Strip footing distributes the building load along a continuous strip beneath load-bearing walls, ideal for supporting linear structures, while pad footing supports individual columns by spreading the load over a square or rectangular area. Choose your footing type based on structural requirements and soil conditions to ensure stability and load distribution efficiency.
Table of Comparison
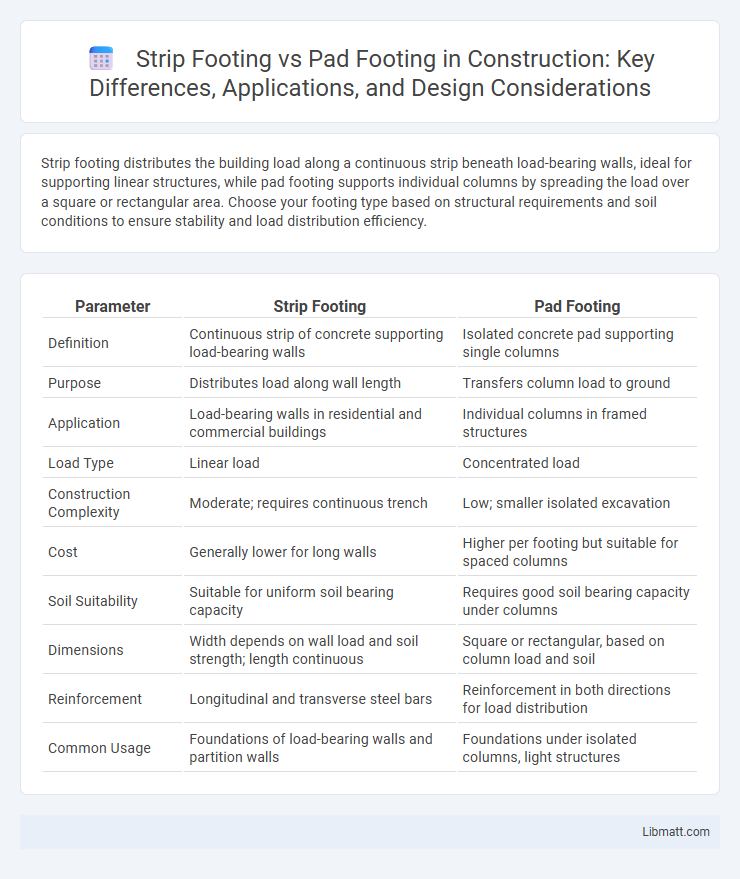
| Parameter | Strip Footing | Pad Footing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous strip of concrete supporting load-bearing walls | Isolated concrete pad supporting single columns |
| Purpose | Distributes load along wall length | Transfers column load to ground |
| Application | Load-bearing walls in residential and commercial buildings | Individual columns in framed structures |
| Load Type | Linear load | Concentrated load |
| Construction Complexity | Moderate; requires continuous trench | Low; smaller isolated excavation |
| Cost | Generally lower for long walls | Higher per footing but suitable for spaced columns |
| Soil Suitability | Suitable for uniform soil bearing capacity | Requires good soil bearing capacity under columns |
| Dimensions | Width depends on wall load and soil strength; length continuous | Square or rectangular, based on column load and soil |
| Reinforcement | Longitudinal and transverse steel bars | Reinforcement in both directions for load distribution |
| Common Usage | Foundations of load-bearing walls and partition walls | Foundations under isolated columns, light structures |
Introduction to Strip Footing and Pad Footing
Strip footing is a continuous, linear foundation typically used to support load-bearing walls, distributing structural weight evenly along the length of the wall. Pad footing consists of isolated, square or rectangular concrete pads that support individual columns or piers, transferring loads directly to the soil below. Understanding these fundamental differences helps you select the appropriate foundation type for your specific structural requirements.
Definition of Strip Footing
Strip footing is a continuous, reinforced concrete foundation that supports load-bearing walls by distributing the weight along a linear strip. Unlike pad footing, which supports individual columns, strip footing runs underneath walls to provide uniform support and prevent settlement. Your choice between strip and pad footing depends on the structural design and soil conditions for optimal stability.
Definition of Pad Footing
Pad footing is a type of shallow foundation designed to support individual columns by distributing their load over a wider area of soil, preventing excessive settlement. Unlike strip footing, which transfers load along a continuous strip beneath load-bearing walls, pad footing is isolated and usually square or rectangular in shape. Your choice of pad footing ensures stability for isolated column structures by effectively managing concentrated loads.
Key Differences Between Strip and Pad Footing
Strip footing is a continuous, linear foundation typically used to support load-bearing walls, distributing weight over a larger area, while pad footing is an isolated, square or rectangular foundation designed to support individual columns. Strip footings are suitable for structures with wall loads, offering consistent load distribution along the length of the wall, whereas pad footings concentrate the load from a single point, making them ideal for column-supported frameworks. Soil conditions, load type, and structural design dictate the choice between strip and pad footing, impacting excavation, material use, and overall foundation stability.
Load Distribution Methods
Strip footing distributes loads from load-bearing walls uniformly along a continuous strip, effectively spreading the weight over a larger soil area to reduce pressure. Pad footing concentrates loads from individual columns into isolated rectangular or square pads that transfer the load directly to the soil beneath. Strip footing is ideal for linear loads, while pad footing suits point loads, optimizing stability and soil bearing capacity in foundation design.
Suitable Applications for Strip Footing
Strip footing is ideal for supporting load-bearing walls in low to medium-rise buildings where soil conditions are stable and uniformly strong. It efficiently distributes the load along continuous strips, making it suitable for structures with linear foundations such as row houses or partition walls. This foundation type is commonly used in residential construction with moderate loads and shallow depths.
Suitable Applications for Pad Footing
Pad footing is ideal for supporting isolated columns where loads are relatively light to moderate, making it suitable for residential buildings, small commercial structures, and light industrial facilities. It efficiently distributes the column load over a larger soil area, preventing excessive settlement on soils with good bearing capacity. You should choose pad footing when foundation requirements are limited to point loads rather than continuous load-bearing walls.
Advantages and Disadvantages Comparison
Strip footing provides continuous load support ideal for long walls, offering uniform settlement and cost efficiency for structures with linear loads. Pad footing supports individual columns, allowing flexible design for varying load conditions but may lead to uneven settlement if loads are unequal. Strip footing requires more excavation and material for extended distances, while pad footing can reduce material use but demands precise load distribution assessment.
Cost Implications: Strip vs Pad Footing
Strip footing generally incurs lower material costs than pad footing due to its linear design, requiring less concrete and reinforcement over extended lengths. Pad footing often demands more concrete volume and steel reinforcement concentrated under columns, raising overall expenses, especially for heavier loads or poor soil conditions. Your project's budget can significantly benefit from choosing strip footing for continuous load-bearing walls, while pad footing suits isolated column foundations despite higher costs.
Choosing the Right Footing for Your Project
Selecting the right footing between strip footing and pad footing depends on soil conditions and load distribution requirements. Strip footings are ideal for supporting load-bearing walls over a continuous area, while pad footings suit isolated column loads, offering localized support. Evaluating your project's structural needs and soil bearing capacity ensures optimal foundation performance and longevity.
Strip footing vs pad footing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com