Screw piles offer faster installation with minimal soil disturbance, making them ideal for lighter or temporary structures, while bored piles provide greater load-bearing capacity and stability for heavy or permanent foundations. Your choice depends on project requirements, soil conditions, and desired foundation performance.
Table of Comparison
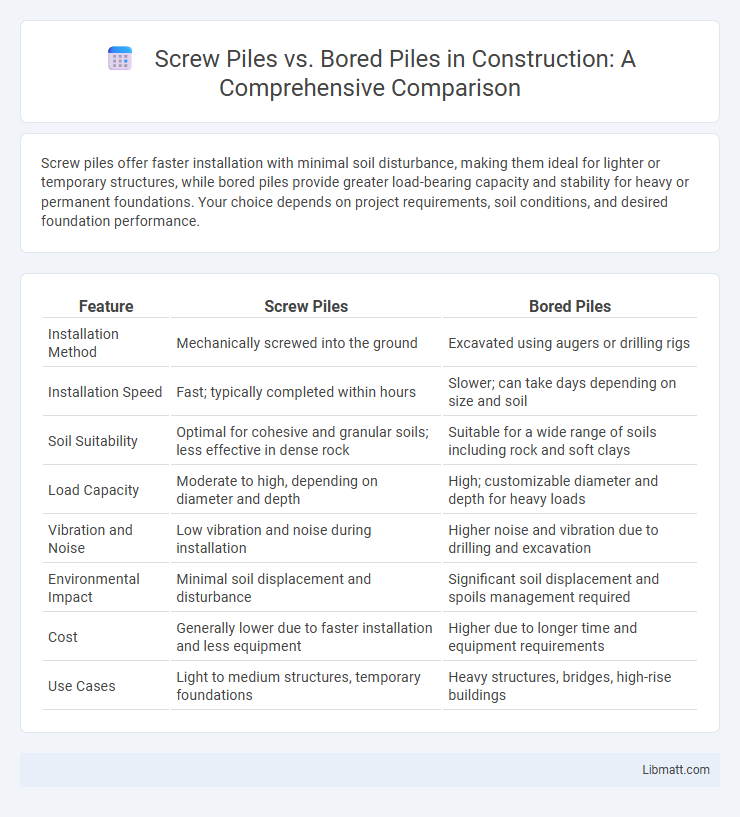
| Feature | Screw Piles | Bored Piles |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Method | Mechanically screwed into the ground | Excavated using augers or drilling rigs |
| Installation Speed | Fast; typically completed within hours | Slower; can take days depending on size and soil |
| Soil Suitability | Optimal for cohesive and granular soils; less effective in dense rock | Suitable for a wide range of soils including rock and soft clays |
| Load Capacity | Moderate to high, depending on diameter and depth | High; customizable diameter and depth for heavy loads |
| Vibration and Noise | Low vibration and noise during installation | Higher noise and vibration due to drilling and excavation |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal soil displacement and disturbance | Significant soil displacement and spoils management required |
| Cost | Generally lower due to faster installation and less equipment | Higher due to longer time and equipment requirements |
| Use Cases | Light to medium structures, temporary foundations | Heavy structures, bridges, high-rise buildings |
Introduction to Screw Piles and Bored Piles
Screw piles are helical-shaped steel shafts installed by twisting into the ground to provide foundation support, offering rapid installation and minimal soil disturbance. Bored piles involve drilling a cylindrical hole into the soil, then filling it with concrete and reinforcing steel to create deep foundations capable of bearing heavy loads. You can choose screw piles for lightweight or temporary structures, while bored piles suit projects requiring high load capacity and stability.
Key Differences Between Screw Piles and Bored Piles
Screw piles are helical steel shafts twisted into the ground, offering rapid installation and minimal soil disturbance, whereas bored piles involve drilling a cylindrical hole before filling it with concrete and reinforcement. Screw piles provide immediate load-bearing capacity with less vibration, suitable for lighter structures and unstable soil conditions, while bored piles support heavy loads and are preferred for deep foundations requiring high bearing capacity. Cost-wise, screw piles are generally more economical and faster to install, but bored piles offer greater versatility for larger, complex projects requiring customized pile diameters and depths.
Installation Methods Compared
Screw piles are installed by rotating a helical blade into the ground, offering rapid deployment with minimal soil disturbance and immediate load-bearing capacity. Bored piles require drilling a deep cylindrical hole followed by concrete pouring, allowing for customization in diameter and depth but involving longer installation times and potential soil displacement. Your choice depends on site conditions, load requirements, and project timelines, with screw piles providing efficiency in softer soils and bored piles suiting heavier structural loads in varied ground conditions.
Load-Bearing Capacity Analysis
Screw piles provide excellent load-bearing capacity through helical plates that transfer structural loads deep into stable soil layers, making them ideal for lightweight to medium-heavy constructions. Bored piles achieve high load-bearing capacity by creating large-diameter, cast-in-situ concrete shafts that can sustain heavy loads in diverse soil conditions. Your choice depends on soil type, load requirements, and installation speed, with screw piles offering faster installation and bored piles providing superior capacity for very heavy loads.
Soil Suitability and Ground Conditions
Screw piles perform exceptionally well in soft, loose, and water-logged soils where rapid installation and load transfer are critical, making them ideal for sites with poor ground conditions. Bored piles are better suited for dense, cohesive soils and heterogeneous stratigraphy, as they rely on displacement and soil friction around the pile shaft for stability. Both types require thorough geotechnical analysis, but screw piles offer advantage in unstable or low-bearing capacity soils due to their helical design enabling deeper, more stable anchorage.
Construction Speed and Project Timelines
Screw piles offer significantly faster installation times compared to bored piles, often reducing construction speed by up to 50%, which can accelerate project timelines substantially. Their quick deployment minimizes the need for extensive excavation and curing periods required for bored piles, allowing Your foundation work to progress with less disruption. Prioritizing screw piles can lead to more efficient scheduling and cost savings on labor and equipment, especially in time-sensitive construction projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Screw piles offer significant environmental benefits by minimizing soil disturbance and reducing carbon emissions compared to traditional bored piles, which require extensive excavation and generate more waste. Their rapid installation process lessens noise and disturbance, making them a sustainable choice for sensitive sites. You can enhance your project's sustainability by selecting screw piles, promoting eco-friendly construction practices with lower environmental footprints.
Cost Comparison: Screw Piles vs Bored Piles
Screw piles typically offer lower installation costs compared to bored piles due to faster installation times and reduced labor requirements. Bored piles incur higher expenses because of extensive excavation, concrete pouring, and longer curing periods. Overall, screw piles provide a cost-effective foundation solution, especially for projects with soil conditions favorable to minimal disturbance.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Screw piles are commonly used for lightweight structures such as residential buildings, decks, and temporary installations due to their quick installation and minimal soil disturbance. Bored piles are preferred for heavy-load-bearing foundations in large-scale construction projects like bridges, high-rise buildings, and industrial facilities because they provide greater load capacity and stability. Your choice between screw piles and bored piles depends on project scale, soil conditions, and load requirements.
Choosing the Right Pile for Your Project
Choosing the right pile for your project depends on soil conditions, load requirements, and installation speed. Screw piles offer rapid installation and are ideal for weak or waterlogged soils, providing minimal vibration and disturbance. Bored piles suit heavier loads and urban environments with space constraints, offering deeper foundation support but requiring more time and equipment.
Screw piles vs bored piles Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com