Solar PV systems convert sunlight directly into electricity, making them ideal for powering homes, businesses, and electric devices efficiently. Solar thermal systems harness sunlight to produce heat for water heating or space heating, offering a cost-effective solution for reducing energy bills and increasing your home's energy efficiency.
Table of Comparison
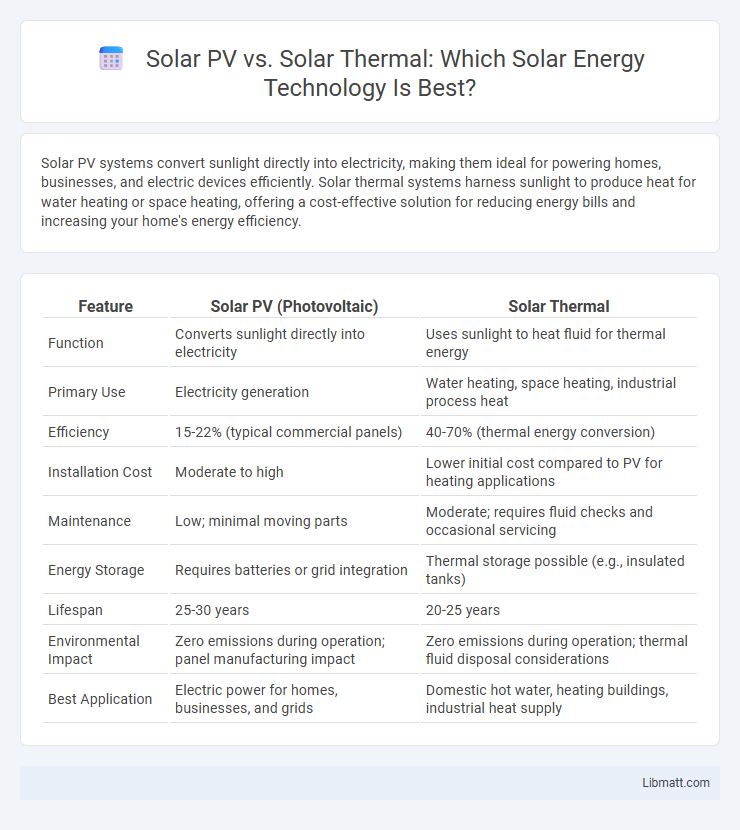
| Feature | Solar PV (Photovoltaic) | Solar Thermal |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts sunlight directly into electricity | Uses sunlight to heat fluid for thermal energy |
| Primary Use | Electricity generation | Water heating, space heating, industrial process heat |
| Efficiency | 15-22% (typical commercial panels) | 40-70% (thermal energy conversion) |
| Installation Cost | Moderate to high | Lower initial cost compared to PV for heating applications |
| Maintenance | Low; minimal moving parts | Moderate; requires fluid checks and occasional servicing |
| Energy Storage | Requires batteries or grid integration | Thermal storage possible (e.g., insulated tanks) |
| Lifespan | 25-30 years | 20-25 years |
| Environmental Impact | Zero emissions during operation; panel manufacturing impact | Zero emissions during operation; thermal fluid disposal considerations |
| Best Application | Electric power for homes, businesses, and grids | Domestic hot water, heating buildings, industrial heat supply |
Introduction to Solar PV and Solar Thermal
Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems convert sunlight directly into electricity using semiconductor materials, making them ideal for residential and commercial power generation. Solar thermal technology captures sunlight to generate heat, typically used for water heating or space heating through solar collectors and thermal storage. Both technologies harness solar energy but serve different applications based on energy conversion to electricity versus heat.
How Solar PV Systems Work
Solar PV systems convert sunlight directly into electricity using photovoltaic cells made of semiconductor materials, typically silicon. When sunlight strikes these cells, it excites electrons, generating an electric current that can be used to power homes or feed into the grid. The efficiency of solar PV panels ranges from 15% to 22%, depending on technology and conditions.
How Solar Thermal Systems Operate
Solar thermal systems operate by capturing sunlight through solar collectors, which heat a transfer fluid such as water or antifreeze. This heated fluid circulates through a heat exchanger, transferring thermal energy to a water storage tank for domestic hot water or space heating. Your home can benefit from the efficient conversion of solar energy into usable heat without reliance on electricity, making solar thermal a cost-effective solution for renewable heating needs.
Key Differences: Solar PV vs Solar Thermal
Solar PV systems convert sunlight directly into electricity using photovoltaic cells, making them ideal for residential and commercial power generation. Solar thermal systems capture and concentrate sunlight to produce heat, commonly used for water heating, space heating, or industrial processes. Key differences include the output type--electricity for solar PV and heat for solar thermal--and the system components, where solar PV requires inverters and solar panels, while solar thermal involves collectors, heat exchangers, and storage tanks.
Energy Conversion Efficiency Comparison
Solar PV systems convert sunlight directly into electricity with an average efficiency range of 15-22%, while solar thermal systems typically achieve higher energy conversion efficiencies of 40-70% by harnessing sunlight to produce heat. The efficiency of solar thermal is influenced by collector type and operating temperature, making it highly effective for heating applications such as water and space heating. Your choice depends on energy needs: solar PV excels in electricity generation, whereas solar thermal provides superior efficiency for thermal energy requirements.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Maintenance
Solar PV systems typically have higher initial installation costs compared to solar thermal systems due to the expense of photovoltaic panels and inverters, but they generally require lower maintenance. Solar thermal systems often involve more complex plumbing and mechanical components, leading to higher ongoing maintenance expenses despite lower upfront costs. Your choice depends on balancing the long-term maintenance savings of Solar PV against the potentially lower initial investment of solar thermal technology.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Solar PV systems convert sunlight directly into electricity, making them ideal for residential and commercial power generation, off-grid installations, and portable devices. Solar Thermal technology is best suited for heating applications such as water heating, space heating, and industrial process heat, where capturing solar heat is more efficient than generating electricity. You should choose Solar PV for electricity needs and Solar Thermal for cost-effective heating solutions tailored to your specific energy demands.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Solar PV systems convert sunlight directly into electricity using semiconductor materials, producing zero emissions during operation and requiring fewer water resources, making them environmentally sustainable. Solar Thermal technology captures solar energy to generate heat, often used for water heating or industrial processes, but its manufacturing and installation can involve higher material use and environmental footprints due to complex components like mirrors and heat transfer fluids. Both technologies contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, yet Solar PV generally offers a lower overall environmental impact and greater scalability for sustainable energy production.
Pros and Cons of Solar PV and Solar Thermal
Solar PV systems offer high versatility and can generate electricity even in low light conditions, but their efficiency drops with high temperatures and initial installation costs are relatively high. Solar thermal systems excel in heating applications with higher efficiency and lower operating costs, though they depend heavily on consistent sunlight and require more maintenance to prevent issues like scaling and corrosion. Choosing between them depends on energy needs, climate, and budget, with solar PV suited for electricity generation and solar thermal ideal for water or space heating.
Choosing the Right Solar Solution for Your Needs
Solar PV systems convert sunlight directly into electricity, making them ideal for powering homes and businesses with renewable energy, while solar thermal systems capture heat for water heating or space heating applications. Consider factors such as energy needs, installation costs, available space, and local climate when choosing between solar PV and solar thermal solutions. Solar PV is typically better for electricity generation and integration with battery storage, whereas solar thermal excels in efficient, cost-effective heating.
Solar PV vs Solar Thermal Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com