Shelf life testing evaluates the duration a product remains safe and effective under normal storage conditions, while stability testing examines how different environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and light impact your product's quality over time. Understanding both ensures your product maintains its intended performance from manufacture to end-use.
Table of Comparison
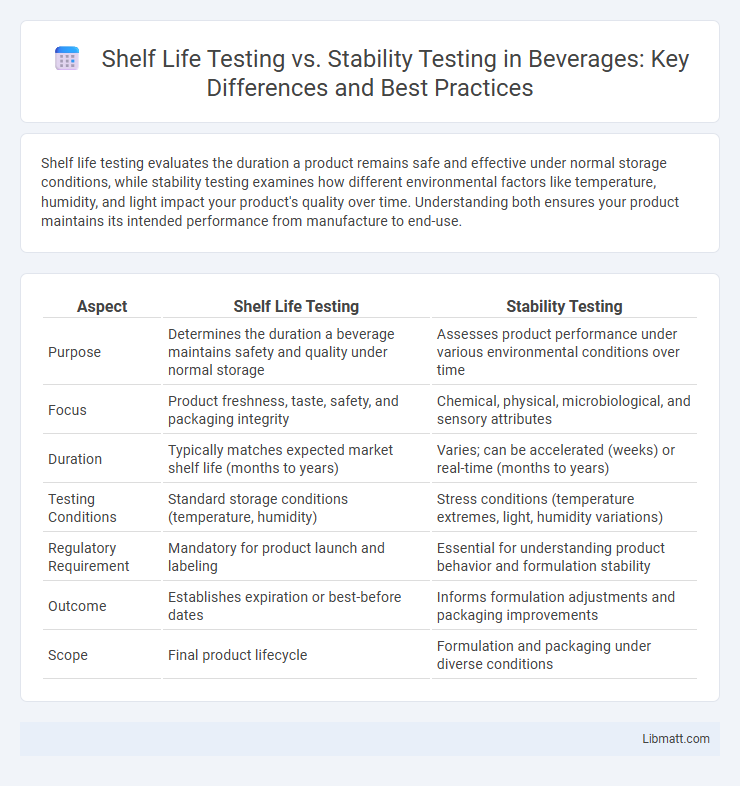
| Aspect | Shelf Life Testing | Stability Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Determines the duration a beverage maintains safety and quality under normal storage | Assesses product performance under various environmental conditions over time |
| Focus | Product freshness, taste, safety, and packaging integrity | Chemical, physical, microbiological, and sensory attributes |
| Duration | Typically matches expected market shelf life (months to years) | Varies; can be accelerated (weeks) or real-time (months to years) |
| Testing Conditions | Standard storage conditions (temperature, humidity) | Stress conditions (temperature extremes, light, humidity variations) |
| Regulatory Requirement | Mandatory for product launch and labeling | Essential for understanding product behavior and formulation stability |
| Outcome | Establishes expiration or best-before dates | Informs formulation adjustments and packaging improvements |
| Scope | Final product lifecycle | Formulation and packaging under diverse conditions |
Introduction to Shelf Life and Stability Testing
Shelf life testing determines the duration a product maintains its quality and safety under specified storage conditions. Stability testing evaluates how environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and light affect a product's chemical, physical, and microbiological characteristics over time. Understanding these processes helps you ensure consistent product performance and regulatory compliance.
Defining Shelf Life Testing
Shelf life testing determines the duration a product maintains its intended quality, safety, and effectiveness under specified storage conditions. It involves evaluating physical, chemical, microbiological, and sensory characteristics to set expiration or use-by dates. This testing is crucial for ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and consumer safety throughout a product's market availability.
Understanding Stability Testing
Stability testing evaluates how a product maintains its quality, safety, and efficacy under various environmental conditions over time. It provides critical data on the shelf life by simulating real-life storage scenarios, helping you determine expiration dates and storage guidelines. This testing ensures that products meet regulatory standards and perform consistently throughout their intended use.
Key Differences Between Shelf Life and Stability Testing
Shelf life testing determines the duration a product maintains its intended quality and safety under specific storage conditions, while stability testing assesses the product's chemical, physical, microbiological, and functional attributes over time. Shelf life testing primarily defines expiration dates, whereas stability testing provides detailed data on how environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and light impact product integrity. Understanding these differences ensures Your product complies with regulatory requirements and maintains consumer trust throughout its lifecycle.
Importance of Shelf Life Testing in Product Development
Shelf life testing determines the duration a product maintains its intended quality and safety under specific storage conditions, making it crucial in product development to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and customer satisfaction. It identifies the optimal time frame for product usage without degradation, preventing potential failures or recalls that could damage brand reputation. Stability testing complements this by evaluating product performance over time, but shelf life testing provides the definitive expiration period essential for accurate labeling and market success.
Significance of Stability Testing Across Industries
Stability testing is crucial across industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics to ensure product safety, efficacy, and quality over time under various environmental conditions. Unlike shelf life testing, which primarily estimates the product's usable life, stability testing provides comprehensive data on how formulation, packaging, and storage impact product integrity. Investing in your stability testing processes safeguards regulatory compliance and consumer trust by preventing product degradation and ensuring consistent performance.
Methods and Protocols for Shelf Life Testing
Shelf life testing methods primarily involve accelerated aging procedures and real-time aging studies to evaluate the degradation rate of products under specific environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure. Protocols for shelf life testing often follow international standards like ICH Q1A(R2) for pharmaceuticals or ASTM guidelines for food and cosmetics, incorporating both physical, chemical, and microbiological assessments to determine product viability over time. Stability testing, while overlapping, emphasizes comprehensive evaluation under stress conditions to establish shelf life but includes broader criteria such as potency, safety, and efficacy over the product's intended storage period.
Techniques Used in Stability Testing
Stability testing employs techniques such as accelerated aging, photostability testing, and stress testing to evaluate a product's degradation over time under various environmental conditions. Analytical methods include high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), and spectroscopic analysis to monitor chemical stability and potency. These techniques ensure the product maintains safety, efficacy, and quality throughout its intended shelf life.
Regulatory Guidelines for Shelf Life and Stability Testing
Regulatory guidelines for shelf life testing and stability testing are established by agencies such as the FDA, EMA, and ICH, ensuring product safety and efficacy throughout its intended use period. Shelf life testing specifically determines the duration a product maintains its quality under recommended storage conditions, while stability testing assesses the product's performance over time under various environmental stresses, including temperature and humidity. You must comply with these guidelines to guarantee accurate expiration dating and maintain regulatory approval for pharmaceuticals and consumer goods.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Testing Approach
Choosing the right testing approach depends on your product's specific requirements and regulatory guidelines. Shelf life testing evaluates how long a product maintains its quality under expected storage conditions, while stability testing assesses the product's behavior and performance over time under various environmental factors. Selecting between these tests ensures accurate data to support product safety, efficacy, and compliance throughout its lifecycle.
Shelf life testing vs stability testing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com