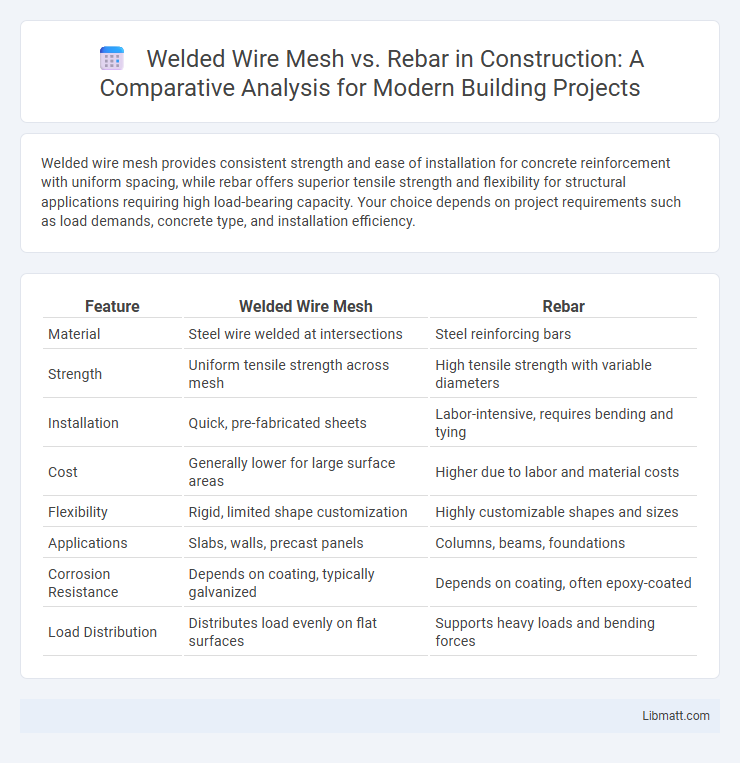
Welded wire mesh provides consistent strength and ease of installation for concrete reinforcement with uniform spacing, while rebar offers superior tensile strength and flexibility for structural applications requiring high load-bearing capacity. Your choice depends on project requirements such as load demands, concrete type, and installation efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Welded Wire Mesh | Rebar |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel wire welded at intersections | Steel reinforcing bars |
| Strength | Uniform tensile strength across mesh | High tensile strength with variable diameters |
| Installation | Quick, pre-fabricated sheets | Labor-intensive, requires bending and tying |
| Cost | Generally lower for large surface areas | Higher due to labor and material costs |
| Flexibility | Rigid, limited shape customization | Highly customizable shapes and sizes |
| Applications | Slabs, walls, precast panels | Columns, beams, foundations |
| Corrosion Resistance | Depends on coating, typically galvanized | Depends on coating, often epoxy-coated |
| Load Distribution | Distributes load evenly on flat surfaces | Supports heavy loads and bending forces |
Introduction to Welded Wire Mesh and Rebar
Welded wire mesh consists of intersecting steel wires welded at joints to form a grid pattern, offering uniform strength and easy installation for concrete reinforcement. Rebar, or reinforcing bar, is a steel bar with surface deformations designed to bond firmly with concrete, providing tensile strength to structural elements. Understanding the differences between welded wire mesh and rebar helps you choose the appropriate reinforcement for your construction project's specific load-bearing and flexibility requirements.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Welded wire mesh consists of steel wires welded together at intersections, typically made from low-carbon steel for corrosion resistance and uniform tensile strength. Rebar, made from carbon steel, is produced through hot rolling, which imparts a ribbed surface to improve concrete bonding. The welded wire mesh manufacturing process involves precise wire gauging and automated spot welding, whereas rebar requires controlled rolling and cooling to achieve specific mechanical properties and deformation patterns.
Structural Strength and Performance
Welded wire mesh offers uniform load distribution and excellent tensile strength due to its factory-controlled manufacturing, making it ideal for thin concrete slabs and surfaces with moderate stress requirements. Rebar provides superior structural strength and performance in high-load and heavy-duty applications, thanks to its larger cross-sectional area and ability to bond deeply with concrete. Choosing between welded wire mesh and rebar depends on the specific load-bearing demands and durability requirements of the construction project.
Flexibility and Application Areas
Welded wire mesh offers greater flexibility in shape and size customization compared to traditional rebar, making it ideal for complex and irregular construction projects. Your choice of welded wire mesh is particularly beneficial for applications like slab reinforcement, precast concrete, and fencing, where uniform distribution of load and easy installation are critical. Rebar, with its higher tensile strength, is better suited for heavy structural components such as beams, columns, and foundations that require robust support.
Installation Time and Labor Requirements
Welded wire mesh offers faster installation times compared to rebar due to its prefabricated grid design, which reduces on-site cutting and tying. Rebar requires more labor-intensive work, including measuring, cutting, bending, and manually tying each piece, extending the project's duration. Your choice significantly impacts labor costs and overall construction schedules.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Welded wire mesh typically offers cost savings compared to rebar due to lower labor expenses and faster installation, making it a budget-friendly choice for many construction projects. Rebar, while sometimes more expensive upfront, provides superior tensile strength and is often preferred for heavy-load applications, which may justify the higher investment depending on structural requirements. Your budget considerations should weigh these factors alongside material availability and project specifications to determine the most economical reinforcement method.
Durability and Longevity in Construction
Welded wire mesh offers consistent strength and uniform load distribution, enhancing durability in concrete reinforcement compared to traditional rebar, which can corrode over time if not properly treated. High-quality steel wire mesh resists cracking and provides long-term stability, making it ideal for structures exposed to harsh environmental conditions. While rebar remains effective in many applications, welded wire mesh typically delivers superior longevity through improved corrosion resistance and reduced maintenance requirements.
Code Compliance and Industry Standards
Welded wire mesh complies with ASTM A1064/A1064M standards, ensuring uniform strength and dimensional accuracy for concrete reinforcement, while rebar typically adheres to ASTM A615/A615M specifications, providing specific yield strength and ductility requirements. Both materials meet International Building Code (IBC) provisions but are selected based on project-specific load and design criteria. Understanding these codes and industry standards is essential for engineers to guarantee structural safety and regulatory compliance in construction projects.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Welded wire mesh offers a more sustainable option compared to traditional rebar due to lower energy consumption during manufacturing and reduced material waste. Its lightweight design decreases transportation emissions and facilitates faster construction, minimizing environmental disruption. Choosing welded wire mesh supports your project's eco-friendly goals by reducing carbon footprint without compromising structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Reinforcement Method
Welded wire mesh offers uniform spacing and consistent strength, making it ideal for slabs and walls requiring distributed reinforcement. Rebar provides greater tensile strength and flexibility, suitable for heavily loaded structural elements such as beams and columns. Selecting between welded wire mesh and rebar depends on the project's load requirements, structural design, and cost-efficiency considerations.
Welded wire mesh vs Rebar Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com