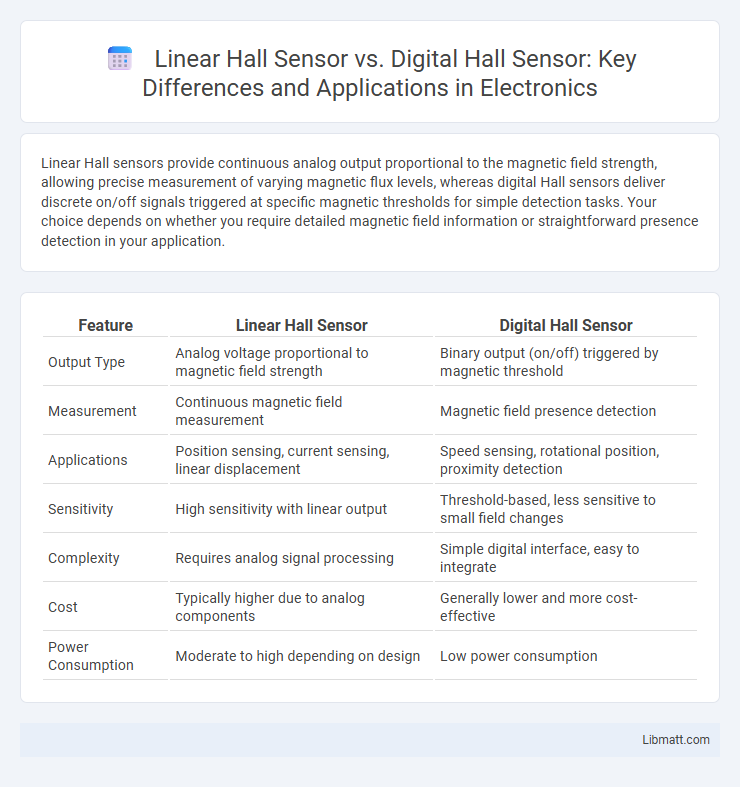
Linear Hall sensors provide continuous analog output proportional to the magnetic field strength, allowing precise measurement of varying magnetic flux levels, whereas digital Hall sensors deliver discrete on/off signals triggered at specific magnetic thresholds for simple detection tasks. Your choice depends on whether you require detailed magnetic field information or straightforward presence detection in your application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Linear Hall Sensor | Digital Hall Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Output Type | Analog voltage proportional to magnetic field strength | Binary output (on/off) triggered by magnetic threshold |
| Measurement | Continuous magnetic field measurement | Magnetic field presence detection |
| Applications | Position sensing, current sensing, linear displacement | Speed sensing, rotational position, proximity detection |
| Sensitivity | High sensitivity with linear output | Threshold-based, less sensitive to small field changes |
| Complexity | Requires analog signal processing | Simple digital interface, easy to integrate |
| Cost | Typically higher due to analog components | Generally lower and more cost-effective |
| Power Consumption | Moderate to high depending on design | Low power consumption |
Overview of Hall Effect Sensors
Hall effect sensors detect magnetic fields by measuring the voltage generated when a magnetic field interacts with a current-carrying conductor. Linear hall sensors provide an analog output proportional to the magnetic field strength, ideal for precise position or proximity measurements. Digital hall sensors output a binary signal indicating the presence or absence of a magnetic field, making them suitable for speed or rotational position detection in your applications.
What is a Linear Hall Sensor?
A Linear Hall Sensor measures the continuous magnetic field strength and outputs a proportional analog voltage, enabling precise detection of magnetic field variations. It differs from a Digital Hall Sensor, which provides a binary output indicating the presence or absence of a magnetic field. Linear Hall Sensors are commonly used in applications requiring accurate position, speed, or current sensing.
What is a Digital Hall Sensor?
A Digital Hall Sensor detects magnetic fields and outputs a binary signal indicating the presence or absence of a magnetic field, typically used for precise switching applications. Unlike Linear Hall Sensors that provide an analog voltage proportional to the magnetic field strength, Digital Hall Sensors operate with discrete ON/OFF signals, simplifying integration with digital systems. This makes Digital Hall Sensors ideal for position sensing, speed detection, and current sensing in automotive and industrial automation.
Working Principle: Linear vs Digital Hall Sensors
Linear Hall sensors measure the continuous strength of a magnetic field and produce an analog voltage output proportional to the field's intensity, enabling precise position or current sensing. Digital Hall sensors detect the presence or absence of a magnetic field and provide a binary output, typically used for switch or speed detection applications. The key difference lies in linear sensors offering variable signals for detailed measurement while digital sensors provide discrete on/off signals for simple detection.
Key Differences Between Linear and Digital Hall Sensors
Linear Hall sensors provide analog output proportional to the magnetic field strength, enabling precise measurements of magnetic flux density. Digital Hall sensors deliver binary output, switching states when the magnetic field crosses a specific threshold, ideal for simple presence or position detection. The key differences lie in output type, sensitivity to magnetic field variations, and application suitability, with linear sensors favored for continuous sensing and digital sensors preferred for on/off detection tasks.
Applications of Linear Hall Sensors
Linear Hall sensors are widely used in applications requiring precise measurement of magnetic field strength, such as current sensing in automotive battery management systems and position detection in industrial automation. Their analog output enables fine-tuned control in brushless DC motors and proximity sensing in consumer electronics, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of your devices. Compared to digital Hall sensors, linear types offer continuous data, making them ideal for dynamic monitoring and feedback systems.
Applications of Digital Hall Sensors
Digital Hall sensors are widely used in applications requiring precise magnetic field detection and position sensing, such as brushless DC motor commutation, speed detection in automotive systems, and proximity switching in consumer electronics. Their output, typically a binary signal, simplifies integration with digital control systems and microcontrollers, making them ideal for rotational speed measurement and gear tooth sensing. Your projects benefit from digital Hall sensors' reliability in detecting magnetic poles accurately, enabling efficient performance in robotics, industrial automation, and electronic compasses.
Advantages and Limitations of Linear Hall Sensors
Linear Hall sensors offer continuous analog output that enables precise measurement of magnetic field strength, making them ideal for applications requiring variable position or current sensing. Their advantage lies in high resolution and sensitivity to small changes in magnetic flux, providing accurate and real-time data. Limitations include susceptibility to noise, temperature drift, and the need for signal conditioning, which can complicate system design compared to discrete on/off digital Hall sensors.
Advantages and Limitations of Digital Hall Sensors
Digital Hall sensors offer precise on/off detection of magnetic fields with simple output signals ideal for binary switching applications, enabling easy integration with microcontrollers. Their advantages include low power consumption, noise immunity, and compact size, making them reliable in automotive and consumer electronics. However, limitations arise from their inability to provide variable magnetic field strength data, restricting their use where proportional sensing is essential compared to linear Hall sensors.
Choosing the Right Hall Sensor for Your Application
Linear Hall sensors provide continuous analog output proportional to magnetic field strength, making them ideal for applications requiring precise position or current measurement. Digital Hall sensors, offering simple on/off outputs, suit applications needing binary detection such as speed sensing or proximity switches. Your choice depends on whether your system demands exact field measurements or straightforward magnetic presence detection.
Linear Hall Sensor vs Digital Hall Sensor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com