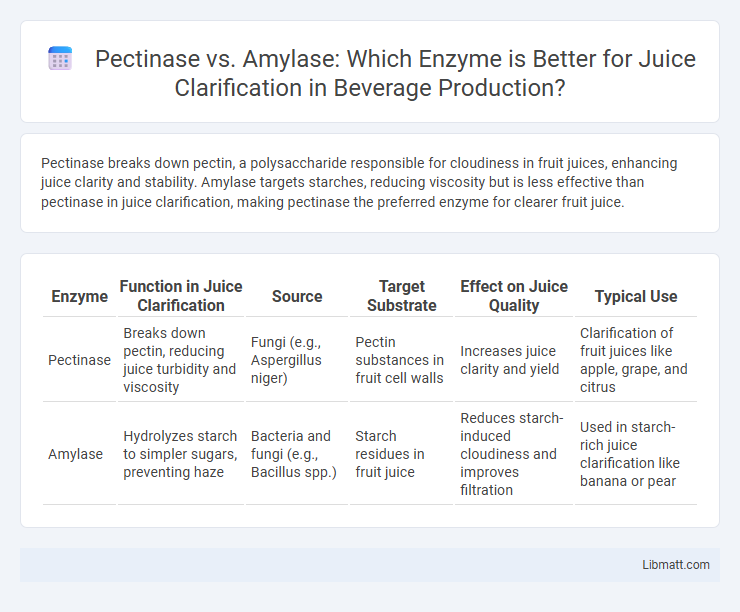
Pectinase breaks down pectin, a polysaccharide responsible for cloudiness in fruit juices, enhancing juice clarity and stability. Amylase targets starches, reducing viscosity but is less effective than pectinase in juice clarification, making pectinase the preferred enzyme for clearer fruit juice.
Table of Comparison
| Enzyme | Function in Juice Clarification | Source | Target Substrate | Effect on Juice Quality | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pectinase | Breaks down pectin, reducing juice turbidity and viscosity | Fungi (e.g., Aspergillus niger) | Pectin substances in fruit cell walls | Increases juice clarity and yield | Clarification of fruit juices like apple, grape, and citrus |
| Amylase | Hydrolyzes starch to simpler sugars, preventing haze | Bacteria and fungi (e.g., Bacillus spp.) | Starch residues in fruit juice | Reduces starch-induced cloudiness and improves filtration | Used in starch-rich juice clarification like banana or pear |
Introduction to Juice Clarification
Juice clarification involves removing suspended solids and haze-causing particles to enhance clarity and stability. Pectinase targets pectin, a structural polysaccharide in fruit cell walls, breaking it down to reduce viscosity and promote juice flow. Amylase, on the other hand, breaks down starch molecules that can cause cloudiness, improving the overall clarity and brightness of Your juice.
What is Pectinase?
Pectinase is an enzyme that breaks down pectin, a structural polysaccharide found in plant cell walls, playing a crucial role in juice clarification by reducing cloudiness and improving filterability. It hydrolyzes pectin substances, facilitating the release of juice from fruit pulp and enhancing yield. Compared to amylase, which targets starch degradation, pectinase specifically targets the pectic substances responsible for juice viscosity and turbidity.
What is Amylase?
Amylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of starch molecules into simpler sugars such as maltose and glucose, playing a crucial role in juice clarification by reducing starch-induced cloudiness. It targets starch residues that cause turbidity and viscosity in fruit juices, improving clarity and stability. Using amylase in juice processing enhances the visual appeal and quality of your final product by ensuring a clearer and more refined juice.
Roles of Pectinase in Juice Clarification
Pectinase plays a crucial role in juice clarification by breaking down pectin, a complex polysaccharide that causes turbidity and cloudiness in fruit juices. This enzymatic action helps to reduce viscosity, improve juice yield, and enhance the clarity and stability of the final product. Your juice processing benefits from more efficient sedimentation and filtration due to the effective degradation of pectin by pectinase.
Roles of Amylase in Juice Clarification
Amylase plays a crucial role in juice clarification by breaking down starch molecules into simpler sugars, which reduces juice viscosity and improves filtration efficiency. This enzymatic action helps prevent haze formation and enhances the clarity and stability of fruit juices. Amylase complements pectinase by targeting starch residues, ensuring a more complete clarification process in juice production.
Mechanisms of Action: Pectinase vs Amylase
Pectinase breaks down pectin, a complex polysaccharide in fruit cell walls, by hydrolyzing the a-1,4-glycosidic bonds, leading to the degradation of the middle lamella and cell separation. Amylase targets starch by catalyzing the hydrolysis of a-1,4-glycosidic linkages in amylose and amylopectin, converting starch into simpler sugars like maltose and glucose. In juice clarification, pectinase reduces viscosity by breaking down pectin, while amylase decreases turbidity by breaking down starch residues.
Impact on Juice Quality and Yield
Pectinase significantly improves juice yield by breaking down pectin substances that cause cloudiness, resulting in clearer, more stable juice with enhanced clarity and brightness. Amylase, while primarily targeting starch breakdown, contributes marginally to juice clarification by reducing viscosity, but its impact on overall yield and clarity is less pronounced compared to pectinase. The combined use of pectinase and amylase enzymes can optimize juice extraction, improving both volume and visual quality, especially in starch-rich fruits.
Comparative Efficiency: Pectinase vs Amylase
Pectinase demonstrates higher efficiency in juice clarification by breaking down pectin substances that cause turbidity and increase juice yield significantly. Amylase, while effective in hydrolyzing starch residues that may cloud juice, plays a secondary role compared to pectinase in clarifying fruit juices. Your juice processing will benefit more from pectinase due to its targeted action on pectin, improving clarity and filtration speed.
Industry Applications and Best Practices
Pectinase and amylase are crucial enzymes in juice clarification, with pectinase primarily breaking down pectin substances that cause turbidity in fruit juices, improving clarity and yield in the fruit juice industry. Amylase targets starch residues that can cause haze or viscosity issues, thus enhancing the filtration and stability of the final product, especially in starch-rich juices like apple or pear. Best practices involve optimizing enzyme concentration, temperature, and pH based on the specific juice matrix to maximize clarity and minimize processing time while preserving nutritional quality.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Enzyme for Juice Clarification
Pectinase targets pectin substances in fruit juices, enhancing juice clarity and yield by breaking down pectic substances effectively, while amylase primarily hydrolyzes starches, which are less prevalent in most fruit juices. For juice clarification, pectinase is generally the preferred enzyme due to its specificity and efficiency in degrading pectins that cause turbidity. Selecting pectinase over amylase leads to clearer juice with better texture, improved filtration, and reduced viscosity, making it the optimal choice for juice clarification processes.
Pectinase vs amylase (juice clarification) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com