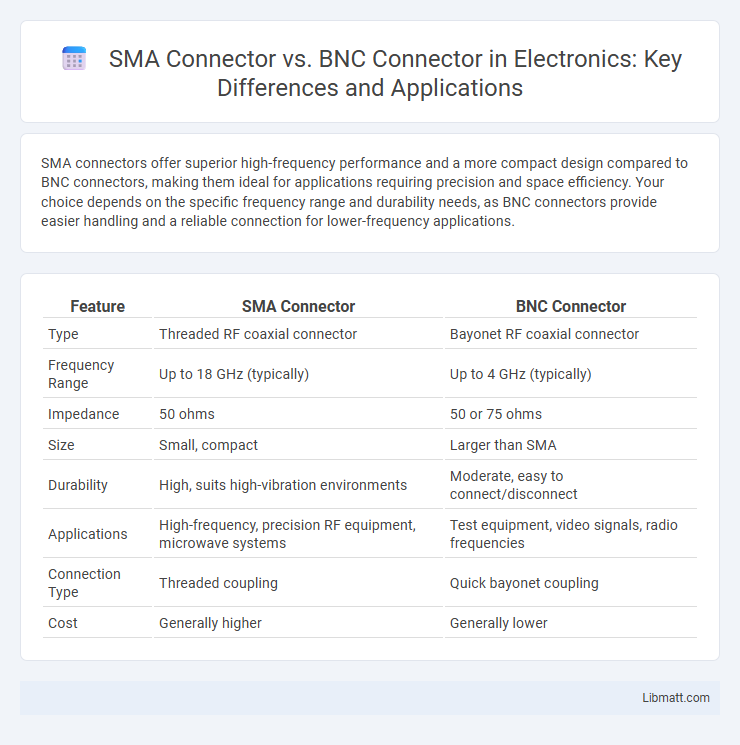
SMA connectors offer superior high-frequency performance and a more compact design compared to BNC connectors, making them ideal for applications requiring precision and space efficiency. Your choice depends on the specific frequency range and durability needs, as BNC connectors provide easier handling and a reliable connection for lower-frequency applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | SMA Connector | BNC Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Threaded RF coaxial connector | Bayonet RF coaxial connector |
| Frequency Range | Up to 18 GHz (typically) | Up to 4 GHz (typically) |
| Impedance | 50 ohms | 50 or 75 ohms |
| Size | Small, compact | Larger than SMA |
| Durability | High, suits high-vibration environments | Moderate, easy to connect/disconnect |
| Applications | High-frequency, precision RF equipment, microwave systems | Test equipment, video signals, radio frequencies |
| Connection Type | Threaded coupling | Quick bayonet coupling |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
Introduction to SMA and BNC Connectors
SMA connectors are precision coaxial RF connectors designed for microwave frequencies up to 18 GHz, offering a threaded interface that ensures secure and reliable connections in high-frequency applications. BNC connectors, on the other hand, feature a bayonet-style coupling mechanism suited for signals up to 4 GHz, commonly used in video and RF test equipment due to their quick-connect capability. Choosing between SMA and BNC connectors depends on your specific frequency requirements and the mechanical durability needed for your signal transmission.
Overview of SMA Connectors
SMA connectors are precision coaxial RF connectors designed for high-frequency applications up to 18 GHz, commonly used in microwave systems, antennas, and telecommunications. Their threaded coupling mechanism ensures reliable, vibration-resistant connections suitable for environments requiring consistent signal integrity. You can expect excellent performance in terms of durability and signal loss when compared to other connector types like BNC connectors.
Overview of BNC Connectors
BNC connectors are widely used coaxial RF connectors known for their quick connect and disconnect bayonet-style coupling mechanism, suitable for frequencies up to 4 GHz. They are commonly employed in video, radio, and networking applications, making them versatile and reliable for signal transmission. Your choice of a BNC connector ensures secure, stable connections in systems requiring easy handling and moderate frequency performance.
Key Differences Between SMA and BNC Connectors
SMA connectors offer higher frequency capabilities up to 18 GHz, making them ideal for microwave and RF applications, whereas BNC connectors are typically limited to frequencies below 4 GHz, suited for video and audio signals. The SMA features a threaded coupling mechanism providing a secure, vibration-resistant connection, contrasting with the bayonet coupling of BNC connectors, which allows quick connect and disconnect but less mechanical stability. Additionally, SMA connectors have a smaller size and superior impedance matching (50 ohms), while BNC connectors come in both 50 and 75-ohm versions, often used for different signal types and applications.
Electrical Performance Comparison
SMA connectors offer superior electrical performance with a frequency range up to 18 GHz and low VSWR, making them ideal for high-frequency RF applications. BNC connectors typically operate up to 4 GHz with higher insertion loss and less stable impedance, which can limit signal integrity in demanding environments. Your choice should consider SMA connectors for precision and minimal signal loss, while BNC connectors are suitable for general-purpose, lower-frequency needs.
Mechanical Design and Durability
SMA connectors feature a threaded coupling mechanism providing secure connections with superior resistance to vibration, making them ideal for high-frequency applications and harsh environments. BNC connectors utilize a bayonet locking system, allowing quick connect and disconnect but offering less mechanical stability under stress or repeated use. The robust metal construction of SMA connectors generally ensures higher durability and longer lifespan compared to BNC connectors, especially in demanding mechanical conditions.
Applications and Use Cases
SMA connectors are widely used in high-frequency applications such as RF and microwave systems, including wireless communications and test equipment, due to their superior performance up to 18 GHz. BNC connectors are commonly employed in video, audio, and networking applications, particularly for analog signal transmission and low-frequency environments like CCTV and radio equipment. Your choice between SMA and BNC connectors depends on the frequency range and signal integrity requirements of your specific application.
Compatibility and Interchangeability
SMA connectors are typically used for high-frequency radio signals up to 18 GHz, offering superior performance in RF and microwave applications, whereas BNC connectors operate effectively up to 4 GHz, making them common in video and radio frequency equipment. Compatibility between SMA and BNC connectors is limited due to differences in design, size, and threading, preventing direct interchangeability without adapters. For Your setup, choosing the correct connector type based on frequency requirements and device specifications ensures optimal signal integrity and prevents connection issues.
Cost and Availability
SMA connectors generally cost more than BNC connectors due to their precision design and higher frequency performance capabilities, with prices varying based on quality and brand. BNC connectors are widely available and often more affordable, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious applications and easily sourced from numerous suppliers. Your choice should consider both the cost difference and the availability relative to your project's frequency requirements and supply options.
Choosing the Right Connector for Your Needs
SMA connectors offer superior performance in high-frequency applications up to 18 GHz, making them ideal for precision RF and microwave systems requiring minimal signal loss. BNC connectors, operating typically up to 4 GHz, are preferred for ease of use and reliable quick connections in test equipment and video signal applications. Your choice should depend on frequency requirements, signal integrity needs, and mechanical durability to ensure optimal connectivity.
SMA Connector vs BNC Connector Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com