweetener Varieties
Popular artificial sweetener varieties include aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin, each offering high sweetness with minimal calories. These synthetic compounds are commonly used to replace sugar in diet sodas, baked goods, and sugar-free products, providing a lower glycemic impact suitable for diabetics. When choosing your sweetener, understanding the potential taste differences and metabolism effects of these varieties can help tailor your dietary preferences effectively.
Health Benefits: Natural vs Artificial Sweeteners
Natural sweeteners like honey, maple syrup, and stevia offer antioxidants, vitamins, and lower glycemic index values, supporting better blood sugar management and reduced inflammation. Artificial sweeteners such as aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin provide calorie-free sweetness but may disrupt gut microbiota and carry potential metabolic risks with excessive use. Choosing natural sweeteners can enhance your overall health by delivering essential nutrients while minimizing reliance on synthetic additives.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Natural sweeteners like stevia and honey generally have fewer side effects but may cause allergic reactions or gastrointestinal discomfort in sensitive individuals. Artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame and sucralose, are linked to potential risks including metabolic disturbances, headaches, and possible impacts on gut microbiota. Your consumption of both types should be moderated to minimize adverse health effects and ensure overall well-being.
Taste and Culinary Uses Comparison
Natural sweeteners like honey and maple syrup offer rich, complex flavors that enhance baked goods and beverages with subtle floral or caramel notes. Artificial sweeteners such as aspartame and sucralose provide intense sweetness without added calories, but their taste can sometimes be perceived as bitter or chemical, affecting recipes that rely on caramelization or browning. Your choice between natural and artificial sweeteners influences texture, aftertaste, and cooking behavior, making it important to select based on desired culinary outcomes.
Impact on Blood Sugar and Weight Management
Natural sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit typically have a lower glycemic index, causing minimal impact on blood sugar levels and supporting better weight management. Artificial sweeteners such as aspartame and sucralose provide sweetness without calories but may influence appetite and insulin response differently, with mixed effects on weight control. Choosing the right sweetener depends on individual metabolic responses and overall dietary habits.
Choosing the Right Sweetener for Your Needs
Natural sweeteners, like honey, maple syrup, and stevia, provide antioxidants and often contain fewer calories, making them a healthier choice for those seeking nutrient-rich options. Artificial sweeteners such as aspartame and sucralose offer zero-calorie alternatives ideal for weight management or blood sugar control but may carry potential health concerns with long-term use. Evaluating your dietary goals, health conditions, and taste preferences will help you choose the right sweetener that aligns with your personal needs and lifestyle.
Natural sweetener vs artificial sweetener Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com