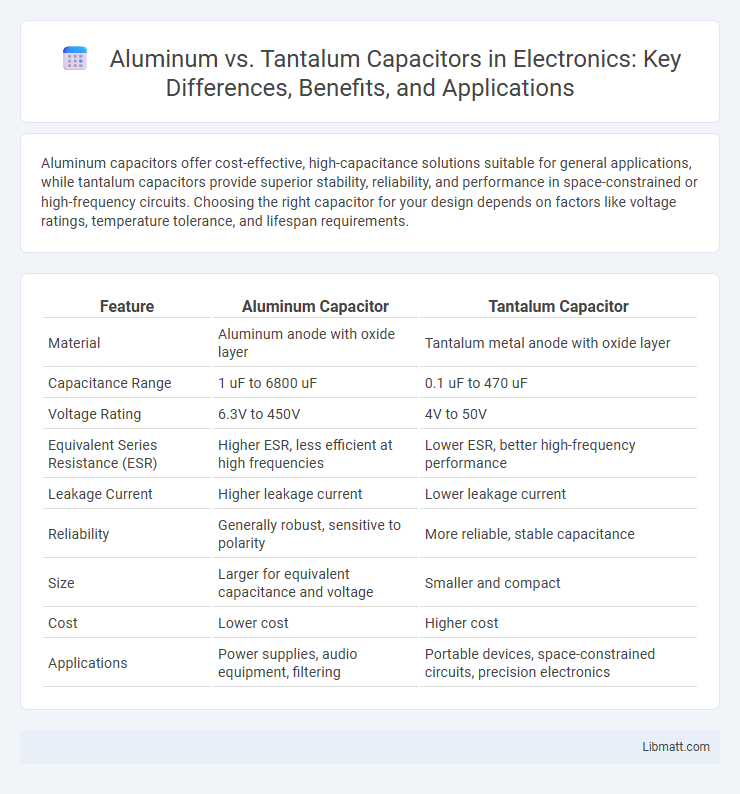
Aluminum capacitors offer cost-effective, high-capacitance solutions suitable for general applications, while tantalum capacitors provide superior stability, reliability, and performance in space-constrained or high-frequency circuits. Choosing the right capacitor for your design depends on factors like voltage ratings, temperature tolerance, and lifespan requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aluminum Capacitor | Tantalum Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Aluminum anode with oxide layer | Tantalum metal anode with oxide layer |
| Capacitance Range | 1 uF to 6800 uF | 0.1 uF to 470 uF |
| Voltage Rating | 6.3V to 450V | 4V to 50V |
| Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) | Higher ESR, less efficient at high frequencies | Lower ESR, better high-frequency performance |
| Leakage Current | Higher leakage current | Lower leakage current |
| Reliability | Generally robust, sensitive to polarity | More reliable, stable capacitance |
| Size | Larger for equivalent capacitance and voltage | Smaller and compact |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Applications | Power supplies, audio equipment, filtering | Portable devices, space-constrained circuits, precision electronics |
Introduction to Aluminum and Tantalum Capacitors
Aluminum capacitors utilize an oxide layer as the dielectric and offer high capacitance with low cost, making them ideal for power supply filtering and audio applications. Tantalum capacitors feature a tantalum pentoxide dielectric, providing higher volumetric efficiency, stability, and longer life, often used in space-constrained and high-reliability electronics. Both types differ significantly in performance characteristics such as equivalent series resistance (ESR) and temperature tolerance, influencing their application in various electronic circuits.
Basic Construction and Materials
Aluminum capacitors feature an anode made of aluminum foil coated with an oxide layer serving as the dielectric, combined with a liquid or solid electrolyte that enhances conductivity. Tantalum capacitors use a tantalum metal powder anode sintered into a solid pellet, with a manganese dioxide or polymer electrolyte acting as the cathode, providing higher capacitance per volume. Your choice depends on the need for a robust dielectric and compact size, as tantalum capacitors offer superior stability and longevity compared to aluminum types.
Electrical Characteristics Comparison
Aluminum capacitors typically exhibit higher equivalent series resistance (ESR) and lower capacitance stability compared to tantalum capacitors, making them less suitable for high-frequency applications. Tantalum capacitors offer superior volumetric efficiency with stable capacitance over a wide temperature range and lower leakage current, enhancing performance in precision circuits. The voltage rating and surge current tolerance of tantalum capacitors generally surpass those of aluminum types, although aluminum capacitors provide better tolerance to voltage spikes and are more cost-effective for bulk storage.
Capacitance and Voltage Ratings
Aluminum capacitors typically offer higher capacitance values ranging from microfarads to several thousand microfarads, while tantalum capacitors provide lower capacitance but with exceptional stability. In voltage ratings, aluminum capacitors generally support a wide range from 6.3V up to 450V, whereas tantalum capacitors usually operate within a lower voltage range, commonly between 2V and 50V. The choice between the two depends on the required capacitance and voltage specifications for specific electronic circuit applications.
Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) Differences
Aluminum capacitors typically exhibit higher Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) compared to tantalum capacitors, affecting their performance in high-frequency applications. Tantalum capacitors maintain lower ESR values, resulting in better efficiency and reduced heat generation under high ripple current conditions. This ESR difference makes tantalum capacitors preferable for compact, stable power supply filtering where low losses are critical.
Reliability and Lifespan Analysis
Tantalum capacitors offer superior reliability and longer lifespan compared to aluminum capacitors due to their stable oxide layer and lower equivalent series resistance (ESR). Aluminum capacitors tend to have shorter lifespans because of electrolyte evaporation and higher ESR, which can lead to premature failure under high temperature and voltage stress. Your choice will impact device durability, with tantalum capacitors favored in critical applications demanding consistent performance over time.
Size and Form Factor Considerations
Aluminum capacitors typically offer larger sizes due to their wound construction, making them less suitable for compact or high-density designs, whereas tantalum capacitors provide smaller, more stable form factors ideal for space-constrained applications. Tantalum capacitors' solid manganese dioxide electrolyte enables a compact, reliable size with consistent performance over time. When designing your circuit, selecting tantalum capacitors can optimize board space without sacrificing capacitance or voltage ratings.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Aluminum capacitors are generally more cost-effective than tantalum capacitors due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making them preferred for bulk applications. Tantalum capacitors offer superior performance in terms of stability and reliability but come at a significantly higher price, reflecting the scarcity and higher processing costs of tantalum metal. In terms of market availability, aluminum capacitors are widely accessible with diverse product ranges, whereas tantalum capacitors have a more limited supply influenced by geopolitical factors affecting tantalum mining regions.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Aluminum capacitors are widely used in power supply filtering, audio equipment, and general-purpose electronic circuits due to their cost-effectiveness and high capacitance values. Tantalum capacitors excel in applications requiring stable capacitance, such as in portable devices, aerospace electronics, and medical implants, where reliability and size are critical. When selecting capacitors for your project, consider aluminum types for bulk energy storage and tantalum capacitors for precision and long-term stability.
Selection Guidelines: Which Capacitor to Choose?
Aluminum capacitors offer high capacitance values and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for general-purpose applications with moderate ripple currents and temperatures. Tantalum capacitors provide superior stability, lower equivalent series resistance (ESR), and better performance in low-voltage, high-reliability circuits, especially in aerospace and medical devices. Choose aluminum capacitors for bulk energy storage and cost-sensitive designs, while tantalum capacitors are preferred for applications requiring long-term reliability and compact sizes with stable performance.
Aluminum vs Tantalum Capacitor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com