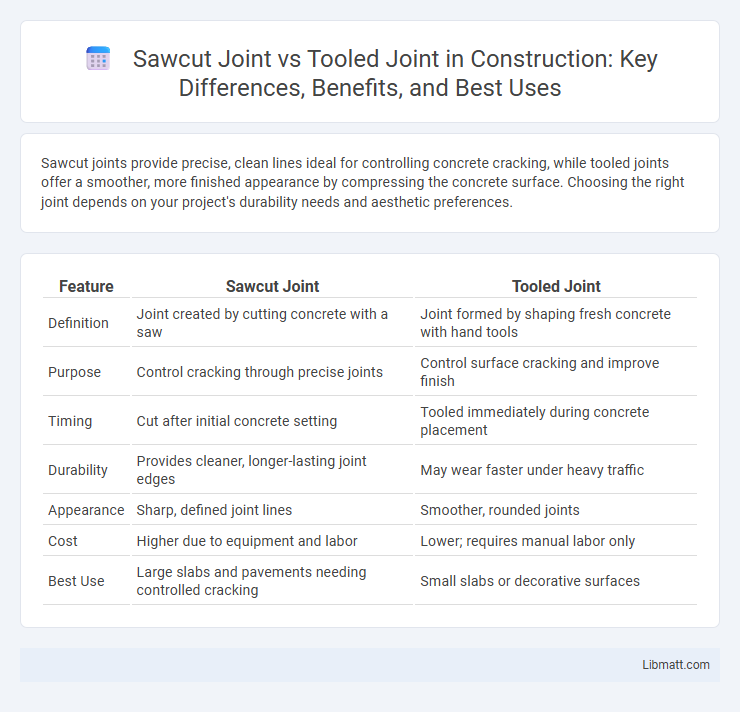
Sawcut joints provide precise, clean lines ideal for controlling concrete cracking, while tooled joints offer a smoother, more finished appearance by compressing the concrete surface. Choosing the right joint depends on your project's durability needs and aesthetic preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sawcut Joint | Tooled Joint |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Joint created by cutting concrete with a saw | Joint formed by shaping fresh concrete with hand tools |
| Purpose | Control cracking through precise joints | Control surface cracking and improve finish |
| Timing | Cut after initial concrete setting | Tooled immediately during concrete placement |
| Durability | Provides cleaner, longer-lasting joint edges | May wear faster under heavy traffic |
| Appearance | Sharp, defined joint lines | Smoother, rounded joints |
| Cost | Higher due to equipment and labor | Lower; requires manual labor only |
| Best Use | Large slabs and pavements needing controlled cracking | Small slabs or decorative surfaces |
Introduction to Concrete Joints
Sawcut joints are created by cutting grooves into fresh concrete within 6 to 18 hours after placement to control cracking, while tooled joints are formed by shaping the surface before the concrete fully sets, usually within the first few hours. Sawcut joints provide precise depth and cleaner edges, enhancing structural integrity and minimizing random cracks. Tooling joints improve surface aesthetics and durability but offer less control over joint depth and crack direction compared to sawcut joints.
What Is a Sawcut Joint?
A sawcut joint is a precise, narrow groove cut into concrete using a diamond blade saw to control cracking and provide a clean edge for expansion or contraction. This type of joint is typically deeper and narrower than a tooled joint, offering better structural integrity and reduced risk of premature surface damage. You can rely on sawcut joints for improved durability in concrete slabs exposed to heavy traffic or environmental stress.
What Is a Tooled Joint?
A tooled joint is a type of control joint in concrete where the edges are finished with a specific tool to create a concave groove, enhancing both the appearance and durability by reducing surface cracking. Unlike sawcut joints, which are created by cutting the concrete after it has partially cured, tooled joints are formed early in the curing process while the concrete is still wet. Your choice between sawcut and tooled joints depends on the timing of the joint formation and the desired aesthetic and performance characteristics.
Purpose of Joints in Concrete Slabs
Sawcut joints in concrete slabs are designed to control cracking by creating a weakened plane where future cracks can form in a predictable, straight line, thereby preventing random surface cracking. Tooled joints, formed while the concrete is still plastic, serve to create a decorative groove that also functions as a controlled crack pattern but with less precision than sawcut joints. Both joint types are essential for maintaining structural integrity and extending the lifespan of concrete slabs by managing stress and shrinkage effectively.
Installation Process: Sawcut vs Tooled
Sawcut joints are created by cutting a groove in hardened concrete using a saw, allowing precise control over depth and spacing, which minimizes random cracking. Tooled joints are formed by running a tool along fresh concrete before it sets, shaping the joint while the material is still pliable but requiring careful timing to ensure proper depth and finish. Your choice between these methods impacts installation speed, precision, and the long-term durability of concrete surfaces.
Timing and Equipment Requirements
Sawcut joints require precise timing, typically performed soon after concrete has hardened sufficiently to avoid cracking, and demand specialized saw equipment for accurate cuts. Tooled joints are created earlier during the concrete's plastic phase using hand tools or groovers, reducing the need for heavy machinery but requiring skilled labor to shape properly. Your choice between the two depends on project scheduling and the availability of timing-sensitive equipment versus manual tooling resources.
Aesthetic Differences and Applications
Sawcut joints create precise, clean lines with a modern, sharp aesthetic favored in contemporary concrete designs, while tooled joints provide a softer, rounded look often used in traditional or decorative concrete applications. Sawcut joints are ideal for controlling cracking in flatwork like driveways and sidewalks, offering functional performance with a minimalist appearance. Tooled joints, manipulated while concrete is still plastic, suit decorative patios and pathways, enhancing visual appeal through texture and form.
Performance and Crack Control
Sawcut joints provide superior crack control by creating precise, straight grooves that allow concrete to crack in a predetermined location, enhancing structural integrity. Tooled joints, while easier to create, may not control cracking as effectively due to less defined edges, potentially leading to uneven stress distribution. Your choice between sawcut and tooled joints impacts performance, with sawcut joints generally offering better long-term durability and minimized random cracking.
Cost Comparison of Sawcut and Tooled Joints
Sawcut joints typically offer a more cost-effective solution due to faster installation and reduced labor requirements compared to tooled joints, which demand skilled craftsmanship and longer working time. The precision of sawcut joints minimizes material waste and decreases the likelihood of costly repairs caused by improper tooling. Your choice between sawcut and tooled joints will largely depend on budget constraints and the desired aesthetic outcome.
Choosing the Right Joint for Your Project
Sawcut joints offer precise, clean lines ideal for controlling concrete cracking and are best suited for large slabs and industrial projects. Tooled joints provide a more decorative finish, enhancing curb appeal while still managing shrinkage but may require more frequent maintenance. Choosing the right joint for your project depends on the balance between functionality and aesthetics, ensuring your concrete surfaces remain durable and visually appealing.
Sawcut joint vs tooled joint Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com