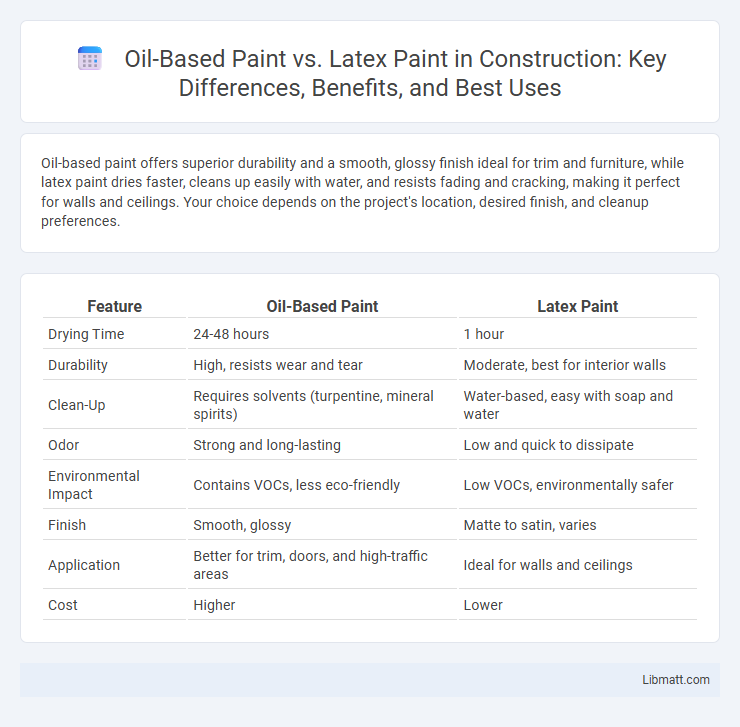
Oil-based paint offers superior durability and a smooth, glossy finish ideal for trim and furniture, while latex paint dries faster, cleans up easily with water, and resists fading and cracking, making it perfect for walls and ceilings. Your choice depends on the project's location, desired finish, and cleanup preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Oil-Based Paint | Latex Paint |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Time | 24-48 hours | 1 hour |
| Durability | High, resists wear and tear | Moderate, best for interior walls |
| Clean-Up | Requires solvents (turpentine, mineral spirits) | Water-based, easy with soap and water |
| Odor | Strong and long-lasting | Low and quick to dissipate |
| Environmental Impact | Contains VOCs, less eco-friendly | Low VOCs, environmentally safer |
| Finish | Smooth, glossy | Matte to satin, varies |
| Application | Better for trim, doors, and high-traffic areas | Ideal for walls and ceilings |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Understanding Oil-Based Paints: Key Characteristics
Oil-based paints possess superior durability and a smoother finish due to their slow drying time and chemical composition, which allows them to adhere well to surfaces like wood and metal. They offer excellent resistance to moisture and wear, making them ideal for high-traffic areas and exterior applications. Understanding these key characteristics helps you choose the right paint based on project needs and environmental conditions.
What is Latex Paint? Composition and Features
Latex paint is a water-based paint composed primarily of acrylic or vinyl polymers, water, pigments, and additives, making it quick-drying and easy to clean with soap and water. Its flexible, durable finish resists cracking and fading, ideal for interior and exterior surfaces where moisture resistance is essential. Choosing latex paint for your project ensures lower VOC emissions compared to oil-based paint, promoting a safer environment and easier application.
Durability Comparison: Oil-Based vs Latex Paint
Oil-based paint offers superior durability, making it more resistant to wear, scratches, and moisture, ideal for high-traffic areas and exterior surfaces. Latex paint, while less durable than oil-based variants, provides better flexibility and resistance to cracking, making it suitable for interior walls and surfaces subject to temperature fluctuations. Advances in latex formulations have narrowed the durability gap, but oil-based paint remains preferred for projects requiring long-lasting, hard finishes.
Surface Applications: Where Each Paint Shines
Oil-based paint excels on surfaces requiring durability and a smooth, hard finish, such as trim, doors, and cabinets, thanks to its strong adhesion and resistance to wear. Latex paint is ideal for walls, ceilings, and exterior siding due to its quick drying time, flexibility, and easy cleanup with water. For high-moisture areas like bathrooms or kitchens, latex paint with mildew-resistant properties outperforms oil-based options by preventing mold growth and peeling.
Ease of Application: Oil-Based vs Latex Paint
Oil-based paint offers a smoother finish and longer drying time, allowing for easier blending and leveling during application. Latex paint dries faster and cleans up easily with water, making it more user-friendly for quick projects and less experienced painters. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize ease of cleanup and fast drying or a flawless, durable finish.
Drying Time and Curing Differences
Oil-based paint typically requires 6 to 8 hours to dry to the touch and up to 24 hours to fully cure, making it slower than latex paint, which usually dries within 1 hour and cures in about 2 weeks. The longer drying and curing times of oil-based paint result from its slow oxidation process, which enhances durability and smooth finish. Your project timeline may benefit from choosing latex paint for quicker turnaround, especially in environments requiring fast recoating.
Paint Finish: Gloss, Sheen, and Texture
Oil-based paint offers a smoother, more durable finish with higher gloss and sheen levels, making it ideal for surfaces requiring a polished look. Latex paint, favoring ease of use and quick drying, provides a range of sheens from matte to semi-gloss but generally has less gloss compared to oil-based options. Texture variations in oil-based paints tend to be richer and thicker, while latex finishes appear thinner and more flexible, suitable for diverse applications.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Oil-based paint releases higher levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to indoor air pollution and posing greater environmental hazards during application and disposal. Latex paint contains fewer VOCs, making it a safer choice for indoor use and reducing its overall environmental footprint. Proper ventilation and protective gear remain essential when handling oil-based paint to minimize health risks linked to toxic fumes and chemical exposure.
Maintenance and Long-Term Performance
Oil-based paint offers superior durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-traffic areas or surfaces prone to moisture, but it requires stronger solvents like mineral spirits for cleaning and longer drying times. Latex paint provides easier maintenance with water-based cleanup, faster drying, and better flexibility to resist cracking and fading over time, which can extend the lifespan of your painted surfaces. Choosing between the two depends on your priorities for ease of upkeep versus long-term toughness in different environmental conditions.
Cost and Value: Choosing the Right Paint for Your Project
Oil-based paint generally costs more upfront but offers superior durability and a smoother finish, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and surfaces requiring a tough, long-lasting coat. Latex paint provides excellent value with lower cost, faster drying times, and easier cleanup, suited for most interior walls and ceilings. Evaluating project requirements, surface type, and budget--oil-based for resilience or latex for cost-efficiency--ensures optimal performance and value.
Oil-based paint vs latex paint Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com