Carbonated water contains dissolved carbon dioxide gas under pressure, creating bubbles and a slightly acidic taste, while sparkling water refers to naturally carbonated water sourced from mineral springs. Understanding the differences allows you to choose the best option for hydration or beverage mixing based on flavor and mineral content preferences.
Table of Comparison
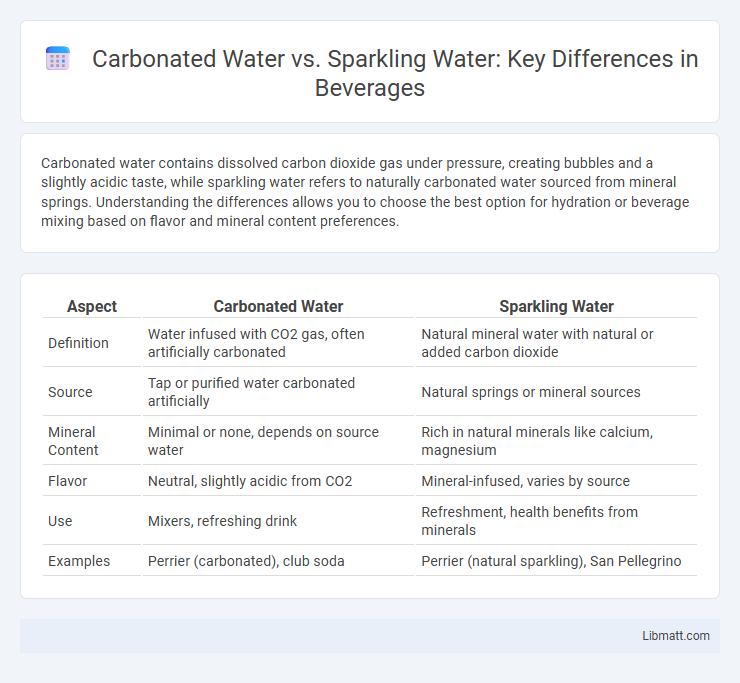
| Aspect | Carbonated Water | Sparkling Water |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Water infused with CO2 gas, often artificially carbonated | Natural mineral water with natural or added carbon dioxide |
| Source | Tap or purified water carbonated artificially | Natural springs or mineral sources |
| Mineral Content | Minimal or none, depends on source water | Rich in natural minerals like calcium, magnesium |
| Flavor | Neutral, slightly acidic from CO2 | Mineral-infused, varies by source |
| Use | Mixers, refreshing drink | Refreshment, health benefits from minerals |
| Examples | Perrier (carbonated), club soda | Perrier (natural sparkling), San Pellegrino |
Introduction to Carbonated and Sparkling Water
Carbonated water contains dissolved carbon dioxide gas, creating effervescence similar to soda, and can include added minerals or natural flavors. Sparkling water refers specifically to naturally carbonated water sourced from springs, offering a distinctive mineral taste while maintaining natural carbonation. Understanding the difference helps you choose between artificially infused bubbles in carbonated water and naturally occurring carbonation in sparkling water for your hydration preferences.
Defining Carbonated Water
Carbonated water is water infused with carbon dioxide gas under pressure, creating fizzy bubbles and a slightly tart taste due to the formation of carbonic acid. It serves as a base for various beverages including sodas, tonic water, and flavored sparkling drinks. Unlike sparkling water, carbonated water may include additives such as minerals or flavoring agents to enhance taste and texture.
What is Sparkling Water?
Sparkling water is water infused with carbon dioxide gas under pressure, creating bubbles and a fizzy texture similar to soda but typically without added sugars or flavors. It can occur naturally from mineral springs or be artificially carbonated to enhance refreshment and mouthfeel. You can enjoy sparkling water as a healthier alternative to sugary drinks while still experiencing a lively carbonation.
Key Differences Between Carbonated and Sparkling Water
Carbonated water contains added carbon dioxide gas under pressure, giving it a distinct fizzy sensation and often a slightly acidic taste due to carbonic acid formation. Sparkling water, a natural or artificially carbonated water type, features naturally occurring minerals and subtle effervescence that provides a smoother mouthfeel. The key differences lie in carbonation source, mineral content, and flavor profile, with carbonated water commonly being artificially carbonated and sparkling water often sourced from natural springs.
Natural vs Artificial Carbonation
Carbonated water is typically infused with carbon dioxide gas artificially, creating bubbles through a manufacturing process, while sparkling water naturally contains carbonation from natural springs where CO2 is dissolved. Natural sparkling water often contains minerals like calcium, magnesium, and sodium, enhancing its flavor and providing health benefits, whereas artificial carbonation adds bubbles without these minerals. Understanding the source of carbonation helps in choosing between naturally carbonated mineral water and artificially carbonated soda water for taste and nutritional content.
Health Benefits and Risks
Carbonated water and sparkling water both provide hydration with the added benefit of bubbles, which can aid digestion and reduce indigestion symptoms. Sparkling water often contains natural minerals that may support bone health and electrolyte balance, while plain carbonated water is free from sugars and calories, making it a healthier alternative to sugary sodas. Excessive consumption of carbonated drinks can lead to dental enamel erosion and bloating due to carbonation, but moderate intake is generally safe and may promote improved digestion.
Taste and Texture Comparison
Carbonated water contains added carbon dioxide, giving it a sharp, tangy taste and a more intense fizz compared to sparkling water, which naturally contains dissolved minerals that create a smoother, subtler effervescence. The texture of carbonated water is often described as more abrasive and biting due to higher levels of carbonation, while sparkling water offers a softer mouthfeel with a balanced mineral finish. Taste variations depend on mineral content in sparkling water, which can range from slightly sweet to mildly salty, whereas carbonated water typically has a neutral or slightly acidic flavor profile.
Common Uses in Beverages and Recipes
Carbonated water, often infused with added minerals and a slightly more intense fizz, is commonly used in mixed drinks and cocktails to enhance flavor and create a crisp mouthfeel. Sparkling water, typically naturally carbonated or lightly carbonated with a more subtle bubble, is favored for refreshing hydration on its own or as a gentle base in fruit-infused beverages and light recipes. Your choice depends on the desired texture and intensity in drinks or culinary creations where effervescence plays a key role.
Environmental Impact and Packaging
Carbonated water and sparkling water often come in single-use plastic or glass bottles, contributing to environmental concerns like plastic waste and carbon emissions from production and transportation. You can reduce environmental impact by choosing sparkling water packaged in recyclable glass bottles or opting for carbonated water made at home with a soda maker, minimizing excessive packaging. Sustainable packaging choices and local sourcing significantly affect the carbon footprint of both beverages.
Which One Should You Choose?
Carbonated water and sparkling water both contain dissolved carbon dioxide, but sparkling water typically comes from a natural mineral source and may include added minerals for flavor, while carbonated water is artificially infused with CO2. Choosing between the two depends on taste preference and dietary needs, with sparkling water offering a mineral-rich option and carbonated water providing a neutral, customizable base. For hydration with added minerals, sparkling water is ideal, but for a pure carbonation experience without extra flavors, carbonated water is the better choice.
Carbonated water vs sparkling water Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com