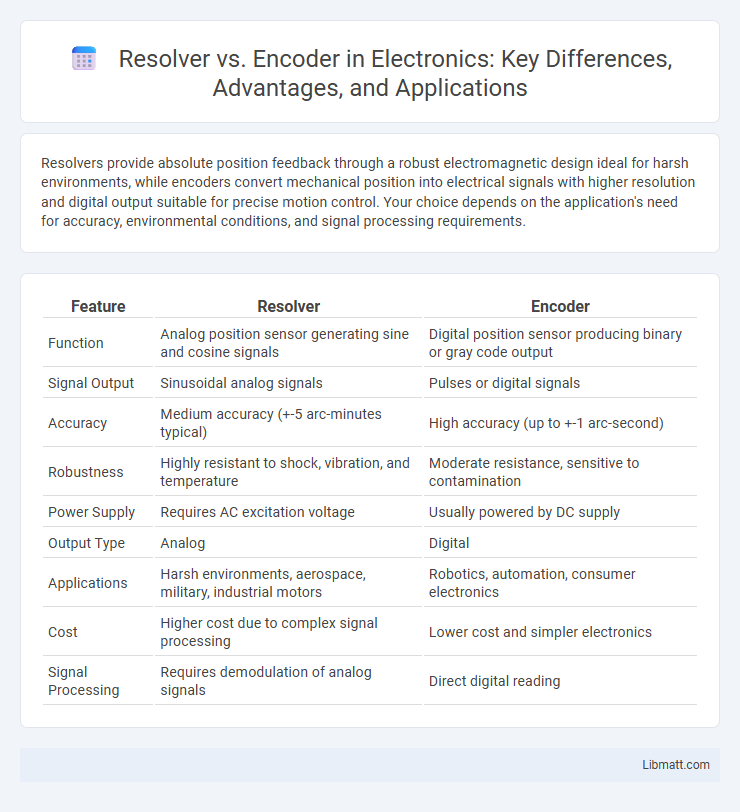
Resolvers provide absolute position feedback through a robust electromagnetic design ideal for harsh environments, while encoders convert mechanical position into electrical signals with higher resolution and digital output suitable for precise motion control. Your choice depends on the application's need for accuracy, environmental conditions, and signal processing requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Resolver | Encoder |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Analog position sensor generating sine and cosine signals | Digital position sensor producing binary or gray code output |
| Signal Output | Sinusoidal analog signals | Pulses or digital signals |
| Accuracy | Medium accuracy (+-5 arc-minutes typical) | High accuracy (up to +-1 arc-second) |
| Robustness | Highly resistant to shock, vibration, and temperature | Moderate resistance, sensitive to contamination |
| Power Supply | Requires AC excitation voltage | Usually powered by DC supply |
| Output Type | Analog | Digital |
| Applications | Harsh environments, aerospace, military, industrial motors | Robotics, automation, consumer electronics |
| Cost | Higher cost due to complex signal processing | Lower cost and simpler electronics |
| Signal Processing | Requires demodulation of analog signals | Direct digital reading |
Introduction to Resolver and Encoder
A resolver is an electromechanical sensor that converts angular position or motion into an analog electrical signal, commonly used in aerospace and industrial applications for precise rotor angle measurement. An encoder transmits position feedback by converting mechanical position to digital signals, often found in robotics, CNC machines, and automation systems for high-resolution motion control. Both devices serve as critical components in feedback loops for motion control, but resolvers excel in harsh environments while encoders provide higher accuracy and ease of integration with digital systems.
Basic Working Principles
Resolvers operate as rotary transformers with two windings on the rotor and stator, generating sine and cosine analog signals corresponding to angular position for precise shaft angle measurement. Encoders use optical or magnetic sensors to convert mechanical position into digital or pulse signals, enabling accurate detection of position and speed. The resolver's continuous analog output contrasts with the encoder's discrete digital pulses, making each suitable for different control system requirements.
Key Differences Between Resolver and Encoder
Resolvers operate as rotary electrical transformers providing precise angular position feedback using sine and cosine signals, ideal for harsh environments due to their robust, contactless construction. Encoders convert mechanical motion into digital signals through optical or magnetic sensors, offering higher resolution and direct digital output suitable for applications requiring precise position data. Key differences include the resolver's analog signal output and ruggedness versus the encoder's digital output and higher accuracy.
Accuracy and Resolution Comparison
Resolvers offer robust position feedback with moderate accuracy typically around +-0.1deg to +-0.5deg, making them suitable for harsh environments. Encoders provide higher resolution and accuracy, often reaching sub-arcminute precision and resolutions exceeding 10,000 pulses per revolution (PPR), ideal for precision motion control. The choice depends on the required precision and environmental conditions, with encoders excelling in detailed positional data and resolvers favored for durability.
Applications and Use Cases
Resolvers excel in harsh environments for precise rotor position sensing in aerospace, military, and industrial automation, ensuring reliable motor control despite high temperatures and vibrations. Encoders offer high-resolution feedback ideal for robotics, CNC machines, and 3D printers, providing accurate speed and position data for complex motion control systems. Your choice depends on whether durability under extreme conditions or detailed positional accuracy is paramount for your application.
Environmental Suitability
Resolvers excel in harsh environmental conditions due to their rugged, brushless design, which resists dust, moisture, vibration, and extreme temperatures, making them ideal for aerospace, military, and industrial applications. Encoders typically offer higher resolution and precision but may require more protective housing to operate reliably in environments with contaminants or severe mechanical stress. Your choice should consider the operational environment's demands, where resolvers provide superior durability, while encoders deliver detailed positional feedback in cleaner, controlled settings.
Cost and Maintenance Factors
Resolvers typically offer lower maintenance costs due to their robust, non-contact design, making them highly reliable in harsh environments. Encoders often have higher initial costs and require more frequent maintenance to ensure accuracy, especially in dirty or high-vibration settings. The total cost of ownership for resolvers is generally lower over time, while encoders may incur additional expenses from replacement parts and calibration.
Advantages of Resolvers
Resolvers offer robust performance in harsh environments due to their rugged construction and immunity to dust, moisture, and vibrations. They provide absolute position feedback without the need for an external power source or complex electronics, ensuring reliable operation even in extreme temperatures. Their ability to deliver accurate, high-resolution angular position makes them ideal for aerospace, industrial, and military applications requiring precision and durability.
Benefits of Encoders
Encoders offer the benefit of precise position feedback by converting mechanical motion into electrical signals, enhancing accuracy in servo systems and robotics. Their ability to provide real-time data improves control and reduces errors in automated applications. You can achieve seamless integration with digital control systems, boosting overall operational efficiency.
Choosing the Right Technology
Choosing the right technology between a resolver and an encoder depends on the application's precision, environmental conditions, and cost constraints. Resolvers offer robust performance in harsh environments with high reliability and absolute position sensing, making them ideal for industrial and aerospace uses. Encoders provide higher resolution and speed capabilities with easier integration in digital systems, suitable for robotics, automation, and consumer electronics.
Resolver vs Encoder Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com