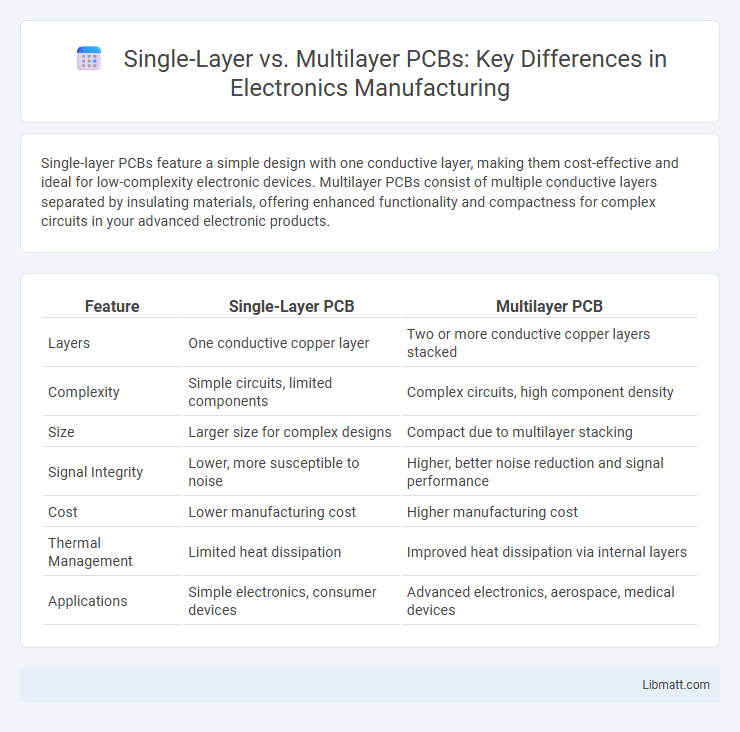
Single-layer PCBs feature a simple design with one conductive layer, making them cost-effective and ideal for low-complexity electronic devices. Multilayer PCBs consist of multiple conductive layers separated by insulating materials, offering enhanced functionality and compactness for complex circuits in your advanced electronic products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Single-Layer PCB | Multilayer PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Layers | One conductive copper layer | Two or more conductive copper layers stacked |
| Complexity | Simple circuits, limited components | Complex circuits, high component density |
| Size | Larger size for complex designs | Compact due to multilayer stacking |
| Signal Integrity | Lower, more susceptible to noise | Higher, better noise reduction and signal performance |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost | Higher manufacturing cost |
| Thermal Management | Limited heat dissipation | Improved heat dissipation via internal layers |
| Applications | Simple electronics, consumer devices | Advanced electronics, aerospace, medical devices |
Introduction to PCB Technologies
Single-layer PCBs consist of a single conductive layer for circuitry, typically used in simple electronic devices, offering cost-effective and straightforward design solutions. Multilayer PCBs contain multiple stacked conductive layers insulated by dielectric materials, enabling complex circuit designs with enhanced functionality and reduced size for advanced electronics. These PCB technologies play a critical role in determining device performance, signal integrity, and manufacturing costs in various applications.
What is a Single-Layer PCB?
A Single-Layer PCB consists of a single conductive copper layer on one side of a non-conductive substrate, forming the simplest type of circuit board. It is commonly used in low-complexity electronic devices due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. Your project benefits from Single-Layer PCBs when minimal component density and straightforward circuit design are required.
What is a Multilayer PCB?
A multilayer PCB consists of three or more conductive copper layers stacked and separated by insulating dielectric materials, enabling complex circuit designs with higher component density. These layers are interconnected through vias, which allow electrical signals to pass vertically through the board, optimizing space and performance. Multilayer PCBs are essential in advanced electronics such as smartphones, medical devices, and aerospace systems due to their enhanced electrical performance and compact size.
Construction Differences: Single-Layer vs Multilayer
Single-layer PCBs consist of a single conductive copper layer on one side of the substrate, making them simpler and cheaper to manufacture but limited in circuit complexity. Multilayer PCBs contain multiple alternating layers of conductive copper and insulating substrate, allowing for high-density circuit design and improved electrical performance within a compact form. The construction differences directly impact the PCB's durability, signal integrity, and application scope in electronic devices.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Single-layer PCBs offer simpler electrical pathways with lower signal interference, making them suitable for basic circuits with minimal components. Multilayer PCBs enhance electrical performance by enabling complex routing, improved signal integrity, and reduced electromagnetic interference through additional ground and power planes. Your choice depends on circuit complexity and the need for stable high-frequency performance in electronic devices.
Design Flexibility and Complexity
Single-layer PCBs offer limited design flexibility due to their simple structure, restricting circuit complexity and component placement to one side only. Multilayer PCBs provide enhanced design flexibility by allowing multiple circuit layers, enabling intricate and compact layouts suitable for advanced electronic devices. Your choice between single-layer and multilayer PCBs directly impacts the complexity, performance, and scalability of your electronic design.
Cost Implications
Single-layer PCBs typically have lower manufacturing costs due to simpler design and fewer materials, making them ideal for budget-sensitive projects with basic circuit requirements. Multilayer PCBs, while more expensive, support complex designs and higher component density, which can reduce overall system costs by minimizing board size and improving performance. Cost implications also include assembly and testing expenses, which tend to increase with the number of layers because of increased complexity and quality control needs.
Applications of Single-Layer PCBs
Single-layer PCBs are ideal for simple, low-cost electronic devices such as calculators, power supplies, and LED lighting systems due to their straightforward design and ease of manufacture. They are commonly used in applications where minimal component density and basic circuit functionality are required, making them suitable for household appliances and basic industrial equipment. Your choice of a single-layer PCB can enhance reliability and reduce production expenses in projects with uncomplicated electrical requirements.
Applications of Multilayer PCBs
Multilayer PCBs are widely used in advanced electronic devices such as smartphones, medical equipment, aerospace systems, and computer hardware due to their ability to support complex circuitry within a compact space. These PCBs enhance signal integrity, reduce electromagnetic interference, and improve overall device performance by providing multiple layers for power distribution and signal routing. Your choice of multilayer PCB can significantly impact device reliability and functionality in high-performance applications.
Choosing the Right PCB for Your Project
Choosing the right PCB for your project depends on complexity, space constraints, and budget. Single-layer PCBs are ideal for simple circuits with low component density and cost-effectiveness, while multilayer PCBs support high-density circuits, improved signal integrity, and enhanced electrical performance for advanced applications. Evaluating factors like signal speed, electromagnetic interference, and mechanical durability helps determine whether a single-layer or multilayer PCB best fits your design requirements.
Single-Layer vs Multilayer PCB Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com