HVLS fans provide superior air circulation by moving large volumes of air at low speeds, creating a gentle breeze that improves comfort and reduces energy costs. Traditional fans typically operate at higher speeds with smaller blades, resulting in focused airflow and less energy efficiency compared to HVLS fans.
Table of Comparison
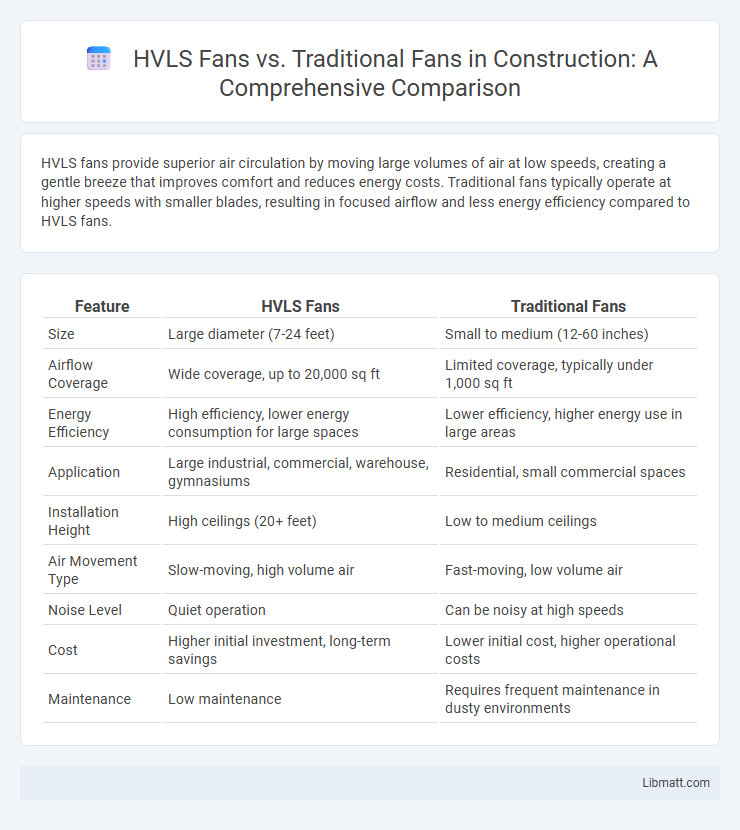
| Feature | HVLS Fans | Traditional Fans |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Large diameter (7-24 feet) | Small to medium (12-60 inches) |
| Airflow Coverage | Wide coverage, up to 20,000 sq ft | Limited coverage, typically under 1,000 sq ft |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency, lower energy consumption for large spaces | Lower efficiency, higher energy use in large areas |
| Application | Large industrial, commercial, warehouse, gymnasiums | Residential, small commercial spaces |
| Installation Height | High ceilings (20+ feet) | Low to medium ceilings |
| Air Movement Type | Slow-moving, high volume air | Fast-moving, low volume air |
| Noise Level | Quiet operation | Can be noisy at high speeds |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, long-term savings | Lower initial cost, higher operational costs |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Requires frequent maintenance in dusty environments |
Introduction to HVLS Fans and Traditional Fans
HVLS (High Volume Low Speed) fans operate at low speeds with large diameters, efficiently moving vast amounts of air to improve ventilation and temperature regulation in expansive spaces. Traditional fans typically run at higher speeds with smaller blades, offering localized airflow but less effective air circulation over large areas. HVLS fans reduce energy costs and enhance comfort by distributing air evenly, contrasting with the spot cooling effect provided by conventional fans.
Key Differences Between HVLS and Traditional Fans
HVLS (High-Volume Low-Speed) fans move large volumes of air at low rotational speeds, creating a gentle and consistent airflow ideal for cooling large spaces efficiently, while traditional fans operate at higher speeds with smaller blades, resulting in more focused but less energy-efficient airflow. HVLS fans typically have diameters ranging from 7 to 24 feet, enabling coverage of up to 20,000 square feet per fan, compared to traditional fans that cover limited areas and require multiple units. The energy consumption of HVLS fans is significantly lower per cubic foot of circulated air, making them more cost-effective for commercial and industrial environments.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
HVLS (High Volume Low Speed) fans deliver superior energy efficiency compared to traditional fans by moving larger volumes of air at lower speeds, significantly reducing electricity consumption. Their wide blade span creates gentle, consistent airflow that cools more effectively, allowing HVAC systems to operate less frequently and lowering overall energy costs. Choosing HVLS fans can enhance your energy savings while maintaining optimal comfort in large spaces.
Airflow Coverage and Distribution
HVLS (High Volume Low Speed) fans provide superior airflow coverage by moving large volumes of air at low speeds, effectively circulating air across expansive areas up to 20,000 square feet per unit. Traditional fans typically focus airflow in a concentrated area with higher speed, resulting in uneven air distribution and hotspots in large spaces. The broad, gentle airflow of HVLS fans promotes consistent temperature regulation and improved ventilation in warehouses, gyms, and industrial facilities.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
HVLS fans require professional installation due to their large size and ceiling-mounted design, often needing structural support assessment, while traditional fans are simpler to install and typically fit standard mounting brackets. Maintenance for HVLS fans involves periodic inspections of motor components, belt tensioning, and blade alignment to ensure optimal airflow, contrasting with traditional fans that require minimal upkeep such as dusting and occasional lubrication. The complexity and cost of maintaining HVLS fans are higher, but they offer energy-efficient performance in large industrial or commercial spaces compared to traditional fans suited for smaller areas.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs. Operational Savings
HVLS fans require a higher initial investment compared to traditional fans but deliver significant operational savings through reduced energy consumption and lower maintenance costs. Their aerodynamic design moves large volumes of air at low speeds, improving HVAC efficiency and decreasing utility bills over time. Your long-term cost benefits often outweigh the upfront expense, making HVLS fans a financially sound choice for large commercial or industrial spaces.
Noise Levels and Workplace Comfort
HVLS fans operate with significantly lower noise levels compared to traditional fans, creating a quieter workplace environment that enhances employee concentration and reduces stress. The larger blade diameter and slower rotation of HVLS fans produce a gentle, consistent airflow that improves overall comfort without disruptive noise. Your workspace benefits from this technology by maintaining a peaceful atmosphere while ensuring effective air circulation.
Applications: Ideal Use Cases for Each Fan Type
HVLS fans excel in large industrial spaces, warehouses, and agricultural settings by providing gentle, energy-efficient air circulation that improves comfort and reduces humidity. Traditional fans are well-suited for smaller, confined areas like offices, homes, or retail spaces where targeted airflow is needed for quick cooling. Your choice depends on the scale and nature of the environment, with HVLS fans ideal for broad coverage and traditional fans for localized ventilation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
HVLS fans consume significantly less energy than traditional fans, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and lowering a building's carbon footprint. Their large blades distribute air more efficiently, minimizing the need for multiple smaller fans and decreasing overall energy consumption. In commercial and industrial settings, HVLS fans support sustainable building practices by enhancing HVAC system efficiency and promoting energy savings.
Choosing the Right Fan: Factors to Consider
HVLS fans deliver superior air circulation and energy efficiency compared to traditional fans, making them ideal for large spaces requiring consistent airflow. Factors to consider include ceiling height, room size, airflow requirements, and installation costs. Your decision should weigh long-term energy savings and comfort against initial investment and maintenance needs.
HVLS fans vs traditional fans Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com