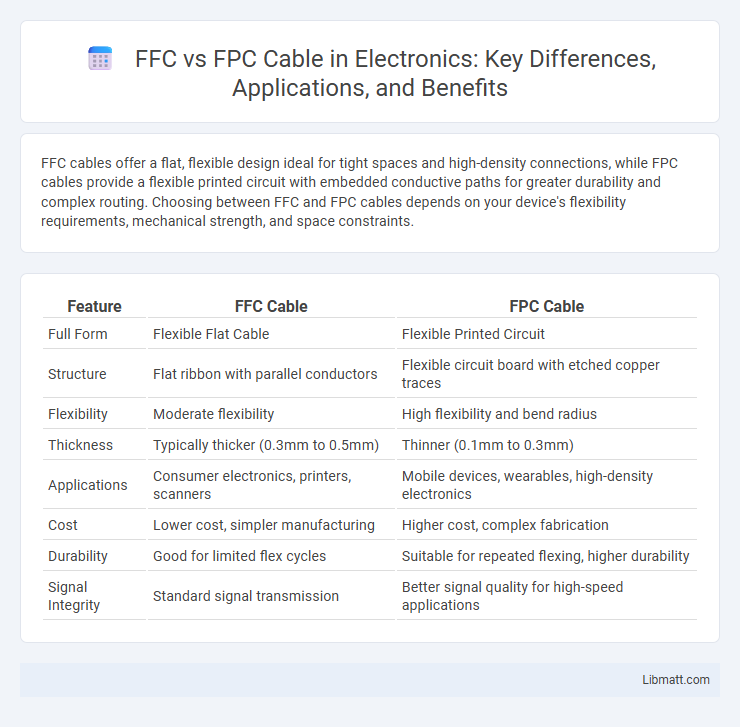
FFC cables offer a flat, flexible design ideal for tight spaces and high-density connections, while FPC cables provide a flexible printed circuit with embedded conductive paths for greater durability and complex routing. Choosing between FFC and FPC cables depends on your device's flexibility requirements, mechanical strength, and space constraints.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | FFC Cable | FPC Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Flexible Flat Cable | Flexible Printed Circuit |
| Structure | Flat ribbon with parallel conductors | Flexible circuit board with etched copper traces |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility and bend radius |
| Thickness | Typically thicker (0.3mm to 0.5mm) | Thinner (0.1mm to 0.3mm) |
| Applications | Consumer electronics, printers, scanners | Mobile devices, wearables, high-density electronics |
| Cost | Lower cost, simpler manufacturing | Higher cost, complex fabrication |
| Durability | Good for limited flex cycles | Suitable for repeated flexing, higher durability |
| Signal Integrity | Standard signal transmission | Better signal quality for high-speed applications |
Introduction to FFC and FPC Cables
FFC (Flat Flexible Cable) and FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) cables are essential components in modern electronic devices, designed to provide compact and reliable connections. FFC cables consist of multiple flat copper conductors laminated between insulating films, ideal for flexible and space-saving wiring solutions. FPC cables feature a flexible substrate with printed copper circuitry, offering higher density connections and enhanced durability for intricate electronic applications, helping you optimize device performance.
Understanding FFC Cable Technology
FFC cable technology features flat, flexible conductors laminated between insulating layers, enabling compact and space-saving connections in electronic devices. Unlike FPC cables, which use flexible printed circuits, FFC cables maintain straight, parallel conductive strips without additional circuit elements. This design offers enhanced durability and reliable signal transmission for applications requiring frequent bending and flexing.
Overview of FPC Cable Construction
FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) cables consist of a thin insulating polymer film with multiple copper conductive traces bonded using a laminated process, allowing them to bend without damaging electrical connections. Their construction includes a base polyester or polyimide layer, copper conductors etched to create the circuit, and a protective overlay to insulate and reinforce the cable. Your choice of FPC cable ensures compact, lightweight, and highly flexible interconnections ideal for modern electronic devices.
Key Differences Between FFC and FPC
FFC (Flat Flexible Cable) consists of multiple flat metallic conductors laminated between layers of insulating film, offering excellent flexibility for tight spaces and consistent electrical performance. FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit), on the other hand, integrates conductive copper traces on a flexible polymer substrate, allowing for complex circuit designs with multiple layers and components. Your choice between FFC and FPC depends on factors like design complexity, space constraints, and electrical requirements, with FFC ideal for simple connections and FPC suited for intricate circuitry.
Common Applications of FFC Cables
FFC cables are commonly used in compact electronic devices such as laptops, printers, and smartphones for their flexibility and space-saving design. These flat flexible cables facilitate reliable connections between printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other components without adding bulk. Your devices benefit from enhanced performance and durability due to the efficient signal transmission these cables provide in tight spaces.
Typical Uses of FPC Cables
FPC cables, known for their flexibility and compact size, are typically used in applications requiring tight bending and space-saving solutions, such as smartphones, laptops, and digital cameras. These cables efficiently connect small electronic components within confined spaces, providing reliable signal transmission without bulk. Their adaptability makes them ideal for wearable devices, medical equipment, and other compact electronic assemblies.
Advantages of FFC Over FPC
FFC cables offer superior flexibility and thinner profiles compared to FPC cables, making them ideal for compact electronic devices requiring precise space management. Their flat, ribbon-like design enhances signal integrity and reduces electromagnetic interference, ensuring reliable data transmission. FFC cables also provide easier installation and replacement due to their standard connectors, lowering maintenance time and costs.
Benefits of FPC Compared to FFC
FPC cables offer superior flexibility and a thinner profile compared to FFC cables, making them ideal for compact electronic devices and intricate circuit designs. Their enhanced durability and resistance to bending stress extend the lifespan of connections in dynamic applications. FPC cables also provide better electrical performance due to reduced impedance and interference, improving signal integrity in high-frequency circuits.
Selecting the Right Cable for Your Project
Choosing between FFC (Flexible Flat Cable) and FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) depends on your project's electrical requirements and mechanical constraints. FFCs offer cost-effective, easy-to-install solutions ideal for low-pin-count connections, while FPCs provide higher density interconnections with customizable layouts suitable for complex electronic assemblies. Evaluating factors such as flexibility, space limitations, current carrying capacity, and signal integrity ensures optimal cable selection for reliable performance.
Future Trends in Flexible Cable Technology
Future trends in flexible cable technology emphasize the integration of advanced materials like ultra-thin polymers and conductive nanomaterials to enhance flexibility and durability in both FFC and FPC cables. Innovations in miniaturization and multi-layered designs improve signal integrity and allow higher data transmission rates, critical for evolving electronics in smartphones, wearables, and automotive applications. The adoption of smart flexible cables with embedded sensors and self-healing capabilities is expected to revolutionize connectivity solutions in IoT and flexible electronics markets.
FFC vs FPC Cable Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com