Radial capacitors feature leads extending from the same side, making them ideal for compact circuit board layouts with limited height, while axial capacitors have leads on opposite ends, providing better mechanical stability in applications with vibration or movement. Choosing the right capacitor depends on your specific design needs, including space constraints and the required durability for long-term performance.
Table of Comparison
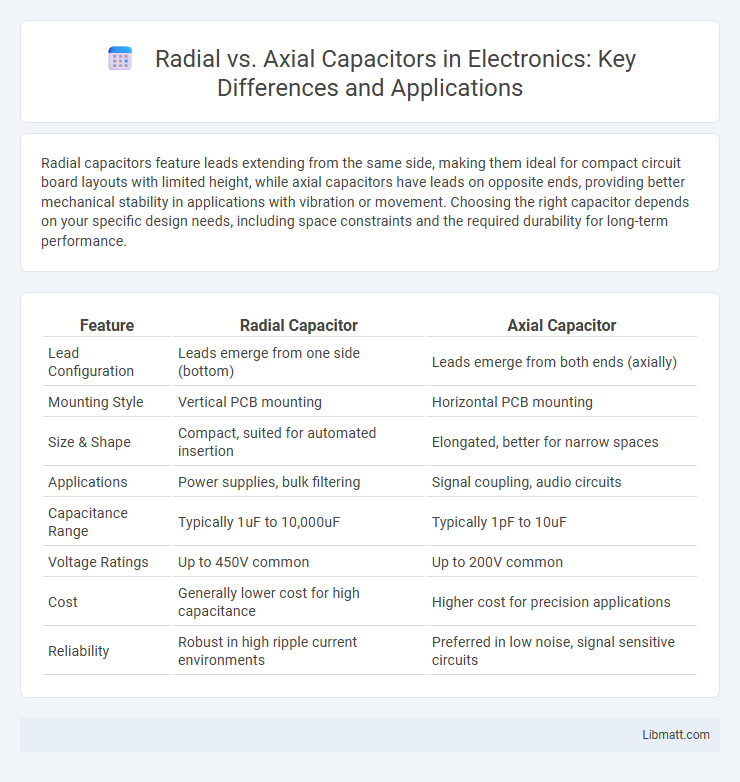
| Feature | Radial Capacitor | Axial Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Lead Configuration | Leads emerge from one side (bottom) | Leads emerge from both ends (axially) |
| Mounting Style | Vertical PCB mounting | Horizontal PCB mounting |
| Size & Shape | Compact, suited for automated insertion | Elongated, better for narrow spaces |
| Applications | Power supplies, bulk filtering | Signal coupling, audio circuits |
| Capacitance Range | Typically 1uF to 10,000uF | Typically 1pF to 10uF |
| Voltage Ratings | Up to 450V common | Up to 200V common |
| Cost | Generally lower cost for high capacitance | Higher cost for precision applications |
| Reliability | Robust in high ripple current environments | Preferred in low noise, signal sensitive circuits |
Introduction to Capacitor Types
Radial and axial capacitors differ primarily in their lead configuration, affecting ease of mounting and space utilization on circuit boards. Radial capacitors have both leads emerging from one end, making them ideal for vertical mounting and compact layouts, while axial capacitors feature leads on opposite ends, offering stable horizontal mounting suitable for point-to-point wiring. Understanding these capacitor types helps you select the right component for efficient circuit design and reliable performance.
What Is a Radial Capacitor?
A radial capacitor features leads extending from one side of a cylindrical or rectangular body, allowing compact and efficient placement on printed circuit boards (PCBs). This design supports automated assembly processes and is commonly used in power supplies, filtering, and signal processing applications. Your choice of a radial capacitor benefits from its ease of installation and reliable performance in space-constrained electronic devices.
What Is an Axial Capacitor?
An axial capacitor features leads extending from both ends of its cylindrical body, facilitating easy insertion into through-hole circuit boards, especially in tight spaces. Its design offers stable performance in applications requiring minimal mechanical stress and provides uniform lead spacing for reliable solder connections. Your electronic projects benefit from axial capacitors when compact component layout and consistent electrical characteristics are essential.
Structural Differences Between Radial and Axial Capacitors
Radial capacitors feature leads extending from the same end, allowing for compact vertical mounting on printed circuit boards (PCBs), while axial capacitors have leads protruding from opposite ends, facilitating horizontal placement. The structural design of radial capacitors supports higher capacitance in a smaller footprint, making them ideal for space-constrained applications. Axial capacitors provide mechanical stability and are suited for through-hole mounting where axial strain relief is required.
Installation and Mounting Methods
Radial capacitors feature two leads extending from the bottom, making them ideal for vertical mounting on printed circuit boards, which simplifies automated assembly and soldering processes. Axial capacitors have leads on opposite ends, allowing them to be mounted horizontally, suitable for applications with limited vertical space or when connecting components in series along a circuit path. Your choice between radial and axial capacitors should consider the PCB layout and mechanical stress conditions to ensure optimal installation and reliable performance.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Radial capacitors typically offer higher capacitance values and better high-frequency performance due to their shorter lead lengths and compact design, which reduces inductance and improves electrical efficiency. Axial capacitors provide greater mechanical stability and are often selected for applications requiring long-term reliability under vibration or thermal stress, despite generally having higher equivalent series resistance (ESR). Your choice between radial and axial capacitors should consider these electrical performance differences based on the specific demands of your circuit design.
Applications of Radial Capacitors
Radial capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits requiring high capacitance within a compact footprint, such as power supplies, audio amplifiers, and signal filtering applications. Their design, featuring leads exiting from one side, allows for easy insertion into printed circuit boards (PCBs) and enhances mechanical stability in vertical mounting configurations. You will often find radial capacitors favored in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and industrial equipment due to their reliable performance and efficient space utilization.
Applications of Axial Capacitors
Axial capacitors are widely used in applications requiring stability and compact mounting, such as in audio equipment, medical devices, and automotive electronics due to their long, narrow shape that fits well in tight spaces and provides reliable performance. They excel in through-hole circuit boards where durability against vibration is critical, making them ideal for power supplies, industrial controls, and lighting systems. Your projects benefit from axial capacitors when consistent capacitance and physical endurance are essential in demanding environments.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Radial vs Axial
Radial capacitors offer a compact design with a smaller footprint, making them ideal for high-density circuit boards, but their lead orientation can limit mounting options compared to axial capacitors. Axial capacitors provide versatile mounting flexibility due to leads extending from both ends, which is beneficial for certain circuit layouts, although they generally occupy more space and may not fit well in compact assemblies. Radial capacitors tend to have better mechanical stability and are often preferred in automated assembly processes, whereas axial capacitors excel in applications requiring strain relief and easy replacement.
How to Choose Between Radial and Axial Capacitors
Choosing between radial and axial capacitors depends on your specific application requirements such as space constraints and lead configuration. Radial capacitors feature leads on one side, making them ideal for compact, vertical mounting on circuit boards, while axial capacitors have leads on both ends, suited for low-profile, horizontal placement. Understanding your device's layout and electrical needs will help you determine which capacitor type offers the best fit for optimal performance and assembly efficiency.
Radial vs Axial Capacitor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com