EEPROM offers byte-level data erasure and rewriting, making it ideal for storing small amounts of data that require frequent updates, while Flash memory erases and writes data in large blocks, providing faster performance and higher storage capacity. Your choice depends on the need for granular data modification versus the demand for speed and volume in memory storage.
Table of Comparison
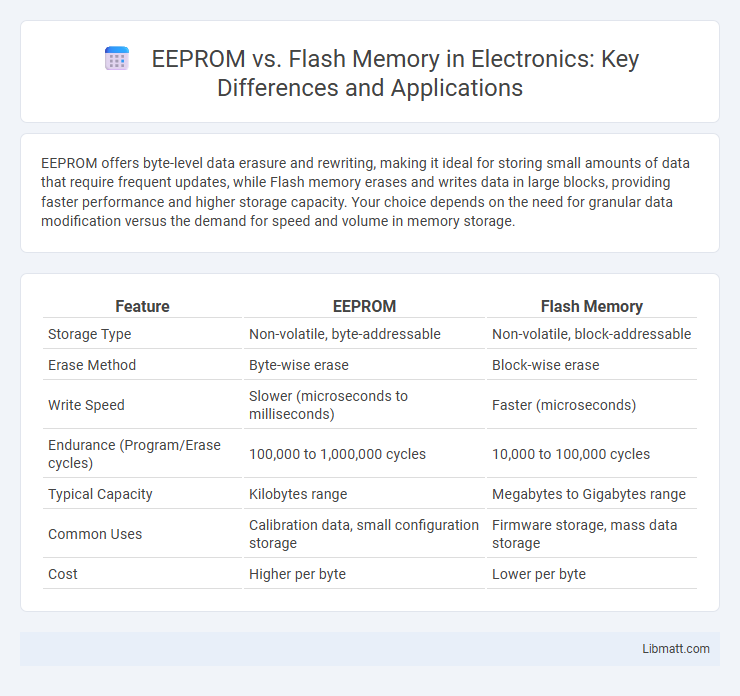
| Feature | EEPROM | Flash Memory |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Type | Non-volatile, byte-addressable | Non-volatile, block-addressable |
| Erase Method | Byte-wise erase | Block-wise erase |
| Write Speed | Slower (microseconds to milliseconds) | Faster (microseconds) |
| Endurance (Program/Erase cycles) | 100,000 to 1,000,000 cycles | 10,000 to 100,000 cycles |
| Typical Capacity | Kilobytes range | Megabytes to Gigabytes range |
| Common Uses | Calibration data, small configuration storage | Firmware storage, mass data storage |
| Cost | Higher per byte | Lower per byte |
Introduction to EEPROM and Flash Memory
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) and Flash memory are non-volatile storage technologies widely used in embedded systems for data retention without power. EEPROM allows byte-level erasure and programming, offering flexibility for frequent updates, whereas Flash memory erases and programs data in larger blocks, providing higher density and faster write speeds. These differences influence their applications in microcontrollers, firmware storage, and system configuration data.
Fundamental Differences Between EEPROM and Flash
EEPROM stores data in small, byte-addressable memory cells allowing individual bytes to be erased and rewritten, whereas Flash memory erases data in larger blocks or sectors, making it faster but less granular. Flash memory typically offers higher density and faster write speeds, making it ideal for storage-intensive applications, while EEPROM provides greater flexibility for frequent, fine-grained data updates. The fundamental difference lies in their architecture and erase mechanisms, with EEPROM supporting byte-level updates and Flash emphasizing bulk data handling.
How EEPROM Works
EEPROM stores data by trapping electrons in a floating gate transistor, allowing individual bytes to be electrically erased and rewritten without removing the chip from the circuit. This precise byte-level write capability distinguishes EEPROM from Flash memory, which erases data in larger blocks. Your applications benefit from EEPROM's fine-grained memory management in scenarios requiring frequent and selective data updates.
How Flash Memory Works
Flash memory stores data in an array of memory cells made from floating-gate transistors, allowing electrons to be trapped in a floating gate to represent binary data. It operates by erasing large blocks of data simultaneously before writing new information, which makes it faster and more efficient for bulk storage compared to EEPROM. The ability to retain data without power and support high write-erase cycles makes flash memory ideal for use in USB drives, SSDs, and memory cards.
Data Retention and Endurance Comparison
EEPROM typically offers superior data retention, often lasting up to 20 years, while flash memory data retention ranges from 10 to 15 years, depending on the technology and usage conditions. When it comes to endurance, EEPROM supports around 1 million write/erase cycles, significantly higher than most flash memories, which generally endure between 10,000 to 100,000 cycles. Your choice between EEPROM and flash should consider these factors for applications requiring frequent data updates and long-term reliability.
Speed and Performance Analysis
EEPROM offers slower write speeds, typically in the range of milliseconds per byte, due to its ability to perform byte-level erase and write operations, making it suitable for infrequent data updates. Flash memory excels in speed with block-level erase and write capabilities, often completing operations in microseconds to milliseconds, which supports high-performance applications requiring rapid data transfers. While EEPROM provides precision for small-scale data modifications, flash memory's superior speed and efficiency make it ideal for large data storage and frequent read/write cycles.
Use Cases and Applications
EEPROM excels in applications requiring small data storage with frequent, byte-level updates such as configuration settings, calibration data, and device identification in embedded systems. Flash memory suits larger data storage needs like firmware updates, operating system images, and bulk data logging in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and IoT devices. The choice depends on factors like write endurance, speed, and memory size, with EEPROM offering higher endurance for small writes and Flash providing cost-effective, high-capacity storage.
Cost Considerations
EEPROM typically costs more per megabyte compared to Flash memory due to its byte-level erase and write capabilities, which require more complex circuitry. Flash memory offers higher storage density and lower cost per bit, making it ideal for applications needing large storage volumes at a reduced expense. Understanding these cost differences helps you select the most economically viable non-volatile memory for your specific project requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Technology
EEPROM offers byte-level erase and write capabilities, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent, small data updates, though it typically has slower write speeds and higher cost per bit compared to Flash memory. Flash memory supports block-level erase and write operations with faster speeds and higher density, making it suitable for large data storage, but its limited erase cycles and inability to modify data at the byte level can reduce flexibility. Both technologies provide non-volatile data retention, yet design choices depend on balancing endurance, speed, granularity of writes, and cost efficiency.
Choosing Between EEPROM and Flash: Key Factors
Choosing between EEPROM and Flash memory depends on your application's write frequency, data retention needs, and storage capacity requirements. EEPROM offers byte-level erase and write capabilities ideal for frequent, small data updates, while Flash provides faster erase/write cycles suitable for large data blocks and firmware storage. Your decision should balance endurance, speed, and the granularity of data manipulation to optimize memory performance.
EEPROM vs Flash Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com