eMMC storage offers a cost-effective solution with moderate performance suitable for budget devices, while UFS storage delivers significantly faster data transfer speeds and improved multitasking capabilities, enhancing overall device responsiveness. Choosing UFS storage can greatly boost your device's performance, especially for demanding applications and high-speed data access.
Table of Comparison
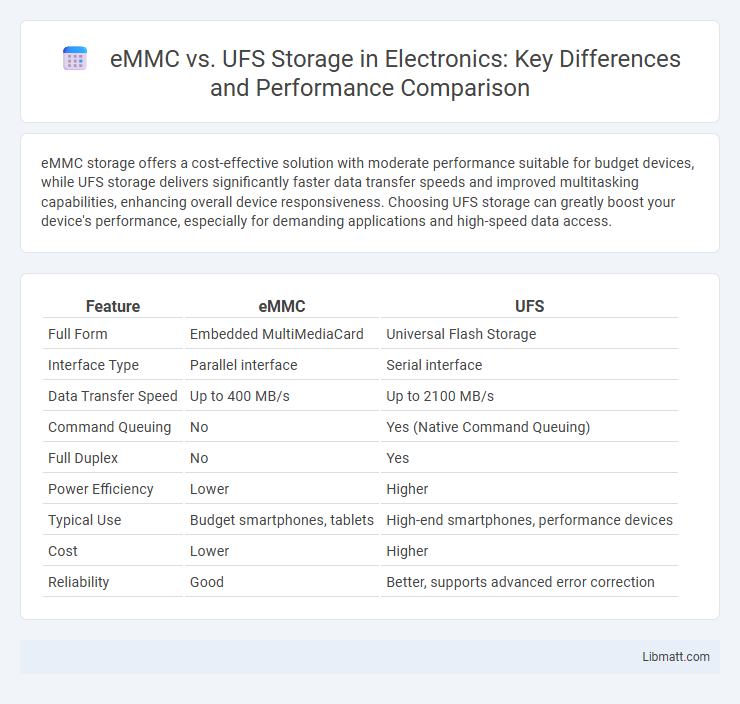
| Feature | eMMC | UFS |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Embedded MultiMediaCard | Universal Flash Storage |
| Interface Type | Parallel interface | Serial interface |
| Data Transfer Speed | Up to 400 MB/s | Up to 2100 MB/s |
| Command Queuing | No | Yes (Native Command Queuing) |
| Full Duplex | No | Yes |
| Power Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Use | Budget smartphones, tablets | High-end smartphones, performance devices |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Reliability | Good | Better, supports advanced error correction |
Introduction to Flash Storage Technologies
Flash storage technologies such as eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard) and UFS (Universal Flash Storage) represent significant advancements in data storage, offering faster read/write speeds and improved efficiency over traditional HDDs. eMMC, commonly used in budget devices, combines a flash memory and a controller in a single package, while UFS provides higher performance through parallel data transfer and command queuing. Your device's responsiveness and multitasking capabilities can be greatly enhanced by choosing UFS over eMMC due to its superior architecture and speed.
What is eMMC Storage?
eMMC storage, or Embedded MultiMediaCard, is a type of flash storage commonly used in smartphones, tablets, and budget laptops for internal data storage. It integrates the flash memory and controller on a single chip, offering moderate read/write speeds suitable for everyday tasks but slower compared to UFS (Universal Flash Storage). eMMC is cost-effective and widely adopted in entry-level devices due to its compact size and sufficient performance for basic applications.
What is UFS Storage?
UFS (Universal Flash Storage) is a high-performance storage standard designed for smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices, offering faster data transfer speeds and lower power consumption compared to eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard). UFS utilizes a full-duplex serial interface, enabling simultaneous read and write operations that significantly improve multitasking and overall device responsiveness. Its advanced architecture supports higher command queue depths and improved reliability, making UFS the preferred choice for modern mobile storage solutions.
Key Differences Between eMMC and UFS
eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard) storage offers slower data transfer speeds and lower efficiency compared to UFS (Universal Flash Storage), which boasts higher performance due to full-duplex communication and advanced command queuing. UFS supports faster read/write speeds, better power management, and improved multitasking capabilities, making it ideal for high-end smartphones and devices requiring rapid data access. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right storage technology based on your device's performance needs and budget constraints.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Efficiency
UFS storage outperforms eMMC significantly in speed and efficiency, offering sequential read/write speeds up to 2100 MB/s compared to eMMC's maximum of around 400 MB/s. UFS uses full-duplex technology allowing simultaneous read and write operations, improving multitasking and reducing latency, whereas eMMC operates in half-duplex mode. Energy efficiency is higher in UFS due to advanced power management, making it ideal for high-performance mobile devices and applications demanding rapid data access.
Reliability and Durability Factors
UFS (Universal Flash Storage) offers superior reliability and durability compared to eMMC due to its advanced error correction algorithms and efficient wear leveling technologies. eMMC utilizes a simpler controller, which can lead to faster wear and reduced lifespan under intensive read/write cycles. UFS's high-speed, full-duplex interface reduces heat generation and power consumption, directly contributing to enhanced data integrity and long-term device stability.
Power Consumption and Battery Impact
UFS storage technology offers significantly lower power consumption compared to eMMC, improving overall energy efficiency in mobile devices. UFS utilizes a full-duplex interface and optimized command queuing, resulting in faster data transfer rates and reduced active usage time, which minimizes battery drain. Devices equipped with UFS storage typically exhibit longer battery life due to these power-saving architectural advancements.
eMMC vs UFS: Use Cases and Applications
eMMC storage is commonly used in budget smartphones, tablets, and entry-level devices due to its cost-effectiveness and satisfactory performance for everyday tasks. UFS storage is preferred in flagship smartphones, high-end tablets, and ultrabooks because it offers faster data transfer speeds, better multitasking, and enhanced power efficiency. Devices requiring rapid read/write operations and improved responsiveness, such as gaming phones and advanced mobile computing, benefit significantly from UFS technology.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
eMMC storage remains a cost-effective solution widely available in budget devices, making it a preferred choice for manufacturers aiming to minimize production expenses while delivering reliable performance. UFS storage, though more expensive due to its advanced speed and efficiency features, is increasingly accessible in mid-range and premium smartphones, reflecting growing market adoption. Evaluating your device needs against budget constraints helps determine the most suitable storage technology based on cost and availability.
Which Storage is Right for You?
eMMC storage offers affordable, reliable performance suitable for budget smartphones and basic devices, while UFS storage delivers faster read/write speeds and enhanced multitasking capabilities ideal for high-end smartphones and consumer electronics. Consider UFS for gaming, 4K video recording, and intensive applications requiring rapid data access, whereas eMMC works well for everyday tasks and cost-sensitive devices. Choosing the right storage depends on your device's performance needs and budget constraints.
eMMC vs UFS Storage Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com