Reverse polarity occurs when the positive and negative connections are swapped, potentially damaging electrical devices or causing malfunction. An open circuit means there is a break in the wiring or connection, preventing current flow and rendering the circuit non-functional.
Table of Comparison
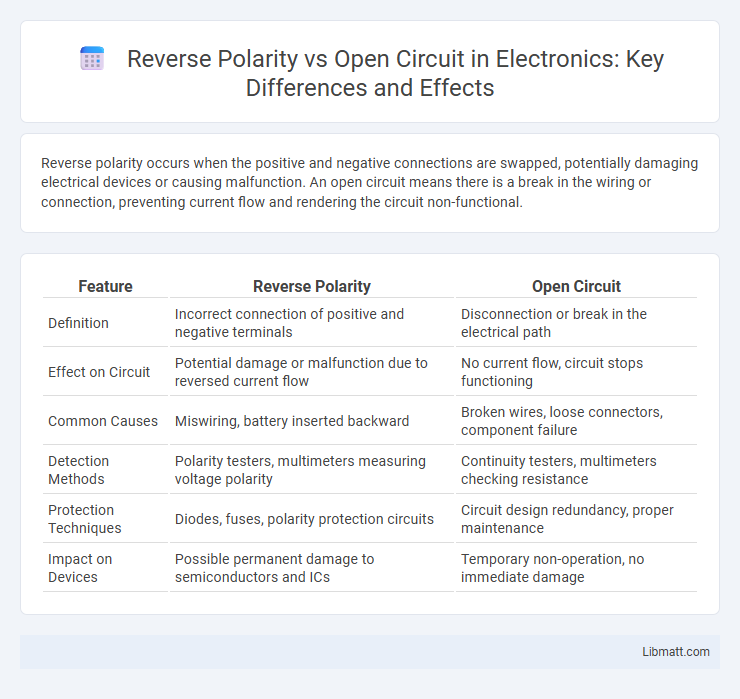
| Feature | Reverse Polarity | Open Circuit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incorrect connection of positive and negative terminals | Disconnection or break in the electrical path |
| Effect on Circuit | Potential damage or malfunction due to reversed current flow | No current flow, circuit stops functioning |
| Common Causes | Miswiring, battery inserted backward | Broken wires, loose connectors, component failure |
| Detection Methods | Polarity testers, multimeters measuring voltage polarity | Continuity testers, multimeters checking resistance |
| Protection Techniques | Diodes, fuses, polarity protection circuits | Circuit design redundancy, proper maintenance |
| Impact on Devices | Possible permanent damage to semiconductors and ICs | Temporary non-operation, no immediate damage |
Understanding Reverse Polarity
Reverse polarity occurs when the positive and negative connections in an electrical circuit are swapped, causing current to flow in the opposite direction. This miswiring can result in damage to sensitive electronic components, malfunctioning devices, or even safety hazards such as electrical shorts. Unlike an open circuit, which interrupts current flow completely, reverse polarity allows current to pass but with incorrect polarity, making it crucial to ensure proper wiring for device protection and performance.
What is an Open Circuit?
An open circuit occurs when there is a break or gap in an electrical path, preventing current from flowing through the circuit. Unlike reverse polarity, which involves incorrect wiring connections causing damage or malfunction, an open circuit simply stops electrical flow without reversing polarity. Understanding open circuits helps you diagnose issues like non-functional devices or interrupted power delivery caused by disconnected wires or broken components.
Key Differences Between Reverse Polarity and Open Circuit
Reverse polarity occurs when the positive and negative terminals of a circuit are connected incorrectly, causing current to flow in the wrong direction and potentially damaging electronic components. Open circuit refers to a break in the electrical path, resulting in no current flow and causing devices to malfunction or shut down. While reverse polarity involves incorrect wiring leading to harmful voltage direction, open circuit is characterized by a disconnected or broken conductor that interrupts the electrical continuity.
Causes of Reverse Polarity in Electrical Systems
Reverse polarity in electrical systems is primarily caused by incorrect wiring during installation or maintenance, where the live and neutral wires are swapped. Faulty outlets, damaged plugs, or improper connections in appliances can also lead to reverse polarity conditions. Ensuring your electrical system is correctly wired and regularly inspected helps prevent potential hazards and equipment failure caused by reversed polarity.
Common Reasons for Open Circuits
Open circuits often result from broken wires, loose connections, or damaged components disrupting electrical continuity. Corroded terminals and blown fuses frequently cause open circuits by preventing current flow within the circuit. Unlike reverse polarity, which involves incorrect voltage direction, open circuits specifically indicate a physical break or disconnection in the electrical path.
Effects of Reverse Polarity on Devices
Reverse polarity can cause immediate damage to electronic devices by forcing current flow in the unintended direction, leading to potential component burnout, overheating, or permanent circuit failure. Unlike an open circuit, which simply interrupts current flow and prevents device operation without damage, reverse polarity actively stresses sensitive components like diodes, capacitors, and integrated circuits. Proper polarity protection, such as diodes or polarity protection circuits, is essential to prevent costly malfunctions and ensure device longevity.
Impact of Open Circuits on Electrical Performance
Open circuits cause a complete interruption of current flow, leading to a loss of power and malfunction in electrical devices. Unlike reverse polarity, which may damage components due to incorrect voltage orientation, open circuits primarily result in total signal or power failure. Diagnosing open circuits is critical for maintaining circuit integrity and ensuring consistent electrical performance in systems.
How to Detect Reverse Polarity
Detecting reverse polarity involves using a multimeter to measure voltage across the circuit terminals, where a negative reading indicates reversed connections. A polarity tester or LED polarity indicator can also visually highlight incorrect wiring by showing no light or a reversed-lit LED. Proper detection prevents damage to electronic components and ensures safe operation of electrical devices.
Troubleshooting and Repairing Open Circuits
Troubleshooting and repairing open circuits involves identifying breaks or interruptions in the electrical path that prevent current flow, often detected through continuity testing with a multimeter. Reverse polarity, which occurs when positive and negative connections are swapped, does not cause an open circuit but can damage components or cause malfunction, so verifying proper polarity is crucial during repairs. Your repair strategy should focus on isolating the exact open point using systematic testing and replacing or reconnecting broken wires or components to restore circuit continuity.
Safety Tips for Preventing Reverse Polarity and Open Circuits
To prevent reverse polarity, always double-check the positive and negative terminals before making electrical connections, and use polarity protection devices like diodes or polarized connectors. For open circuits, regularly inspect wiring and connections for wear or damage, and ensure all terminals are securely tightened to maintain continuous electrical flow. Employing circuit breakers and fuses enhances safety by detecting faults and minimizing risk of electrical hazards.
Reverse polarity vs Open circuit Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com