The subgrade is the natural soil or prepared surface beneath the pavement structure, providing foundational support, while the subbase is a layer of material placed between the subgrade and the base course to enhance load distribution and improve drainage. Choosing the right materials for your subgrade and subbase ensures durability and stability in your pavement construction.
Table of Comparison
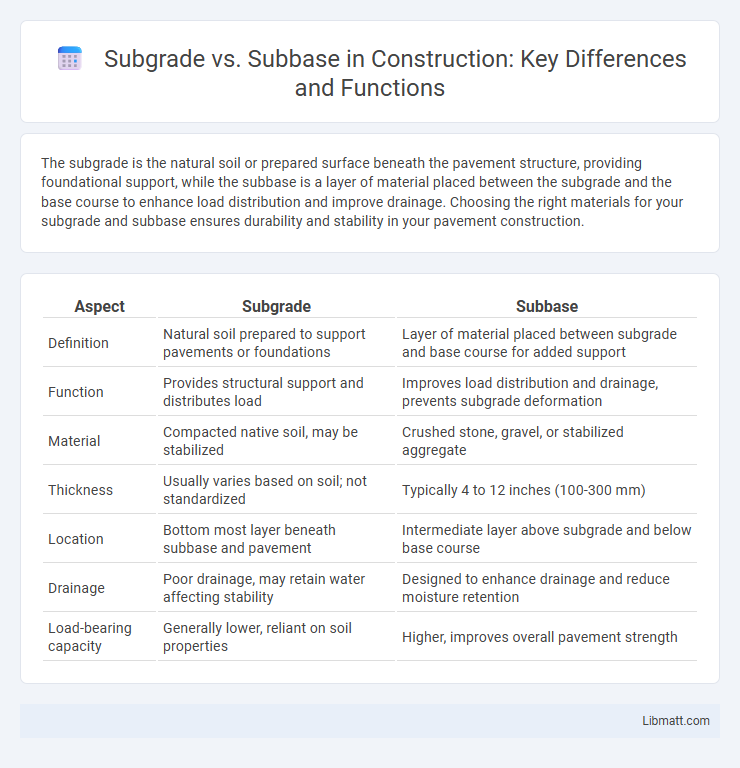
| Aspect | Subgrade | Subbase |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Natural soil prepared to support pavements or foundations | Layer of material placed between subgrade and base course for added support |
| Function | Provides structural support and distributes load | Improves load distribution and drainage, prevents subgrade deformation |
| Material | Compacted native soil, may be stabilized | Crushed stone, gravel, or stabilized aggregate |
| Thickness | Usually varies based on soil; not standardized | Typically 4 to 12 inches (100-300 mm) |
| Location | Bottom most layer beneath subbase and pavement | Intermediate layer above subgrade and below base course |
| Drainage | Poor drainage, may retain water affecting stability | Designed to enhance drainage and reduce moisture retention |
| Load-bearing capacity | Generally lower, reliant on soil properties | Higher, improves overall pavement strength |
Introduction to Subgrade and Subbase
Subgrade is the natural soil prepared to support the layers of a pavement structure, providing foundational strength and stability. Subbase is a layer of granular material placed directly above the subgrade to improve load distribution and drainage. Your pavement's durability relies on the proper preparation and compaction of both subgrade and subbase layers.
Definitions: What is Subgrade?
Subgrade is the natural soil or improved soil layer that serves as the foundation for pavement structures, providing crucial support and stability. It is the prepared surface on which the subbase and base layers are constructed to distribute loads effectively and prevent pavement failure. Ensuring your subgrade has proper compaction and strength directly impacts the longevity and performance of the entire pavement system.
Definitions: What is Subbase?
Subbase is a layer of granular material placed between the subgrade and the base course in road construction, providing additional load distribution and drainage. It improves the stability of the pavement structure by reducing stress on the subgrade soil and minimizing frost action effects. Subbase materials typically include crushed stone, gravel, or recycled aggregates, designed to enhance durability and support traffic loads.
Key Differences Between Subgrade and Subbase
Subgrade is the natural soil prepared to support the layers above, while the subbase is a layer of material placed directly on top of the subgrade to provide additional stability and load distribution. The subgrade primarily serves as the foundation layer, whereas the subbase improves drainage and prevents deformation under traffic loads. Understanding these key differences helps optimize your pavement or road construction for durability and performance.
Functions of Subgrade in Pavement Construction
Subgrade serves as the natural soil foundation that supports the entire pavement structure by distributing applied loads and providing stability. It ensures adequate drainage and prevents excessive deformation under traffic loads, maintaining the pavement's long-term performance. Your pavement's durability depends significantly on the subgrade's strength and preparation before placing the subbase.
Functions of Subbase in Pavement Design
The subbase in pavement design functions as a structural layer that distributes traffic loads evenly to the subgrade, enhancing overall pavement stability and durability. It provides drainage to prevent water infiltration that can weaken the subgrade and cause pavement distress. The subbase also serves as a working platform for construction, protecting the subgrade from damage during the pavement installation process.
Material Types for Subgrade vs Subbase
Subgrade material primarily consists of native soil compacted to provide foundational support, often classified based on soil type and bearing capacity, such as clay, silt, sand, or gravel. Subbase material, on the other hand, is typically composed of granular aggregates like crushed stone, gravel, or recycled concrete, designed to enhance load distribution and drainage beneath the pavement structure. Proper selection and compaction of subgrade and subbase materials are critical for pavement durability and performance under various traffic and environmental conditions.
Construction Methods: Subgrade vs Subbase
Subgrade construction involves compacting native soil to create a stable foundation, often achieved through soil stabilization, moisture control, and proper grading techniques. Subbase construction requires placing and compacting granular materials, such as crushed stone or gravel, over the subgrade to enhance load distribution, drainage, and frost protection. Both methods emphasize compaction quality and moisture management to ensure pavement performance and longevity.
Importance of Proper Subgrade and Subbase Preparation
Proper subgrade and subbase preparation ensures the stability and longevity of pavements and structures by providing a strong, uniform foundation that distributes loads effectively. A well-compacted subgrade minimizes settlement and prevents water infiltration, while an appropriately selected and installed subbase enhances drainage and load-bearing capacity. Your construction project's success depends on this critical preparation to avoid costly repairs and structural failures.
Common Issues and Maintenance Considerations
Subgrade issues often include poor compaction and drainage problems, leading to uneven settlement and pavement distress. Subbase problems typically involve inadequate thickness or contamination, which compromise load distribution and reduce structural support. Regular maintenance such as proper moisture control, timely grading, and replacement of compromised layers ensures long-term pavement stability and performance.
Subgrade vs subbase Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com