Electrogalvanized steel features a thin, uniform zinc coating applied through an electrolytic process, offering excellent surface finish and corrosion resistance ideal for indoor use. Your choice of hot-dip galvanized steel, coated with a thicker layer of molten zinc, provides superior durability and protection against harsh outdoor environments, making it better suited for heavy-duty applications.
Table of Comparison
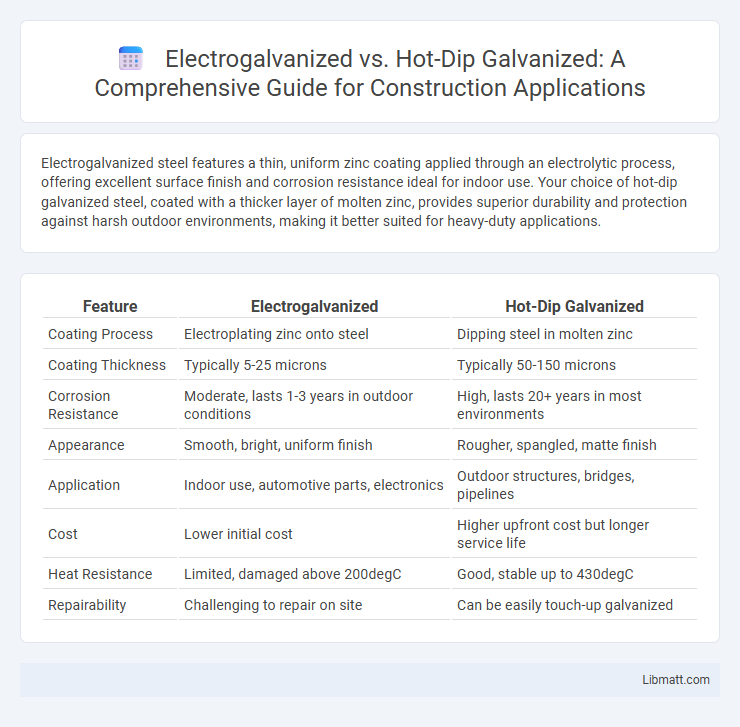
| Feature | Electrogalvanized | Hot-Dip Galvanized |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Process | Electroplating zinc onto steel | Dipping steel in molten zinc |
| Coating Thickness | Typically 5-25 microns | Typically 50-150 microns |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, lasts 1-3 years in outdoor conditions | High, lasts 20+ years in most environments |
| Appearance | Smooth, bright, uniform finish | Rougher, spangled, matte finish |
| Application | Indoor use, automotive parts, electronics | Outdoor structures, bridges, pipelines |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher upfront cost but longer service life |
| Heat Resistance | Limited, damaged above 200degC | Good, stable up to 430degC |
| Repairability | Challenging to repair on site | Can be easily touch-up galvanized |
Introduction to Galvanization
Galvanization is a protective process that applies a zinc coating to steel to prevent corrosion and enhance durability. Electrogalvanized steel features a thin, uniform zinc layer deposited through electrolytic plating, offering smooth surface finish and moderate corrosion resistance. Hot-dip galvanized steel involves immersing steel in molten zinc, resulting in a thicker, rugged coating ideal for heavy-duty corrosion protection in harsh environments.
What Is Electrogalvanization?
Electrogalvanization is a process that applies a thin layer of zinc onto a metal surface using an electrical current, creating a uniform, corrosion-resistant coating. This method provides a smooth finish ideal for automotive and electronic components, where precise coating thickness and aesthetics are critical. Compared to hot-dip galvanizing, electrogalvanized coatings are thinner and offer less sacrificial protection but excel in applications requiring superior surface quality and paint adherence.
What Is Hot-Dip Galvanization?
Hot-dip galvanization involves immersing steel or iron into molten zinc, creating a robust, corrosion-resistant coating that penetrates the metal's surface. This process provides thicker protection than electrogalvanized coatings, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial environments exposed to harsh weather conditions. Your choice between electrogalvanized and hot-dip galvanized depends on the required durability and exposure, with hot-dip offering superior long-term corrosion resistance.
Key Differences Between Electrogalvanized and Hot-Dip Galvanized
Electrogalvanized steel features a thin, uniform zinc coating applied through an electroplating process, providing a smooth finish ideal for automotive and appliance parts requiring precise dimensions. Hot-dip galvanized steel undergoes immersion in molten zinc, resulting in a thicker, more durable coating that offers superior corrosion resistance, especially in outdoor or industrial environments. Your choice depends on the required corrosion protection level and surface finish, with hot-dip galvanizing favored for long-term durability and electrogalvanizing chosen for aesthetic and dimensional control.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Electrogalvanized steel features a thinner zinc coating, offering moderate corrosion resistance suitable for indoor applications or environments with low moisture exposure. Hot-dip galvanized steel undergoes a thicker, more durable zinc layer formed by immersing the steel in molten zinc, providing superior protection against rust and corrosion in harsh outdoor or industrial environments. The enhanced corrosion resistance of hot-dip galvanizing significantly extends the lifespan of steel structures exposed to rain, salt, and other corrosive elements compared to electrogalvanized finishes.
Surface Finish and Appearance
Electrogalvanized steel offers a smooth, bright, and uniform surface finish due to the controlled electroplating process, making it ideal for applications where aesthetics are critical. Hot-dip galvanized steel features a thicker, rougher coating with a spangled or matte appearance resulting from the molten zinc bath, providing superior corrosion resistance but a less polished look. The choice between the two depends on whether the priority is a lustrous finish or enhanced durability in harsh environments.
Application Suitability
Electrogalvanized steel provides a smooth, uniform coating ideal for indoor applications and environments with minimal exposure to moisture, commonly used in automotive parts, appliances, and electronics. Hot-dip galvanized steel features a thicker, more robust zinc layer that offers superior corrosion resistance, making it highly suitable for outdoor structures, construction materials, and heavy-duty industrial applications. Selecting between electrogalvanized and hot-dip galvanized steel depends on the required durability, environmental exposure, and aesthetic finish needed for the specific application.
Cost and Economic Analysis
Electrogalvanized coatings typically cost less upfront due to lower material use and faster application but offer thinner protection, potentially leading to higher maintenance expenses over time. Hot-dip galvanized steel provides thicker, more durable corrosion resistance, which can reduce long-term costs despite higher initial investment. Your choice should balance immediate budget constraints with the anticipated lifespan and maintenance costs in your specific environment.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Electrogalvanized steel typically offers a lifespan of around 5 to 10 years and requires minimal maintenance due to its thin zinc coating that resists corrosion in indoor or mild environments. Hot-dip galvanized steel, with its thicker zinc layer averaging 50 to 100 microns, provides superior corrosion protection lasting 20 to 50 years, especially in harsh outdoor conditions, and demands less frequent maintenance. Longevity and upkeep needs strongly depend on environmental exposure, with hot-dip galvanizing preferred for applications requiring extended durability and lower maintenance over time.
Choosing the Right Galvanization Method
Electrogalvanized steel offers a smooth, thin zinc coating ideal for indoor applications requiring aesthetic finishes and moderate corrosion resistance. Hot-dip galvanized steel provides a thicker, more durable zinc layer, making it suitable for outdoor or harsh environments with extended exposure to moisture and corrosive elements. Selecting between electrogalvanizing and hot-dip galvanizing depends on factors such as environmental conditions, required durability, coating thickness, and budget constraints.
Electrogalvanized vs hot-dip galvanized Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com