X7R capacitors offer higher capacitance and better temperature stability compared to standard ceramic types, making them suitable for applications requiring moderate precision and stability across a wide temperature range. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize the ultra-stable, low-loss characteristics of C0G capacitors or the cost-effective, higher capacitance benefits of X7R types.
Table of Comparison
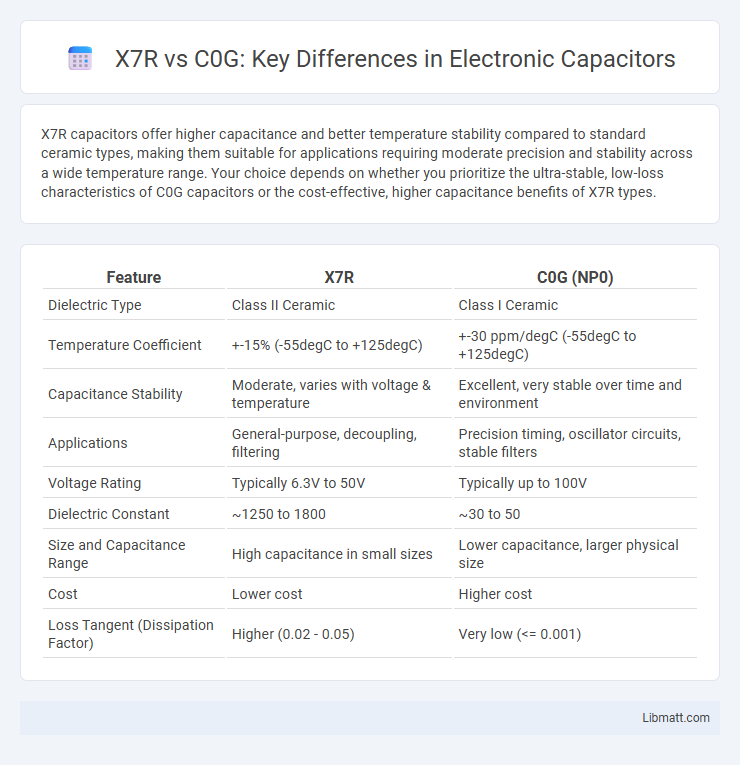
| Feature | X7R | C0G (NP0) |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Type | Class II Ceramic | Class I Ceramic |
| Temperature Coefficient | +-15% (-55degC to +125degC) | +-30 ppm/degC (-55degC to +125degC) |
| Capacitance Stability | Moderate, varies with voltage & temperature | Excellent, very stable over time and environment |
| Applications | General-purpose, decoupling, filtering | Precision timing, oscillator circuits, stable filters |
| Voltage Rating | Typically 6.3V to 50V | Typically up to 100V |
| Dielectric Constant | ~1250 to 1800 | ~30 to 50 |
| Size and Capacitance Range | High capacitance in small sizes | Lower capacitance, larger physical size |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Loss Tangent (Dissipation Factor) | Higher (0.02 - 0.05) | Very low (<= 0.001) |
Introduction to X7R and C0G Capacitors
X7R and C0G capacitors differ primarily in their dielectric materials and performance characteristics; X7R uses a ceramic dielectric that offers high capacitance with moderate temperature stability, while C0G (also known as NP0) capacitors provide excellent temperature stability and low loss with a stable dielectric. X7R capacitors are suitable for applications requiring larger capacitance values and cost-effectiveness, whereas C0G capacitors are preferred in precision circuits demanding minimal capacitance variation. Understanding these differences helps you select the right capacitor for balancing performance and reliability in electronic designs.
Understanding Dielectric Types: X7R vs C0G
X7R capacitors offer a high dielectric constant with moderate temperature stability of +-15% over -55degC to 125degC, making them suitable for applications requiring larger capacitance in smaller sizes. C0G capacitors feature a very stable dielectric material with near-zero temperature coefficient (+-30 ppm/degC) and minimal aging, ideal for precision circuits demanding consistent performance. Selecting between X7R and C0G depends on balancing capacitance density and stability for specific electronic applications.
Electrical Characteristics Comparison
X7R and C0G capacitors differ significantly in electrical characteristics, with X7R offering higher capacitance values but exhibiting greater temperature and voltage coefficients, causing capacitance variation up to +-15%. C0G capacitors provide near-zero temperature coefficient (+-30 ppm/degC) and minimal voltage dependence, ensuring stable capacitance over wide environmental conditions. Your choice depends on the application's need for stability versus capacitance density.
Temperature Stability and Performance
X7R capacitors offer moderate temperature stability with capacitance changes typically within +-15% over a temperature range of -55degC to +125degC, making them suitable for general-purpose applications requiring higher capacitance values. C0G (NP0) capacitors provide superior temperature stability with capacitance variation close to +-30 ppm/degC and minimal performance drift up to +125degC, ideal for precision circuits demanding consistent electrical characteristics. The choice between X7R and C0G depends on the balance between capacitance density and tolerance to temperature-induced performance changes.
Capacitance Variation and Tolerance
X7R capacitors exhibit a capacitance variation of +-15% and can vary significantly with temperature changes, typically within -55degC to 125degC, making them suitable for general-purpose applications where large tolerance is acceptable. C0G capacitors provide exceptional stability with capacitance variation limited to +-30 ppm/degC and a tight tolerance around +-5%, ensuring minimal drift over temperature ranges from -55degC to 125degC. Your choice between X7R and C0G should consider the importance of capacitance stability and tolerance for precision circuits versus cost and size efficiency.
Applications: Where X7R and C0G are Used
X7R capacitors are commonly used in applications requiring moderate stability and high capacitance, such as decoupling and filtering in power supply circuits, audio equipment, and general-purpose electronic devices. C0G capacitors find extensive use in precision circuits including oscillators, RF circuits, and timing devices due to their low loss, high stability, and minimal temperature coefficient. The choice between X7R and C0G depends on the balance of stability, capacitance, and cost required by the specific application.
Advantages and Disadvantages of X7R
X7R capacitors offer high volumetric efficiency and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for applications requiring moderate capacitance with stable performance over a wide temperature range (-55degC to +125degC). However, X7R capacitors exhibit higher dielectric loss and significant capacitance variation under voltage and temperature stress compared to C0G capacitors, limiting their use in precision filtering or timing circuits where low loss and stable capacitance are critical. Their ability to handle higher capacitance values in a smaller package makes them ideal for power supply decoupling but less ideal for high-frequency, high-precision applications.
Pros and Cons of C0G Dielectrics
C0G dielectrics are highly stable ceramic capacitors with minimal temperature coefficient, offering excellent precision and reliability in high-frequency and timing circuits. Their pros include low dissipation factor, negligible aging, and excellent electrical performance, making them ideal for applications demanding accuracy and stability. However, C0G capacitors have lower capacitance values and are typically more expensive than X7R types, which may limit their use in cost-sensitive or space-constrained designs.
Cost Considerations and Availability
X7R capacitors typically offer a lower cost compared to C0G capacitors due to their widespread use in general-purpose applications and less stringent material requirements. C0G capacitors, known for their superior stability and precision, are often more expensive and less available in high capacitance values, which can impact procurement for specialized circuits. Availability for X7R capacitors tends to be higher with numerous manufacturers providing a broad range of options, while C0G capacitors may have limited suppliers and stock, especially in larger sizes.
Choosing Between X7R and C0G: Key Factors
Choosing between X7R and C0G capacitors depends on factors such as temperature stability, dielectric constant, and application requirements. C0G capacitors offer excellent temperature stability with low dielectric losses, making them ideal for precision circuits, while X7R capacitors provide higher capacitance values and better volumetric efficiency but with moderate temperature dependence. Considerations include circuit sensitivity to capacitance variation, operating temperature range, and physical size constraints when selecting the appropriate capacitor type.
X7R vs C0G Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com