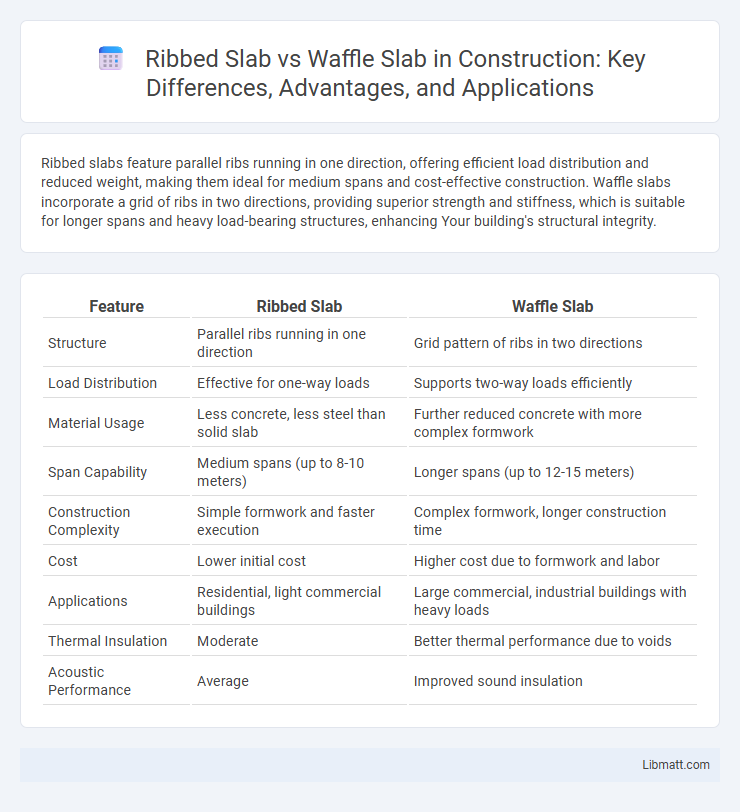
Ribbed slabs feature parallel ribs running in one direction, offering efficient load distribution and reduced weight, making them ideal for medium spans and cost-effective construction. Waffle slabs incorporate a grid of ribs in two directions, providing superior strength and stiffness, which is suitable for longer spans and heavy load-bearing structures, enhancing Your building's structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ribbed Slab | Waffle Slab |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Parallel ribs running in one direction | Grid pattern of ribs in two directions |
| Load Distribution | Effective for one-way loads | Supports two-way loads efficiently |
| Material Usage | Less concrete, less steel than solid slab | Further reduced concrete with more complex formwork |
| Span Capability | Medium spans (up to 8-10 meters) | Longer spans (up to 12-15 meters) |
| Construction Complexity | Simple formwork and faster execution | Complex formwork, longer construction time |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher cost due to formwork and labor |
| Applications | Residential, light commercial buildings | Large commercial, industrial buildings with heavy loads |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate | Better thermal performance due to voids |
| Acoustic Performance | Average | Improved sound insulation |
Introduction to Ribbed Slab and Waffle Slab
Ribbed slabs consist of a series of parallel ribs with a topping slab, providing efficient load distribution and reduced material usage in concrete floors. Waffle slabs feature a grid pattern of ribs in two directions, offering enhanced strength and rigidity for larger spans and heavy loads. Both slab types optimize structural performance while minimizing weight and concrete consumption in construction projects.
Structural Design Overview
Ribbed slabs feature parallel beams (ribs) beneath a thin concrete slab, optimizing load distribution and reducing material use while supporting substantial structural loads. Waffle slabs consist of two-way ribbed systems forming a grid pattern, offering enhanced stiffness and strength, making them ideal for longer spans and heavy load requirements. Both slab types utilize reinforced concrete but differ in geometry and load transfer mechanisms, influencing their selection based on architectural and structural demands.
Material Requirements and Efficiency
Ribbed slabs use less concrete and steel reinforcement compared to waffle slabs, making them more material-efficient for medium spans and uniformly distributed loads. Waffle slabs require more formwork and intricate reinforcement patterns, leading to higher material costs but offering superior load distribution for heavy or irregular loads. Your choice should consider project-specific load demands and budget constraints to optimize material usage and structural performance.
Load Distribution and Strength
Ribbed slabs feature parallel beams that efficiently distribute loads along their length, providing enhanced load-bearing capacity for medium-span structures. Waffle slabs consist of a grid of ribs running in two directions, offering superior load distribution and structural strength ideal for long spans and heavy loads. The two-way reinforcement in waffle slabs minimizes deflection and increases stiffness compared to the primarily one-way load distribution in ribbed slabs.
Construction Techniques and Processes
Ribbed slabs involve casting concrete over a series of parallel beams with ribs created by steel or precast molds, allowing for efficient material usage and faster construction through repetitive formwork. Waffle slabs use a grid of beams forming a two-dimensional rib pattern beneath the slab, requiring more complex formwork systems with removable pods or molds to create the characteristic voids, enhancing load distribution and reducing slab weight. Both techniques demand precise alignment and reinforcement placement, but waffle slabs typically involve longer curing times due to increased slab thickness and complexity.
Cost Comparison and Budget Implications
Ribbed slabs generally offer lower material and labor costs compared to waffle slabs due to simpler formwork and reduced concrete volume. Waffle slabs, with their two-way ribbed system, provide enhanced load distribution but require more intricate mold fabrication, leading to higher initial expenses. Budget implications favor ribbed slabs for projects with cost constraints, while waffle slabs suit designs prioritizing structural performance despite elevated costs.
Flexibility in Architectural Design
Ribbed slabs offer greater flexibility in architectural design by allowing varied spacing and sizing of ribs to accommodate different load requirements and aesthetic preferences. Waffle slabs provide a distinctive grid pattern that enhances both structural strength and visual appeal, ideal for expansive floor areas requiring minimal support columns. Your choice depends on balancing design creativity with structural performance needs.
Applications and Common Uses
Ribbed slabs are commonly used in commercial buildings, parking garages, and long-span structures due to their efficient load distribution and reduced material usage. Waffle slabs are preferred for large floor areas in schools, auditoriums, and industrial facilities because of their high strength-to-weight ratio and aesthetic ceiling patterns. Your choice depends on project requirements, with ribbed slabs excelling in cost-effectiveness and waffle slabs offering superior structural performance and design flexibility.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Ribbed slabs offer enhanced durability due to their continuous ribs that provide improved structural integrity, reducing the risk of cracks and deformation over time. Waffle slabs, characterized by their grid-like pattern, require more meticulous maintenance to prevent debris buildup in the voids, which may affect longevity if neglected. Your choice should consider the maintenance effort you are willing to invest alongside the desired lifespan and load-bearing requirements of the structure.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Slab System
Ribbed slabs offer cost-effective solutions with reduced material usage and quicker construction, making them ideal for projects requiring moderate load support and long spans. Waffle slabs provide superior strength and load distribution due to their grid pattern, best suited for heavy-load applications and large open spaces. Your choice depends on structural requirements, budget constraints, and architectural design considerations to optimize performance and efficiency.
Ribbed slab vs waffle slab Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com