Coreless motors offer higher efficiency and faster response times due to their lightweight, rotor-free design, while iron core motors provide greater torque and durability for heavy-duty applications. Choosing between coreless and iron core motors depends on whether your priority is precision and speed or strength and robustness.
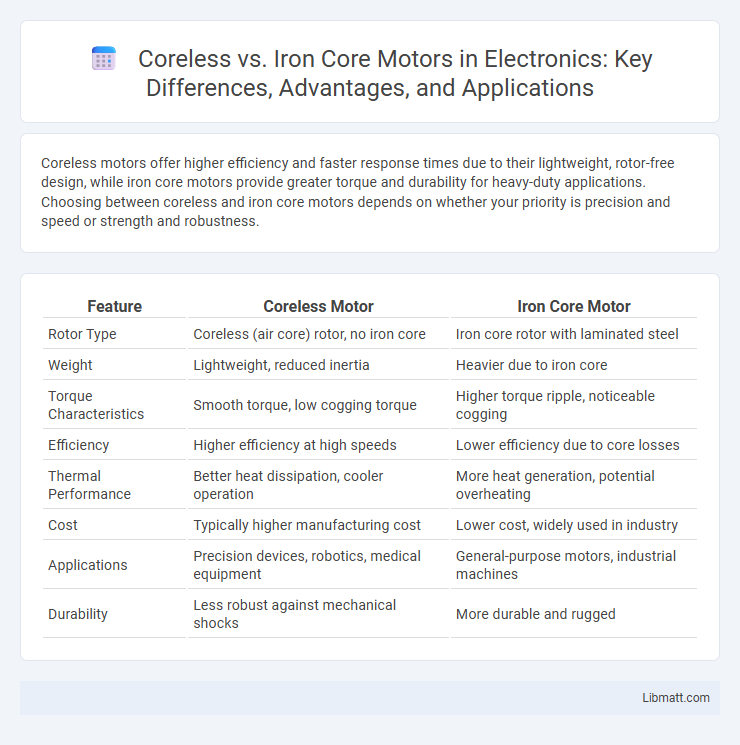
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Coreless Motor | Iron Core Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Rotor Type | Coreless (air core) rotor, no iron core | Iron core rotor with laminated steel |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduced inertia | Heavier due to iron core |
| Torque Characteristics | Smooth torque, low cogging torque | Higher torque ripple, noticeable cogging |
| Efficiency | Higher efficiency at high speeds | Lower efficiency due to core losses |
| Thermal Performance | Better heat dissipation, cooler operation | More heat generation, potential overheating |
| Cost | Typically higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, widely used in industry |
| Applications | Precision devices, robotics, medical equipment | General-purpose motors, industrial machines |
| Durability | Less robust against mechanical shocks | More durable and rugged |
Introduction to Coreless and Iron Core Motors
Coreless motors feature a rotor without an iron core, reducing inertia and enabling faster acceleration and higher efficiency compared to traditional iron core motors. Iron core motors use a solid iron core in the rotor, providing strong magnetic flux and durability but resulting in greater weight and slower response times. Your choice between coreless and iron core motors depends on application needs such as precision, speed, and torque requirements.
What is a Coreless Motor?
A coreless motor features a rotor made without an iron core, typically constructed using a self-supporting coil that reduces weight and inertia. This design allows for faster acceleration, higher efficiency, and lower cogging torque compared to traditional iron core motors. Your choice of a coreless motor can significantly improve precision and responsiveness in applications like robotics and medical devices.
What is an Iron Core Motor?
An iron core motor features a rotor or stator constructed from laminated iron sheets, which enhances magnetic flux and increases motor efficiency by reducing energy loss due to eddy currents. These motors provide higher torque and better performance under heavy load conditions, making them ideal for industrial applications where durability and power are essential. Understanding whether your application demands the strength of an iron core motor can help optimize performance and longevity.
Key Differences Between Coreless and Iron Core Motors
Coreless motors feature a rotor without an iron core, reducing inertia and enabling faster acceleration and smooth operation, while iron core motors contain a solid iron core that enhances magnetic flux and torque output but increases weight and cogging. Coreless motors excel in applications requiring high efficiency and precise control at low speeds, whereas iron core motors are preferred for high-torque, cost-effective uses with robust magnetic performance. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the optimal motor type based on performance needs and design constraints.
Advantages of Coreless Motors
Coreless motors offer superior efficiency due to their lightweight, rotorless design, resulting in reduced inertia and faster response times compared to iron core motors. These motors produce minimal cogging torque, ensuring smoother and quieter operation ideal for precision applications like robotics and medical devices. You benefit from enhanced thermal management and longer lifespan thanks to less heat generation and reduced wear on components.
Benefits of Iron Core Motors
Iron core motors offer enhanced durability and robustness due to their solid laminated steel cores, which provide better magnetic flux and higher torque output compared to coreless motors. Their design allows for improved heat dissipation, ensuring longer operational life and reliable performance under heavy loads. If your application requires sustained power and efficiency, iron core motors are an excellent choice for stable and cost-effective performance.
Applications of Coreless Motors
Coreless motors are highly valued in precision applications like medical devices, drones, and robotics due to their lightweight design, high efficiency, and rapid acceleration. Unlike iron core motors, coreless motors minimize electromagnetic losses and cogging torque, making them ideal for ultra-sensitive instruments and battery-powered equipment where smooth and quiet operation matters. Your choice of a coreless motor can enhance performance in applications demanding compact size and precise control.
Typical Uses for Iron Core Motors
Iron core motors are commonly used in applications requiring high torque and durability, such as industrial machinery, HVAC systems, and automotive components. Their magnetic steel core provides enhanced magnetic flux, making them suitable for heavy-duty tasks and environments with continuous operation demands. This structural design enables efficient heat dissipation and stable performance under mechanical stress.
Choosing the Right Motor: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right motor requires evaluating torque output, efficiency, and application-specific needs, where coreless motors excel in lightweight and high-speed scenarios due to their minimal inertia and low cogging torque. Iron core motors provide higher torque density and robustness, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications requiring sustained power and durability. Consider factors such as operational speed, load requirements, thermal management, and efficiency to determine the most efficient motor type for your specific use case.
Conclusion: Coreless vs Iron Core Motors
Coreless motors provide higher efficiency, faster response, and reduced cogging due to the absence of an iron core, making them ideal for precision applications and low inertia requirements. Iron core motors offer greater torque and durability at a lower cost, suitable for heavy-duty and high-load conditions. Choosing between coreless and iron core motors depends on the specific application demands such as efficiency, torque, size, and cost constraints.
Coreless vs Iron core motor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com