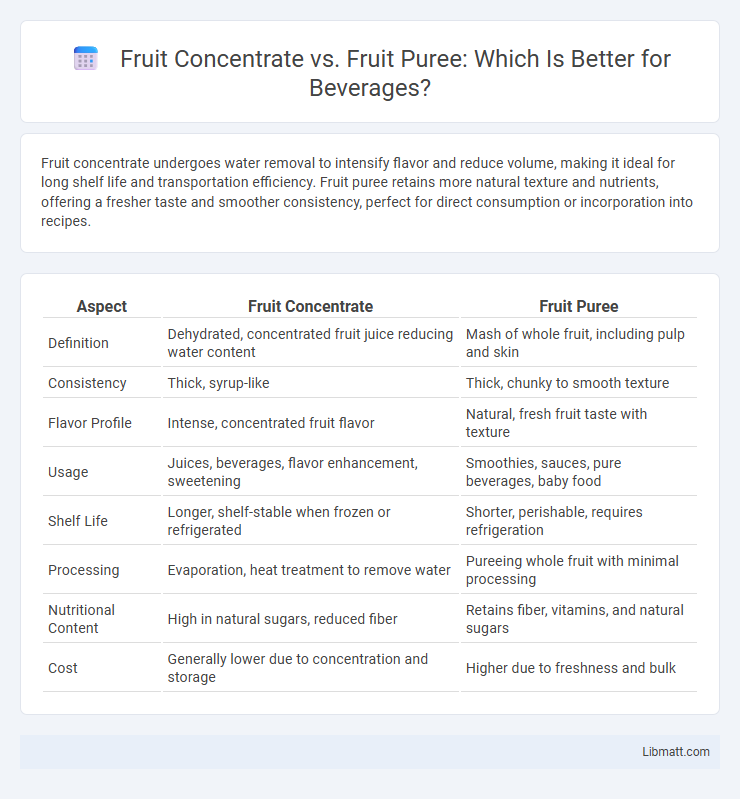
Fruit concentrate undergoes water removal to intensify flavor and reduce volume, making it ideal for long shelf life and transportation efficiency. Fruit puree retains more natural texture and nutrients, offering a fresher taste and smoother consistency, perfect for direct consumption or incorporation into recipes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fruit Concentrate | Fruit Puree |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dehydrated, concentrated fruit juice reducing water content | Mash of whole fruit, including pulp and skin |
| Consistency | Thick, syrup-like | Thick, chunky to smooth texture |
| Flavor Profile | Intense, concentrated fruit flavor | Natural, fresh fruit taste with texture |
| Usage | Juices, beverages, flavor enhancement, sweetening | Smoothies, sauces, pure beverages, baby food |
| Shelf Life | Longer, shelf-stable when frozen or refrigerated | Shorter, perishable, requires refrigeration |
| Processing | Evaporation, heat treatment to remove water | Pureeing whole fruit with minimal processing |
| Nutritional Content | High in natural sugars, reduced fiber | Retains fiber, vitamins, and natural sugars |
| Cost | Generally lower due to concentration and storage | Higher due to freshness and bulk |
Introduction to Fruit Concentrate and Fruit Puree
Fruit concentrate is a dense, syrupy liquid made by removing water from fruit juice, resulting in intensified flavor and longer shelf life. Fruit puree consists of blended whole fruit, including pulp and fiber, offering a thicker texture and more natural fruit integrity. Both forms serve as versatile ingredients in beverages, desserts, and food products, each providing distinct taste and texture profiles.
Key Differences Between Fruit Concentrate and Fruit Puree
Fruit concentrate is a liquid extracted by removing water from fruit juice, resulting in a thicker, sweeter product with higher sugar content and longer shelf life compared to fruit puree. Fruit puree consists of mashed whole fruit, including skin and pulp, retaining more fiber, nutrients, and a natural texture, making it ideal for smoothies and baby food. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right ingredient for your recipe based on desired flavor intensity, texture, and nutritional value.
Production Process: Concentrate vs Puree
Fruit concentrate is produced by removing the water content from fruit juice through evaporation, resulting in a thicker, more shelf-stable product with intensified flavor and nutrients. Fruit puree, on the other hand, involves blending whole fruits, including pulp and skin, into a smooth, thick consistency without removing water, preserving more natural fiber and fresh taste. Understanding these distinct production processes helps you choose the right option based on texture, flavor intensity, and application needs.
Nutritional Value Comparison
Fruit concentrate typically contains a higher sugar content and reduced water compared to fruit puree, resulting in increased calorie density but often lower fiber levels. Fruit puree retains more natural fiber and nutrients such as vitamins and antioxidants due to minimal processing, supporting better digestion and overall health. While concentrate offers longer shelf life and intense flavor, puree provides a more nutrient-rich profile beneficial for balanced nutrition.
Flavor and Texture: What Sets Them Apart
Fruit concentrate offers an intensified flavor profile and a thicker, syrup-like texture due to the removal of water content, making it ideal for adding sweetness and concentrated fruit essence. Fruit puree retains the natural fiber and pulp of the fruit, providing a smoother, more natural texture and a fresher, less concentrated taste. These differences in flavor and texture significantly influence their applications in food products and beverages.
Common Uses in Food and Beverage Industry
Fruit concentrate is widely used in beverages, yogurts, and confectionery for its intense flavor and longer shelf life, making it ideal for juices, smoothies, and flavoring agents. Fruit puree, known for its thicker texture and natural fruit content, is commonly found in baby foods, baked goods, sauces, and dessert fillings, providing a fresh fruit taste and nutritional benefits. Both ingredients serve specific roles in food formulation, with concentrates enhancing sweetness and puree adding texture and fiber.
Shelf Life and Storage Considerations
Fruit concentrate typically offers a longer shelf life than fruit puree due to its reduced water content, which inhibits microbial growth and spoilage. Concentrates can be stored at room temperature in sealed containers for several months, while purees generally require refrigeration and have a shorter shelf life, often lasting only a few weeks. Proper storage conditions such as airtight packaging and controlled temperatures are crucial to maintaining the quality and safety of both fruit concentrate and puree.
Health Benefits and Concerns
Fruit concentrate offers a concentrated source of vitamins and antioxidants, which can boost nutrient intake but often contains added sugars that may impact blood sugar levels and contribute to calorie overload. Fruit puree retains more fiber and natural nutrients, promoting better digestion and satiety while maintaining a lower glycemic index. Both options provide essential nutrients, but puree is generally healthier due to its lower processing level and minimal added sugars.
Cost and Availability
Fruit concentrate generally offers a more cost-effective option due to its reduced water content, which lowers transportation and storage expenses. It is widely available year-round, making it a reliable choice for manufacturers seeking consistent supply and pricing. In contrast, fruit puree is often pricier and less readily available because it retains natural moisture and may have seasonal limitations depending on fruit harvests.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Needs
Fruit concentrate offers a more intense flavor and longer shelf life, making it ideal for beverages, confectionery, and baking where strong fruit taste and preservation are essential. Fruit puree retains more of the fruit's natural texture and nutritional profile, suitable for smoothies, baby foods, and sauces that benefit from a fresh, wholesome consistency. Selecting between fruit concentrate and puree depends on the desired flavor intensity, application, and nutritional requirements of your product or recipe.
Fruit concentrate vs fruit puree Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com