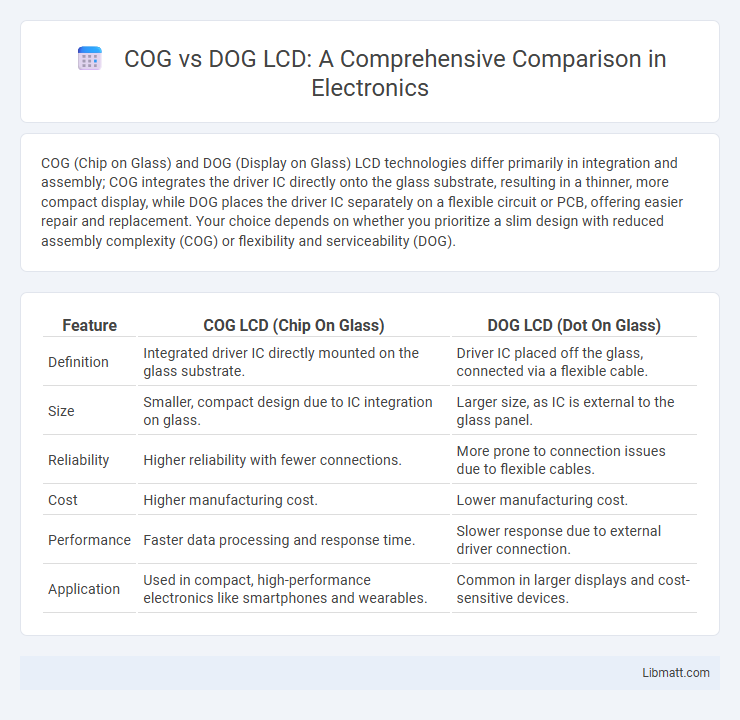
COG (Chip on Glass) and DOG (Display on Glass) LCD technologies differ primarily in integration and assembly; COG integrates the driver IC directly onto the glass substrate, resulting in a thinner, more compact display, while DOG places the driver IC separately on a flexible circuit or PCB, offering easier repair and replacement. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize a slim design with reduced assembly complexity (COG) or flexibility and serviceability (DOG).
Table of Comparison
| Feature | COG LCD (Chip On Glass) | DOG LCD (Dot On Glass) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrated driver IC directly mounted on the glass substrate. | Driver IC placed off the glass, connected via a flexible cable. |
| Size | Smaller, compact design due to IC integration on glass. | Larger size, as IC is external to the glass panel. |
| Reliability | Higher reliability with fewer connections. | More prone to connection issues due to flexible cables. |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost. | Lower manufacturing cost. |
| Performance | Faster data processing and response time. | Slower response due to external driver connection. |
| Application | Used in compact, high-performance electronics like smartphones and wearables. | Common in larger displays and cost-sensitive devices. |
Introduction to COG and DOG LCD Technologies
COG (Chip on Glass) LCD technology integrates the driver IC directly onto the glass substrate of the display, reducing size and improving reliability for compact devices like smartphones and wearables. DOG (Driver on Glass) LCD also places the driver IC on the glass but typically involves a different manufacturing process that balances cost and performance for mid-range LCD panels. Both COG and DOG LCD technologies enhance display efficiency and form factor, making them essential in modern electronic display applications.
What is COG (Chip on Glass) LCD?
COG (Chip on Glass) LCD integrates the driver chip directly onto the glass substrate of the display, reducing component size and enhancing durability. This technology enables thinner panels and improved signal performance by minimizing wiring distance between the chip and the liquid crystal display. Your device benefits from higher resolution and better reliability due to the streamlined structure of COG LCDs compared to traditional discrete driver options like DOG (Driver on Glass).
What is DOG (Display on Glass) LCD?
DOG (Display on Glass) LCD integrates the display driver circuitry directly onto the glass substrate, enhancing display thinness and reducing manufacturing complexity. This technology eliminates the need for separate printed circuit boards, resulting in improved reliability and lower production costs. Your devices benefit from sharper images and more compact designs due to this efficient display architecture.
Key Differences between COG and DOG LCDs
COG (Chip on Glass) LCDs integrate the driver IC directly onto the glass substrate, resulting in a compact design with fewer connection points and improved reliability compared to DOG (Dot on Glass) LCDs, which use discrete driver ICs connected via flexible circuits. COG LCDs typically offer higher display resolution and better signal integrity, whereas DOG LCDs provide greater flexibility in layout and easier repairability. The choice between COG and DOG LCDs depends on factors like device size, manufacturing complexity, and cost constraints.
Advantages of COG LCD Displays
COG LCD displays offer superior compactness by integrating the driver IC directly on the glass substrate, reducing overall module size and thickness. This technology enhances reliability and durability due to fewer connection points and improved resistance to environmental factors. Your device benefits from lower power consumption and better display performance, making COG LCDs ideal for portable and high-precision applications.
Benefits of DOG LCD Displays
DOG LCD displays offer enhanced durability and improved image clarity due to their protective glass overlay, making them ideal for rugged environments. They provide better resistance to scratches and contaminants compared to COG LCDs, extending the lifespan of the display. The superior contrast and brightness levels of DOG LCDs contribute to enhanced visibility in various lighting conditions.
Typical Applications for COG LCDs
COG (Chip-On-Glass) LCDs are widely used in compact electronic devices such as digital watches, calculators, and portable medical instruments due to their slim profile and high reliability. These displays offer enhanced resolution and better performance in smaller form factors, making them ideal for handheld devices and embedded systems. COG LCDs are favored in applications requiring efficient space utilization and robust durability under various environmental conditions.
Common Uses of DOG LCDs
DOG LCDs (Display On Glass) are commonly used in compact devices like digital watches, calculators, and small handheld gaming consoles due to their slim profile and lightweight design. These displays offer superior durability and higher resolution compared to COG (Chip On Glass) LCDs, making them ideal for applications requiring crisp visuals and low power consumption. Industrial instruments and portable medical devices also frequently employ DOG LCDs for their robustness and efficient integration into thin form factors.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between COG and DOG LCDs
When selecting between COG (Chip-On-Glass) and DOG (Digitally Optimized Glass) LCDs, consider factors such as display resolution, durability, and manufacturing cost. COG LCDs offer higher resolution and thinner profiles, making them ideal for compact devices, while DOG LCDs provide enhanced durability and easier repairability. Power consumption and integration complexity also play crucial roles in determining the best LCD type for specific applications.
Future Trends in COG vs DOG LCD Technology
Future trends in COG vs DOG LCD technology highlight increasing adoption of COG (Chip on Glass) due to its superior compactness and enhanced display resolution, making it ideal for wearable devices and smartphones. DOG (Driver on Glass) continues to evolve with improved durability and cost-efficiency, targeting larger screens and industrial applications. Your choice between COG and DOG will depend on device size, performance needs, and integration complexity as these technologies advance.
COG vs DOG LCD Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com