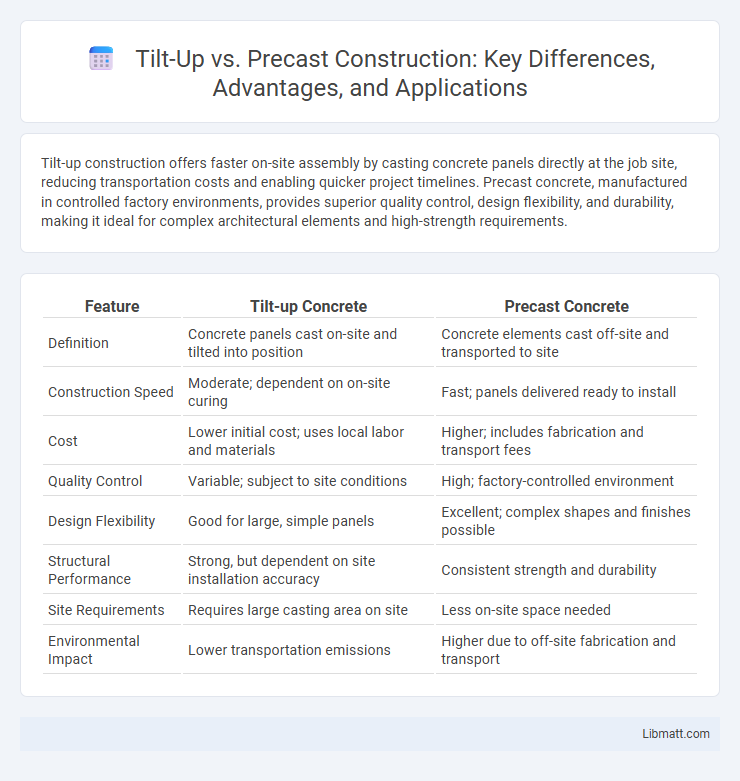
Tilt-up construction offers faster on-site assembly by casting concrete panels directly at the job site, reducing transportation costs and enabling quicker project timelines. Precast concrete, manufactured in controlled factory environments, provides superior quality control, design flexibility, and durability, making it ideal for complex architectural elements and high-strength requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tilt-up Concrete | Precast Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete panels cast on-site and tilted into position | Concrete elements cast off-site and transported to site |
| Construction Speed | Moderate; dependent on on-site curing | Fast; panels delivered ready to install |
| Cost | Lower initial cost; uses local labor and materials | Higher; includes fabrication and transport fees |
| Quality Control | Variable; subject to site conditions | High; factory-controlled environment |
| Design Flexibility | Good for large, simple panels | Excellent; complex shapes and finishes possible |
| Structural Performance | Strong, but dependent on site installation accuracy | Consistent strength and durability |
| Site Requirements | Requires large casting area on site | Less on-site space needed |
| Environmental Impact | Lower transportation emissions | Higher due to off-site fabrication and transport |
Introduction to Tilt-up and Precast Construction
Tilt-up construction involves casting concrete panels on-site and lifting them into place, offering cost-effective and fast building solutions ideal for warehouses and commercial buildings. Precast construction uses factory-made concrete elements transported to the site for assembly, ensuring higher quality control and reduced construction time. Your choice between tilt-up and precast depends on project scale, site constraints, and desired finish quality.
Core Principles of Tilt-up Construction
Tilt-up construction involves casting concrete panels horizontally on-site and lifting them into place using cranes, which reduces transportation costs and allows for faster project completion. The method relies on durable formwork, precise panel design, and strategic reinforcement to ensure structural integrity and thermal performance. It optimizes material usage and minimizes labor requirements by integrating casting and erection processes directly within the construction site.
Fundamentals of Precast Concrete Systems
Precast concrete systems consist of factory-cast elements that are transported and assembled on-site, offering enhanced quality control and faster construction timelines. These systems include structural components such as walls, floors, and columns, which are designed for uniformity and durability. Your choice between tilt-up and precast depends on project specifics, but precast excels in environments requiring precise fabrication and repeatability.
Key Differences Between Tilt-up and Precast
Tilt-up construction involves casting concrete panels on-site and lifting them into place, offering greater flexibility in design changes and reduced transportation costs. Precast concrete elements are manufactured in a controlled factory environment, ensuring higher quality control and faster on-site assembly due to pre-finished components. Key differences include tilt-up's adaptability to unique architectural features versus precast's advantage in accelerated project timelines and consistent product quality.
Comparative Cost Analysis
Tilt-up construction typically offers lower labor costs due to on-site casting and reduced transportation expenses, making it cost-effective for large, flat projects. Precast concrete incurs higher initial costs because of factory fabrication, specialized transport, and crane requirements, yet benefits from faster installation and enhanced quality control. When comparing overall expenses, tilt-up suits projects with ample site space and simpler designs, while precast is advantageous for complex, high-volume builds demanding precision and minimal site disruption.
Speed of Construction and Project Timelines
Tilt-up construction accelerates project timelines by casting concrete panels on-site, eliminating the need for extensive transportation and reducing delays. Precast concrete panels are manufactured off-site in controlled environments, allowing for simultaneous site preparation and panel production, which shortens overall construction duration. While both methods enhance speed, tilt-up is often favored for faster erection on large flat sites, and precast offers more precise scheduling for complex projects.
Design Flexibility and Architectural Possibilities
Tilt-up concrete offers greater design flexibility by allowing on-site casting, which enables customized panel shapes, textures, and finishes tailored to unique architectural visions. Precast concrete panels are manufactured in controlled factory settings, providing consistent quality but less adaptability for last-minute design changes or intricate details. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize creative customization with tilt-up or precise, repeatable designs through precast.
Structural Performance and Durability
Tilt-up construction offers excellent structural performance by forming concrete panels on-site, ensuring strong bonding with the building frame, while precast panels are manufactured under controlled conditions, enhancing uniformity and strength. Precast concrete typically provides superior durability due to factory-controlled curing, reducing porosity and improving resistance to environmental factors such as freeze-thaw cycles, chemicals, and corrosion. Your choice between tilt-up and precast should consider the specific structural demands and long-term durability requirements of your project.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Tilt-up construction minimizes material waste by using on-site concrete casting, reducing transportation emissions and promoting local resource utilization. Precast elements are manufactured in controlled environments, ensuring higher quality control and potential for recycling excess materials, but often involve longer transportation distances, increasing carbon footprint. Your choice depends on balancing local environmental impact with factory efficiencies and material lifecycle benefits.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
Selecting between tilt-up and precast concrete methods depends on project size, budget, and timeline constraints. Tilt-up construction offers cost-effective, fast on-site fabrication ideal for large-scale warehouses and commercial buildings, while precast panels ensure higher quality control and design flexibility through off-site manufacturing. Evaluating project requirements and site conditions helps determine the best balance between speed, cost, and finish quality for optimal structural performance.
Tilt-up vs Precast Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com