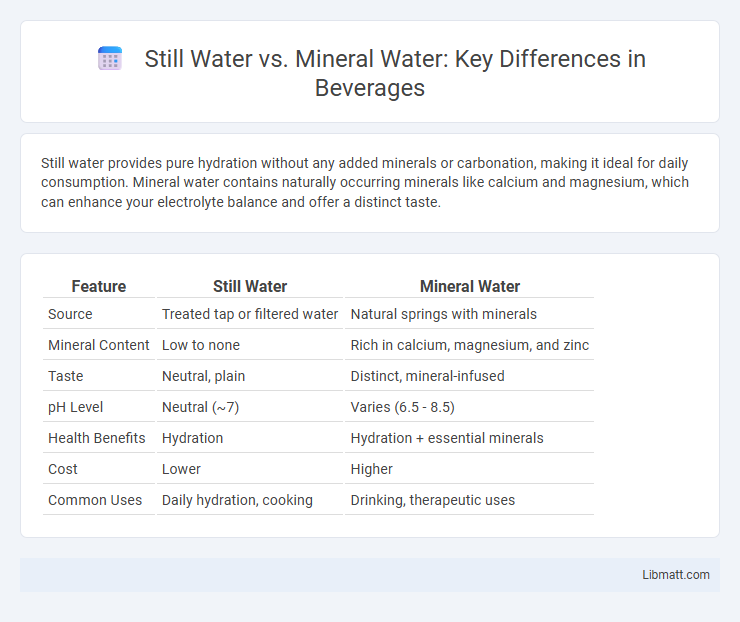
Still water provides pure hydration without any added minerals or carbonation, making it ideal for daily consumption. Mineral water contains naturally occurring minerals like calcium and magnesium, which can enhance your electrolyte balance and offer a distinct taste.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Still Water | Mineral Water |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Treated tap or filtered water | Natural springs with minerals |
| Mineral Content | Low to none | Rich in calcium, magnesium, and zinc |
| Taste | Neutral, plain | Distinct, mineral-infused |
| pH Level | Neutral (~7) | Varies (6.5 - 8.5) |
| Health Benefits | Hydration | Hydration + essential minerals |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Uses | Daily hydration, cooking | Drinking, therapeutic uses |
Introduction: Understanding Still Water and Mineral Water
Still water is natural water free from carbonation, often sourced from springs or purified through filtration, favored for its clean and neutral taste. Mineral water contains dissolved minerals like calcium, magnesium, and sodium, which originate from underground mineral springs, imparting distinct flavors and health benefits. Both types provide essential hydration, but mineral water offers added nutritional value through its unique mineral content.
Definition: What is Still Water?
Still water refers to water that is free from carbonation and has no added gases, making it naturally flat with no bubbles. It can originate from various sources such as springs, wells, or tap supply and typically undergoes filtration to ensure purity. Unlike mineral water, still water may not contain significant amounts of dissolved minerals or salts.
Definition: What is Mineral Water?
Mineral water is a type of water naturally sourced from underground springs, containing various minerals and trace elements like calcium, magnesium, and potassium. Unlike still water, which is typically purified tap or spring water without added minerals, mineral water offers unique health benefits due to its mineral content. Your choice of mineral water can provide both hydration and essential nutrients depending on the source and mineral composition.
Key Differences Between Still Water and Mineral Water
Still water is typically purified and free of minerals, offering a clean, neutral taste that is ideal for hydration without added flavors. Mineral water naturally contains essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which can provide health benefits and a distinct taste profile. Your choice between still water and mineral water depends on whether you prefer pure hydration or the added mineral content for improved taste and nutritional value.
Source and Composition of Still Water
Still water is typically sourced from natural springs, wells, or municipal supplies and is defined by its lack of carbonation and minimal mineral content. Unlike mineral water, which contains specific levels of minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and bicarbonates due to its geological origins, still water has a more neutral mineral composition with trace elements depending on the source. The absence of dissolved gases and lower mineral concentration in still water contributes to its clean, pure taste and its widespread use for hydration and cooking.
Source and Composition of Mineral Water
Mineral water is sourced from natural springs rich in minerals like calcium, magnesium, and sodium, which are naturally dissolved from surrounding rocks, providing unique health benefits and distinct tastes. Still water, on the other hand, typically comes from purified tap water or filtered sources and lacks the essential minerals found in mineral water. When selecting your hydration, understanding the mineral composition can help you choose water that supports your body's mineral balance and overall wellness.
Health Benefits of Still Water
Still water is essential for maintaining optimal hydration, supporting kidney function, and promoting healthy skin without the added minerals that can occasionally cause digestive discomfort. Its purity and lack of dissolved minerals make it an ideal choice for individuals with sensitive digestive systems or those requiring fluid intake without extra sodium or calcium. Consistent consumption of still water aids in regulating body temperature, enhancing metabolic processes, and preventing dehydration-related issues such as headaches and fatigue.
Health Benefits of Mineral Water
Mineral water contains essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which support bone health, cardiovascular function, and electrolyte balance more effectively than still water. The natural mineral content in mineral water aids in improving digestion, hydration, and skin health by providing trace elements crucial for metabolic processes. Choosing mineral water can enhance Your overall wellness by supplying these vital nutrients that plain still water lacks.
Environmental Impact: Still Water vs Mineral Water
Still water generally has a lower environmental impact than mineral water due to simpler processing and less extraction from natural springs. Mineral water often requires more extensive bottling and transportation, increasing its carbon footprint compared to still water sourced locally. Choosing still water can reduce your environmental impact by minimizing resource use and pollution.
Choosing the Right Water: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right water depends on factors such as mineral content, taste preference, and health benefits. Still water typically contains fewer minerals and provides pure hydration, while mineral water offers essential minerals like calcium and magnesium that support bone health and electrolyte balance. You should consider your dietary needs, any specific health conditions, and flavor preferences when selecting between still and mineral water.
Still water vs mineral water Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com