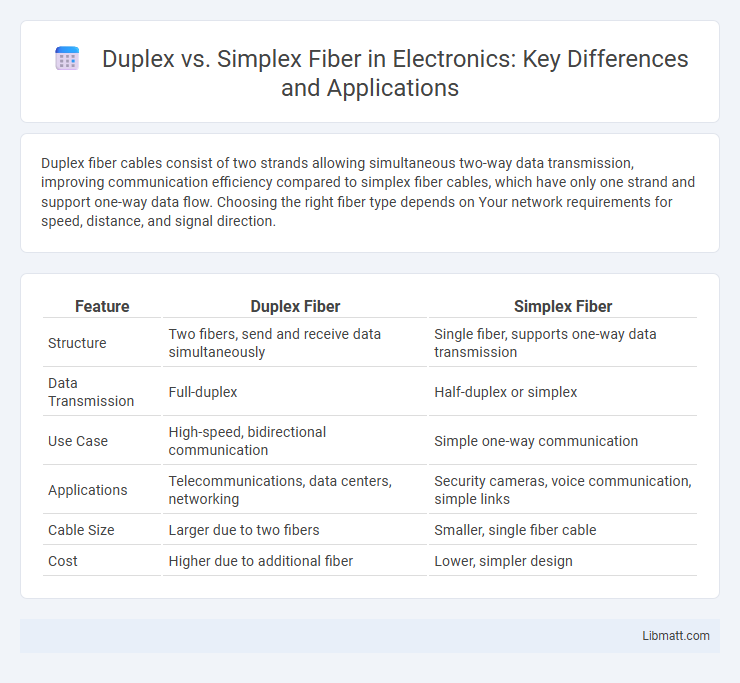
Duplex fiber cables consist of two strands allowing simultaneous two-way data transmission, improving communication efficiency compared to simplex fiber cables, which have only one strand and support one-way data flow. Choosing the right fiber type depends on Your network requirements for speed, distance, and signal direction.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Duplex Fiber | Simplex Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Two fibers, send and receive data simultaneously | Single fiber, supports one-way data transmission |
| Data Transmission | Full-duplex | Half-duplex or simplex |
| Use Case | High-speed, bidirectional communication | Simple one-way communication |
| Applications | Telecommunications, data centers, networking | Security cameras, voice communication, simple links |
| Cable Size | Larger due to two fibers | Smaller, single fiber cable |
| Cost | Higher due to additional fiber | Lower, simpler design |
Introduction to Duplex and Simplex Fiber
Duplex fiber optic cables consist of two strands of fiber, enabling bi-directional communication and improving data transmission efficiency in network systems. Simplex fiber cables contain a single fiber strand designed for one-way data transmission, often used in applications where data flows only in a single direction. Both types support high-speed and long-distance communication, with duplex fiber favored for full-duplex connections and simplex fiber suited for simpler, cost-effective setups.
Understanding Fiber Optic Communication
Duplex fiber optic communication utilizes two fibers or strands allowing simultaneous bi-directional data transmission, making it ideal for high-speed networking and telecommunication systems. Simplex fiber consists of a single fiber used for one-way data transmission, commonly found in applications such as video broadcasting or sensor data collection. The choice between duplex and simplex fiber impacts network design, bandwidth capacity, and overall communication efficiency.
What is Simplex Fiber?
Simplex fiber optic cable consists of a single fiber strand designed to transmit data in one direction, making it ideal for point-to-point communication. Its simple structure reduces cost and complexity, often used in applications like telephone and data networks where one-way data flow is sufficient. Your network setup can benefit from simplex fiber when simplicity and cost-efficiency are prioritized over bidirectional communication.
What is Duplex Fiber?
Duplex fiber consists of two separate optical fibers within a single cable, enabling simultaneous bi-directional data transmission, which enhances network efficiency and speed. This configuration supports full-duplex communication, making it ideal for high-performance applications such as data centers, telecommunications, and enterprise networks. Your choice of duplex fiber ensures faster and more reliable connectivity compared to simplex fiber, which only supports one-way data flow.
Key Differences Between Simplex and Duplex Fiber
Simplex fiber optic cables consist of a single strand used for one-way data transmission, while duplex fiber cables contain two strands for simultaneous bi-directional communication. Duplex fibers are commonly used in network environments requiring high-speed, two-way data flow, such as in Ethernet and telecom applications. Your choice between simplex and duplex fiber depends on whether your system needs single-direction or full-duplex data transmission capabilities.
Advantages of Simplex Fiber
Simplex fiber offers advantages such as lower cost and simpler installation compared to duplex fiber, making it ideal for point-to-point communication where only one signal direction is needed. Its single strand design reduces cable bulk and complexity, which is beneficial in space-constrained environments and for shorter runs. Simplex fiber also allows for easier cable management and quicker upgrades in fiber optic networks.
Benefits of Duplex Fiber
Duplex fiber offers enhanced data transmission capacity by enabling simultaneous bi-directional communication, which reduces latency and improves network efficiency. Its reliable dual-fiber design minimizes the risk of signal interference and supports higher bandwidths, making it ideal for high-speed internet and telecommunications applications. The robust and scalable nature of duplex fiber simplifies maintenance and future network upgrades, delivering long-term cost savings and performance benefits.
Typical Use Cases: Simplex vs Duplex
Simplex fiber is typically used in applications requiring unidirectional data transmission, such as CCTV systems or certain telecommunication setups where data flows in one direction. Duplex fiber supports bidirectional communication, making it ideal for high-speed network environments like Ethernet and data centers where simultaneous sending and receiving of data is crucial. Your choice between simplex and duplex fiber depends on whether your network needs one-way or two-way data transmission for optimal performance.
Choosing the Right Fiber Type for Your Needs
Duplex fiber offers bidirectional communication using two strands, ideal for applications requiring simultaneous send and receive signals, such as full-duplex networks and long-distance data transmission. Simplex fiber uses a single strand for unidirectional data flow, making it cost-effective and suitable for short-distance or one-way communication needs like security systems or industrial settings. Evaluating network requirements, distance, and budget helps determine whether duplex or simplex fiber best supports your connectivity goals.
Conclusion: Duplex or Simplex Fiber?
Duplex fiber is ideal for applications requiring bidirectional data transmission, offering two fibers for simultaneous send and receive capabilities, enhancing network efficiency. Simplex fiber suits scenarios with unidirectional communication needs, providing a single fiber strand that reduces cost and complexity. Choosing duplex or simplex fiber depends on the specific networking demands, balancing performance requirements with budget constraints.
Duplex vs Simplex Fiber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com