A dip switch allows you to configure settings directly on a circuit board by toggling small switches, offering more precise and flexible control compared to a jumper, which requires physically placing or removing a small connector to alter configurations. Your choice between a dip switch and a jumper depends on the ease of access, frequency of changes, and the level of customization needed for your electronic device.
Table of Comparison
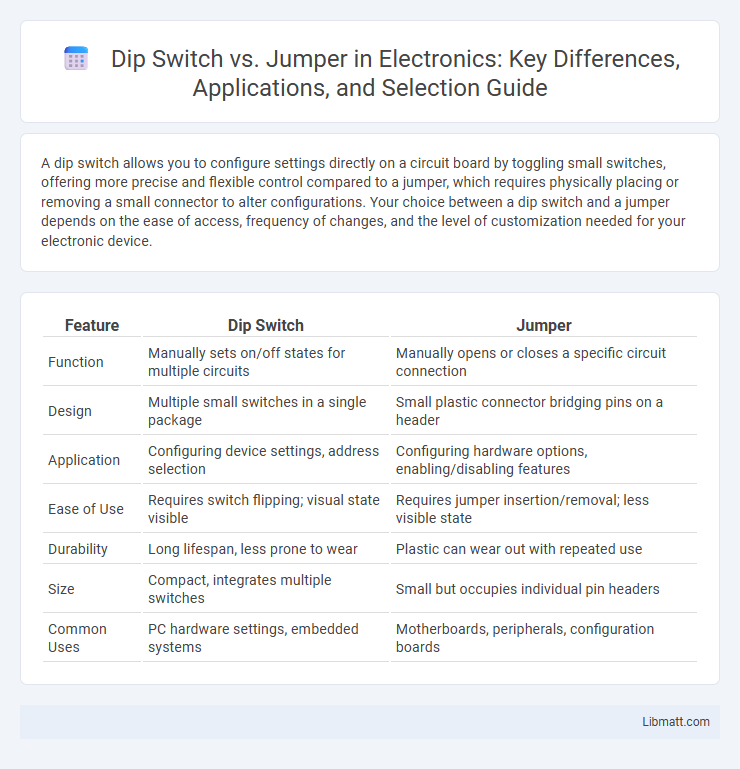
| Feature | Dip Switch | Jumper |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Manually sets on/off states for multiple circuits | Manually opens or closes a specific circuit connection |
| Design | Multiple small switches in a single package | Small plastic connector bridging pins on a header |
| Application | Configuring device settings, address selection | Configuring hardware options, enabling/disabling features |
| Ease of Use | Requires switch flipping; visual state visible | Requires jumper insertion/removal; less visible state |
| Durability | Long lifespan, less prone to wear | Plastic can wear out with repeated use |
| Size | Compact, integrates multiple switches | Small but occupies individual pin headers |
| Common Uses | PC hardware settings, embedded systems | Motherboards, peripherals, configuration boards |
Introduction to Dip Switches and Jumpers
Dip switches are small, manual electronic switches mounted on a circuit board for configuring device settings without soldering. Jumpers consist of small connectors that slide over pairs of pins to create or break electrical connections in hardware configurations. Both enable hardware customization, but dip switches offer multiple toggle positions, while jumpers typically provide binary on/off settings.
What Is a Dip Switch?
A Dip switch is a small manual electric switch packaged in a group that allows users to configure settings on electronic devices by toggling individual switches ON or OFF. It provides a simple and reliable method for setting hardware options or system configurations without the need for soldering or software changes. Your device can be customized easily by adjusting the Dip switch positions for specific functions or modes.
What Is a Jumper?
A jumper is a small connector used on printed circuit boards (PCBs) to close or open electrical circuits by fitting over two or more pins, enabling or disabling specific hardware functions without soldering. Unlike dip switches, jumpers require manual placement or removal to change settings, offering a more straightforward but less flexible means of hardware configuration. Jumper settings are commonly found in motherboards, hard drives, and other electronic devices for tasks like setting device modes or configuring voltage levels.
Key Differences Between Dip Switch and Jumper
Dip switches offer multiple, individually toggleable switches for setting configurations without the need to remove components, while jumpers require physically placing or removing a shunt to connect or disconnect circuit pins. Unlike jumpers, dip switches enable quick, tool-free adjustments directly on the PCB, making them suitable for frequent changes and precise binary settings. Jumpers are typically simpler, used for enabling or disabling features with fewer configuration options, ideal for more static setups.
Advantages of Using Dip Switches
Dip switches offer precise and reliable configuration options with easy on-board adjustments, eliminating the need for soldering or specialized tools. They enable quick and repetitive settings changes, ideal for firmware or hardware configurations in embedded systems. Compact design allows integration into tight spaces, improving device versatility and maintenance efficiency.
Benefits of Using Jumpers
Jumpers offer a simple and reliable method for configuring hardware settings without the need to remember complex binary codes, making adjustments more intuitive and less error-prone. They provide direct physical connections that ensure stable electrical contact, which is especially beneficial in environments with vibrations or movement. Your ability to quickly change configurations without specialized tools also enhances efficiency during setup or troubleshooting.
Typical Applications for Dip Switches
Dip switches are commonly used in electronic devices for setting configurations such as selecting operating modes, addressing hardware components, or enabling/disabling features without the need for software control. Typical applications include industrial machinery controls, consumer electronics, and computer hardware settings where reliable, manual binary input is required. Your devices benefit from dip switches for easy, low-cost customization and troubleshooting in embedded systems and communication equipment.
Common Uses for Jumpers
Jumpers are commonly used in computer motherboards and electronic devices to configure hardware settings such as enabling or disabling integrated components, setting device modes, and clearing CMOS memory. You often find jumpers in hard drive configurations and BIOS reset functions due to their simple and reliable design. Their ease of use makes them ideal for quick, manual hardware adjustments without requiring software intervention.
How to Choose: Dip Switch vs. Jumper
Choosing between a DIP switch and a jumper depends on the level of configurability and physical access required; DIP switches allow easy toggling of multiple settings without removing components, ideal for frequent adjustments, while jumpers provide a simpler, more secure connection suited for infrequent changes. Consider the device's space constraints and electrical signaling needs--DIP switches are preferred in compact circuits needing separate on/off states, whereas jumpers offer reliable, short-circuit connections for hardware configuration. Evaluate maintenance accessibility, as DIP switches facilitate quick changes without tools, contrasting with jumpers that require manual insertion or removal of pins for configuration.
Conclusion: Which Is Best for Your Electronics Project?
Dip switches offer precise control with multiple settings in a compact form, ideal for customizable configurations, while jumpers provide quick and simple circuit connections suitable for basic on/off or binary selections. Your choice depends on the complexity of your electronics project; use dip switches for flexible adjustments and jumpers for straightforward, low-maintenance setups. Consider factors like ease of use, space constraints, and required functionality to select the best component for your needs.
Dip Switch vs Jumper Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com