Daisy chain topology connects devices sequentially, making it simple but prone to network failure if one node breaks, whereas ring topology links devices in a closed loop, ensuring data travels in one direction and providing more reliable fault tolerance. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize ease of setup or enhanced network stability and redundancy.
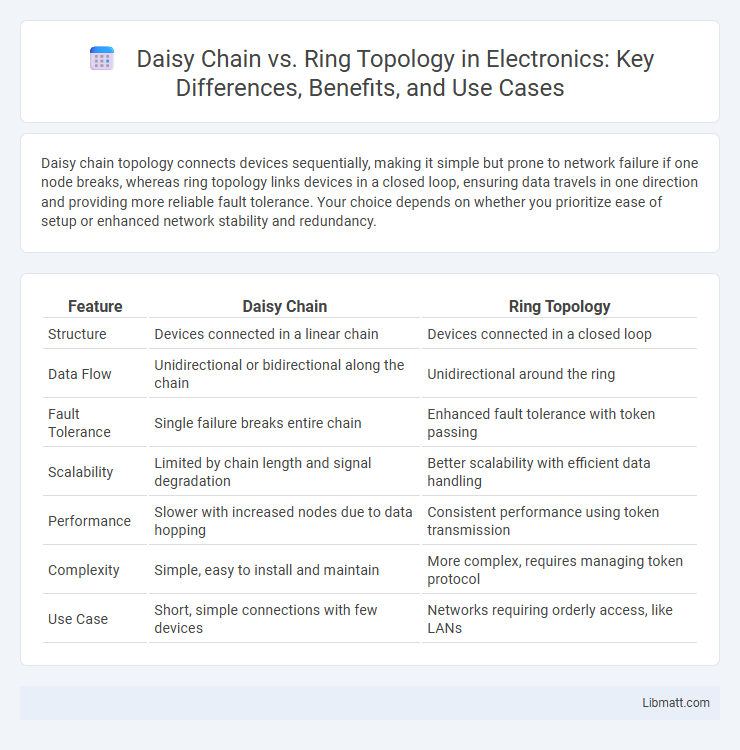
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Daisy Chain | Ring Topology |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Devices connected in a linear chain | Devices connected in a closed loop |
| Data Flow | Unidirectional or bidirectional along the chain | Unidirectional around the ring |
| Fault Tolerance | Single failure breaks entire chain | Enhanced fault tolerance with token passing |
| Scalability | Limited by chain length and signal degradation | Better scalability with efficient data handling |
| Performance | Slower with increased nodes due to data hopping | Consistent performance using token transmission |
| Complexity | Simple, easy to install and maintain | More complex, requires managing token protocol |
| Use Case | Short, simple connections with few devices | Networks requiring orderly access, like LANs |
Introduction to Network Topologies
Network topologies define the arrangement of devices within a network, determining data flow and performance. Daisy Chain topology connects devices in a linear series, ideal for simple setups but vulnerable to single points of failure. Ring topology forms a closed loop where each device has exactly two neighbors, offering redundancy and consistent data transmission that can enhance Your network reliability.
Overview of Daisy Chain Topology
Daisy Chain topology connects devices sequentially in a linear series where each device is linked to exactly two others, except the endpoints. This setup simplifies cabling but can create network vulnerability, as a single failure can disrupt the entire chain. It is commonly used in small or temporary networks, offering straightforward expansion with minimal hardware.
Overview of Ring Topology
Ring topology is a network configuration where each device connects to exactly two other devices, forming a closed loop for data transmission. Data travels in one direction around the ring, passing through each device until it reaches its destination, which minimizes data collisions and enhances orderly communication. This topology is often used in environments requiring predictable network performance and easy fault isolation.
Key Differences Between Daisy Chain and Ring Topologies
Daisy chain topology connects each device linearly, making troubleshooting straightforward but vulnerable to a single point of failure, while ring topology forms a closed loop where data travels in one or both directions, enhancing network stability and fault tolerance. In a daisy chain, the failure of one device interrupts the entire network segment, whereas ring topology maintains communication by rerouting data if one connection breaks. Your choice between these topologies depends on the desired balance between simplicity and resilience in network design.
Advantages of Daisy Chain Topology
Daisy Chain Topology offers simplicity and ease of installation by connecting devices in a linear sequence, reducing the amount of cabling needed compared to other topologies. This setup minimizes costs and is ideal for small networks where quick expansion is necessary without complicated reconfiguration. Your network benefits from straightforward troubleshooting since each device is connected in a clear, sequential order.
Advantages of Ring Topology
Ring topology offers advantages such as predictable data transfer speeds due to its unidirectional data flow, reducing the chances of packet collisions and improving network performance. Its structured layout ensures easy fault isolation, enabling quick detection and resolution of issues without affecting the entire network. You benefit from consistent data transmission and simplified network management, making ring topology ideal for small to medium-sized networks requiring reliable connectivity.
Disadvantages of Daisy Chain Topology
Daisy chain topology suffers from a major disadvantage where a single point of failure can disrupt the entire network, as each device depends on the previous one for communication. Troubleshooting becomes challenging because identifying the exact failure point requires checking each device in sequence. Network scalability is limited due to performance degradation and increased latency with the addition of more devices.
Disadvantages of Ring Topology
Ring topology suffers from a single point of failure because if any device or connection in the ring breaks, the entire network can be disrupted. Troubleshooting and network expansion are difficult due to its closed-loop design, making maintenance time-consuming and costly. Data transmission delays increase as the network grows, impacting overall performance and efficiency.
Use Cases: When to Choose Daisy Chain or Ring Topology
Daisy chain topology is ideal for small networks or devices that require simple, sequential communication with minimal cabling, such as peripheral connections in home or office setups. Ring topology suits larger, more complex networks where reliable data transmission and fault tolerance are crucial, like in metropolitan area networks (MANs) or fiber optic systems. When considering Your network's scalability and fault tolerance needs, choose daisy chain for simplicity and cost-effectiveness, while ring topology offers improved redundancy and performance.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Topology for Your Network
Choosing the right network topology depends on factors like scalability, fault tolerance, and performance needs. Daisy chain topology offers simplicity and ease of installation but suffers from limited fault tolerance since a single failure disrupts the entire network. Ring topology provides better reliability through its closed loop design, allowing data to flow in both directions and minimizing downtime, making it a stronger choice for mission-critical networks.
Daisy Chain vs Ring Topology Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com