Subcontractors perform specific tasks or services within a larger project, directly contributing to its completion, while suppliers provide the necessary materials, equipment, or products needed for the project. Understanding the distinction helps you manage project resources efficiently and ensure timely delivery of both services and materials.
Table of Comparison
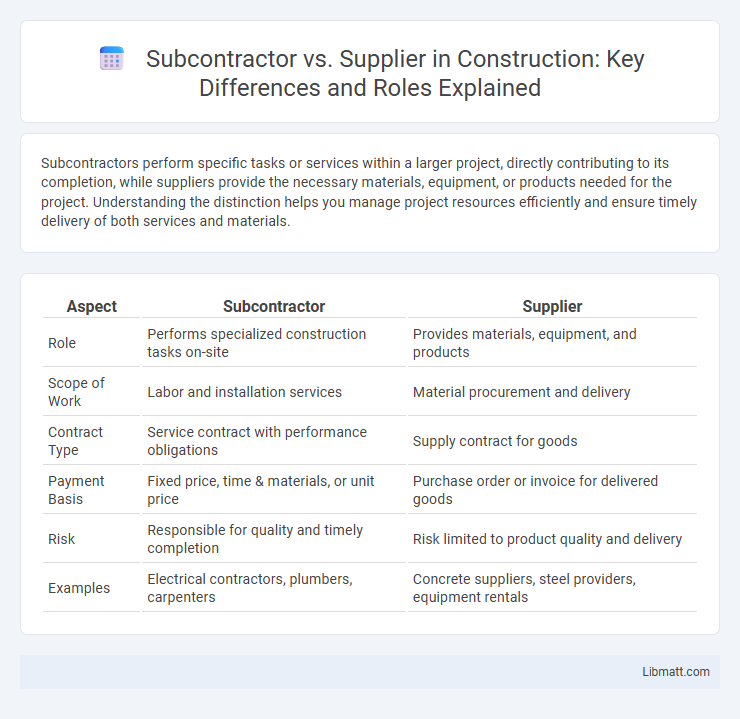
| Aspect | Subcontractor | Supplier |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Performs specialized construction tasks on-site | Provides materials, equipment, and products |
| Scope of Work | Labor and installation services | Material procurement and delivery |
| Contract Type | Service contract with performance obligations | Supply contract for goods |
| Payment Basis | Fixed price, time & materials, or unit price | Purchase order or invoice for delivered goods |
| Risk | Responsible for quality and timely completion | Risk limited to product quality and delivery |
| Examples | Electrical contractors, plumbers, carpenters | Concrete suppliers, steel providers, equipment rentals |
Understanding Subcontractors and Suppliers
Subcontractors provide specialized services or labor to complete specific tasks within a larger project, often under the direct management of the primary contractor. Suppliers deliver materials, equipment, or products necessary for project completion, ensuring your site is stocked with essential resources. Understanding the distinct roles of subcontractors and suppliers helps optimize project planning and procurement strategies.
Key Differences Between Subcontractors and Suppliers
Subcontractors perform specialized tasks or services within a construction or project environment, often managing labor and specific work scopes, whereas suppliers provide the necessary materials, equipment, or products required for project completion. Subcontractors are actively involved in executing parts of the project timeline, while suppliers primarily focus on delivering physical goods. Contractual roles and responsibilities distinguish these entities; subcontractors typically hold contractual obligations related to work performance and labor management, whereas suppliers' contracts revolve around delivery schedules, product quality, and inventory management.
Roles and Responsibilities
Subcontractors primarily manage specific portions of a project, providing specialized labor, equipment, and expertise under the main contractor's supervision. Suppliers are responsible for delivering materials, products, or equipment required for the project's completion, ensuring timely and quality resource availability. Clear delineation of roles ensures efficient workflow, cost control, and adherence to project timelines.
Legal and Contractual Implications
Subcontractors typically enter into contractual agreements directly with the primary contractor, bearing liability for performance and compliance with contract specifications, whereas suppliers contract with either contractors or subcontractors primarily to deliver materials or equipment without assuming performance responsibility. Legal implications for subcontractors often include adherence to labor laws, safety regulations, and project timelines, while suppliers focus on warranty obligations, product quality standards, and delivery schedules. Contract clauses for subcontractors usually cover scopes of work, indemnity, and dispute resolution, contrasting with supplier contracts that emphasize terms of sale, risk of loss, and payment terms.
Cost Considerations
Subcontractors typically incur higher costs due to specialized labor and project-specific expertise, while suppliers generally offer products at scale, reducing unit prices. Budget management must account for subcontractor fees that include labor, equipment, and insurance, whereas supplier costs primarily involve bulk material purchases and delivery. Effective cost control requires comparing subcontractor labor expenses against supplier material prices to optimize overall project expenditures.
Quality Control and Assurance
Subcontractors are directly involved in project execution, making their adherence to quality control protocols critical to ensure compliance with project specifications and standards. Suppliers provide materials or products, requiring stringent quality assurance checks to verify that the items meet contractual and industry quality benchmarks before delivery. Effective coordination between subcontractors and suppliers enhances overall project quality by mitigating risks related to defects and non-conformance.
Project Timeline Impact
Subcontractors directly influence the project timeline by managing specific tasks that require specialized skills, and any delay in their work can cause a domino effect on subsequent phases. Suppliers primarily impact the schedule through the timely delivery of materials and equipment essential for project progression, where procurement delays may halt construction activities. Efficient coordination between subcontractors and suppliers is crucial to minimizing timeline disruptions and ensuring project milestones are met on schedule.
Risk Management in Engaging Subcontractors vs Suppliers
Engaging subcontractors involves higher risk management challenges due to their direct involvement in project execution, requiring strict oversight on quality, timelines, and compliance with safety standards. Suppliers primarily carry risks related to timely delivery and product quality, which can be mitigated through rigorous contract terms and supplier evaluations. Your risk management strategy should prioritize clear communication, thorough vetting, and continuous monitoring to minimize disruptions whether dealing with subcontractors or suppliers.
Choosing the Right Partner for Your Project
Selecting the right partner for your project hinges on understanding the distinct roles of subcontractors and suppliers: subcontractors deliver specialized services or labor, while suppliers provide the necessary materials and equipment. Evaluating project requirements, timelines, and quality standards ensures that you align with subcontractors who offer expert craftsmanship or with suppliers who guarantee reliable material supply. Prioritizing clear communication, contract terms, and proven track records will optimize efficiency and project success.
Best Practices for Managing Subcontractors and Suppliers
Establish clear contracts defining scopes, deliverables, and deadlines to ensure accountability when managing subcontractors and suppliers. Implement regular communication channels and performance reviews to monitor quality, timelines, and compliance with project standards. Utilize centralized project management tools to streamline coordination, track progress, and address issues promptly, optimizing collaboration and minimizing risks.
Subcontractor vs Supplier Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com