LPC (Low Pin Count) and JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) are both serial communication interfaces primarily used for debugging and programming microcontrollers, with LPC focusing on minimal pin usage for reduced complexity and cost, while JTAG offers a standardized protocol for boundary scan testing and in-depth debugging capabilities. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize simplicity and fewer pins (LPC) or comprehensive testing and debugging features (JTAG).
Table of Comparison
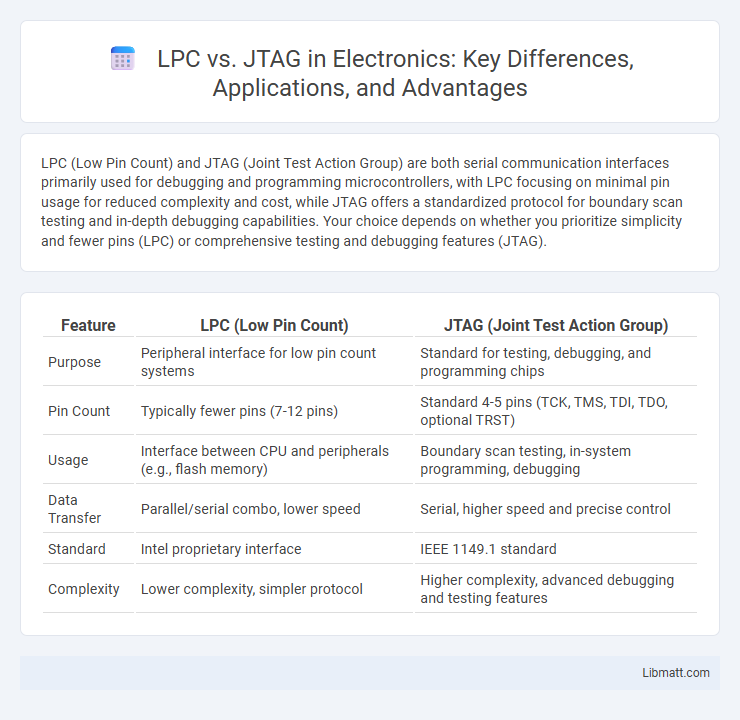
| Feature | LPC (Low Pin Count) | JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Peripheral interface for low pin count systems | Standard for testing, debugging, and programming chips |
| Pin Count | Typically fewer pins (7-12 pins) | Standard 4-5 pins (TCK, TMS, TDI, TDO, optional TRST) |
| Usage | Interface between CPU and peripherals (e.g., flash memory) | Boundary scan testing, in-system programming, debugging |
| Data Transfer | Parallel/serial combo, lower speed | Serial, higher speed and precise control |
| Standard | Intel proprietary interface | IEEE 1149.1 standard |
| Complexity | Lower complexity, simpler protocol | Higher complexity, advanced debugging and testing features |
Introduction to LPC and JTAG
LPC (Low Pin Count) and JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) are essential protocols for embedded system debugging and programming. LPC interface uses fewer pins to facilitate communication with devices like microcontrollers, while JTAG provides a standardized method for testing and verifying integrated circuits through boundary-scan architecture. Understanding both LPC and JTAG enables you to optimize hardware development and debugging processes effectively.
What is LPC?
LPC (Low Pin Count) is a communication interface primarily used for connecting embedded controllers, such as ASICs and microcontrollers, to system chips including BIOS ROMs and I/O controllers. It operates with fewer pins than traditional parallel interfaces, offering a cost-effective and space-saving solution for data transfer in PC architectures. LPC typically supports a single master and multiple slave devices, facilitating essential low-bandwidth system management and control tasks.
What is JTAG?
JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) is a standardized interface used for testing and debugging integrated circuits through a serial communication protocol. It enables boundary-scan testing, device programming, and system diagnostics by accessing internal registers without requiring physical pins for each signal. JTAG is widely implemented in microcontrollers, FPGAs, and ASICs for streamlined hardware verification and firmware development.
Key Differences Between LPC and JTAG
LPC (Low Pin Count) interface uses fewer pins for communication, optimizing board space and reducing cost, while JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) provides a standardized debugging interface with more extensive test functionalities. LPC primarily supports data transfer and programming tasks, whereas JTAG facilitates boundary scan testing, device programming, and real-time debugging of integrated circuits. The speed and complexity of JTAG are higher, making it suitable for in-depth hardware diagnostics, while LPC is designed for efficient, streamlined communication in embedded systems.
Typical Applications of LPC
LPC (Low Pin Count) interface is commonly used in embedded systems for efficient communication between microcontrollers and peripheral devices, offering a simple and cost-effective solution for tasks like BIOS flash memory programming and legacy I/O connectivity. Unlike JTAG, which is primarily designed for debugging, testing, and boundary scan operations, LPC excels in applications requiring lower pin count and lower power consumption. Your design can benefit from LPC in scenarios where space constraints and affordability are crucial, such as in consumer electronics and industrial control systems.
Typical Applications of JTAG
JTAG is primarily used for boundary-scan testing, device programming, and debugging in embedded systems and semiconductor manufacturing. It allows hardware developers and engineers to perform in-circuit testing of printed circuit boards (PCBs), verifying signal integrity and connectivity without physical probes. Your development process benefits from JTAG's ability to provide real-time access to the internal states of chips, enabling efficient fault diagnosis and system validation.
Advantages of Using LPC
LPC (Low Pin Count) interface offers a simplified, cost-effective connection with fewer pins compared to JTAG, reducing PCB complexity and saving space. It supports essential debugging and programming functions while minimizing signal interference and power consumption. LPC is highly efficient for embedded systems requiring compact designs and reliable communication with microcontrollers.
Advantages of Using JTAG
JTAG offers precise boundary-scan testing capabilities that enable in-system debugging and fault isolation without physical probing, reducing time and costs associated with hardware diagnostics. It supports real-time access to internal registers and memory, facilitating effective firmware development and verification across complex integrated circuits. JTAG standards ensure broad compatibility and standardized test access, making it the preferred choice for advanced electronics manufacturing and maintenance.
LPC vs JTAG: Performance Comparison
LPC (Low Pin Count) interfaces deliver higher data transfer rates compared to JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) due to their simplified signaling and reduced pin usage, enabling faster programming and debugging. JTAG offers robust boundary-scan testing and device programming capabilities but generally operates at lower speeds because of its serial communication protocol and extensive pin requirement. In performance-critical environments, LPC's streamlined design results in superior throughput, making it preferable for rapid firmware updates and boot processes.
Choosing the Right Interface for Your Project
Choosing between LPC and JTAG interfaces depends on your project's debugging and programming needs. LPC (Low Pin Count) offers a streamlined connection with fewer pins, ideal for simpler or space-constrained designs, while JTAG provides extensive testing, programming, and debugging capabilities critical for complex embedded systems. Evaluate your hardware's complexity and required debugging depth to select the interface that maximizes efficiency and compatibility for your specific application.
LPC vs JTAG Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com