Trench foundations are narrow and deep, ideal for supporting load-bearing walls in stable soil conditions, while raft foundations spread the load over a large area, making them suitable for weak or expansive soils to prevent uneven settlement. Choosing the right foundation depends on your soil type and load requirements to ensure structural stability and longevity.
Table of Comparison
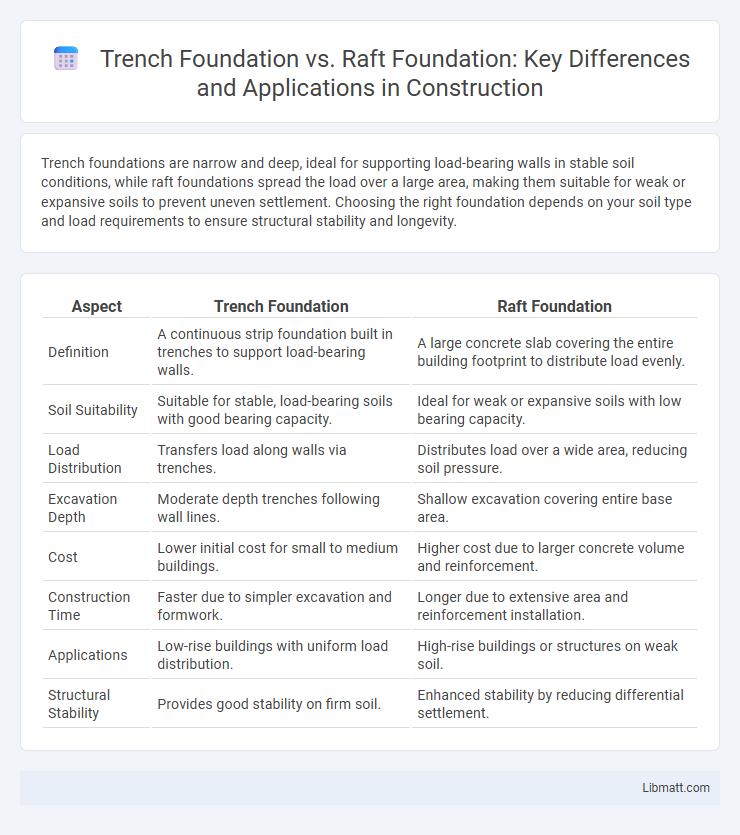
| Aspect | Trench Foundation | Raft Foundation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A continuous strip foundation built in trenches to support load-bearing walls. | A large concrete slab covering the entire building footprint to distribute load evenly. |
| Soil Suitability | Suitable for stable, load-bearing soils with good bearing capacity. | Ideal for weak or expansive soils with low bearing capacity. |
| Load Distribution | Transfers load along walls via trenches. | Distributes load over a wide area, reducing soil pressure. |
| Excavation Depth | Moderate depth trenches following wall lines. | Shallow excavation covering entire base area. |
| Cost | Lower initial cost for small to medium buildings. | Higher cost due to larger concrete volume and reinforcement. |
| Construction Time | Faster due to simpler excavation and formwork. | Longer due to extensive area and reinforcement installation. |
| Applications | Low-rise buildings with uniform load distribution. | High-rise buildings or structures on weak soil. |
| Structural Stability | Provides good stability on firm soil. | Enhanced stability by reducing differential settlement. |
Introduction to Foundation Types
Trench foundations provide continuous support by distributing structural loads along narrow, linear excavations, ideal for load-bearing walls on stable soil. Raft foundations spread loads over a large entire area, suitable for weak or expansive soils requiring uniform pressure distribution. Choosing between trench and raft foundations depends on soil conditions, building loads, and structural requirements to ensure stability and performance.
What is a Trench Foundation?
A trench foundation is a type of shallow foundation constructed by excavating narrow trenches filled with concrete to support load-bearing walls. This foundation is suitable for structures with moderate load requirements and stable soil conditions, providing cost-effective and efficient support. You can choose a trench foundation when site conditions favor minimal excavation and simpler construction methods compared to raft foundations.
What is a Raft Foundation?
A raft foundation is a large, continuous slab of concrete that spreads the building load over a wide area, ideal for weak or expansive soils where individual footings may fail. Unlike trench foundations that use continuous strip footings along load-bearing walls, raft foundations support the entire structure on a single, uniform base, minimizing differential settlement. Choosing a raft foundation can enhance your building's stability on unstable ground by evenly distributing weight across the soil.
Key Differences Between Trench and Raft Foundations
Trench foundations involve continuous strip footings dug to support load-bearing walls, best suited for structures with uniform load distribution and stable soil conditions. Raft foundations, also known as mat foundations, spread the building load over a large area by supporting the entire structure on a single slab, ideal for weak or expansive soils where differential settlement is a concern. Your choice between these foundations depends on soil bearing capacity, structural load, and construction cost efficiency, with trench foundations offering simplicity and raft foundations providing enhanced stability.
Situational Suitability: When to Use Each Foundation
Trench foundations are ideal for structures with load-bearing walls on firm soil and moderate loads, providing deep, narrow support to prevent settling. Raft foundations suit weak or expansive soils and heavy, evenly distributed loads by spreading the building's weight across a large area, minimizing differential settlement. Your choice depends on soil conditions, load requirements, and structural design to ensure optimal stability and durability.
Cost Comparison: Trench vs Raft Foundations
Trench foundations generally cost less than raft foundations due to their simpler excavation and reduced use of concrete, making them ideal for lighter structures on stable soil. Raft foundations, while more expensive, provide better load distribution for buildings on weak or expansive soils, potentially reducing long-term settlement costs. Your choice depends on soil conditions and structural requirements, influencing the overall foundation investment.
Load-Bearing Capacity Analysis
Trench foundations provide enhanced load-bearing capacity by distributing structural loads through deep, narrow excavations, ideal for medium to high load applications on firm soils. Raft foundations, by contrast, spread loads over a large surface area, offering superior stability for weaker, expansive, or uneven soil conditions through a continuous slab. Your choice between trench and raft foundation hinges on soil bearing capacity, load intensity, and project scale to ensure optimal structural support.
Construction Process Overview
Trench foundations involve excavating narrow trenches to the required depth, then filling them with reinforced concrete to support load-bearing walls, making them ideal for uniform soil conditions and moderate structural loads. Raft foundations consist of a large concrete slab covering the entire building footprint, distributing loads evenly across weak or expansive soils, which requires extensive excavation and careful reinforcement placement. Your choice between trench and raft foundations should consider soil bearing capacity, structural load, and site conditions to ensure optimal stability and cost-efficiency.
Pros and Cons of Trench and Raft Foundations
Trench foundations offer cost-effective and easy installation for lightweight structures but may struggle with uneven load distribution and poor soil conditions. Raft foundations provide excellent load distribution and stability on weak or expansive soils but tend to be more expensive and require more extensive excavation. Your choice depends on soil characteristics, load requirements, and project budget.
Final Recommendations and Best Practices
For projects with uniform soil bearing capacity and moderate load, a raft foundation offers cost-effective stability and reduces differential settlement risks. Trench foundations are recommended for structures where loads are concentrated and soil conditions vary, providing targeted support and easier excavation. To ensure optimal performance, conduct thorough soil investigations and align foundation choice with your building's load distribution and site conditions.
Trench foundation vs raft foundation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com