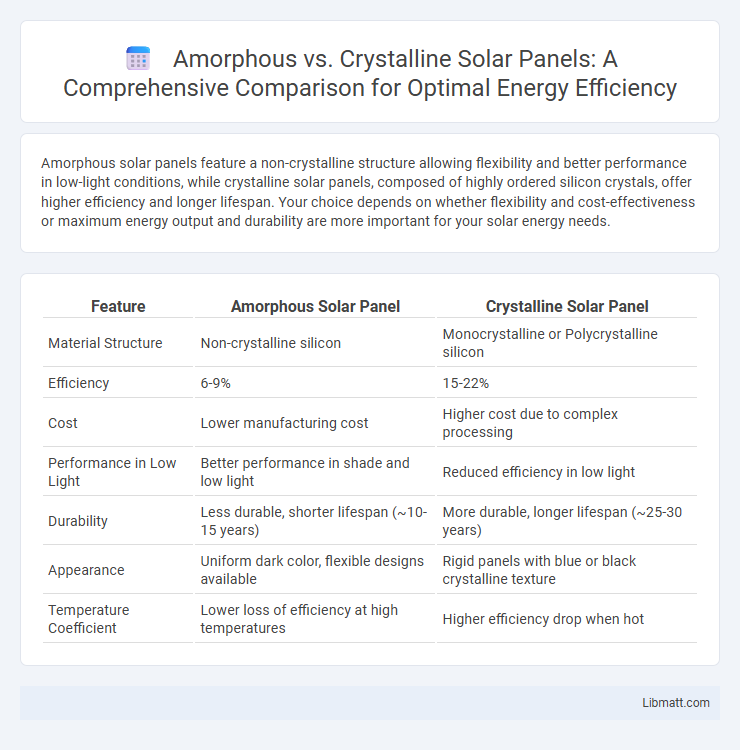
Amorphous solar panels feature a non-crystalline structure allowing flexibility and better performance in low-light conditions, while crystalline solar panels, composed of highly ordered silicon crystals, offer higher efficiency and longer lifespan. Your choice depends on whether flexibility and cost-effectiveness or maximum energy output and durability are more important for your solar energy needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Amorphous Solar Panel | Crystalline Solar Panel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Structure | Non-crystalline silicon | Monocrystalline or Polycrystalline silicon |
| Efficiency | 6-9% | 15-22% |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost | Higher cost due to complex processing |
| Performance in Low Light | Better performance in shade and low light | Reduced efficiency in low light |
| Durability | Less durable, shorter lifespan (~10-15 years) | More durable, longer lifespan (~25-30 years) |
| Appearance | Uniform dark color, flexible designs available | Rigid panels with blue or black crystalline texture |
| Temperature Coefficient | Lower loss of efficiency at high temperatures | Higher efficiency drop when hot |
Introduction to Solar Panel Technologies
Solar panel technologies primarily include amorphous and crystalline types, each with distinct structures and efficiencies. Crystalline solar panels, made from silicon wafers, offer higher efficiency and durability, making them ideal for residential and commercial installations. Amorphous solar panels, characterized by non-crystalline silicon, provide flexibility and better performance in low-light conditions but generally have lower energy conversion rates.
What Are Amorphous Solar Panels?
Amorphous solar panels consist of non-crystalline silicon layers that absorb sunlight more efficiently in low-light conditions compared to crystalline panels. These thin-film solar panels offer flexibility and lightweight design, making them ideal for unconventional installations. Your choice of amorphous panels can enhance energy capture in shaded environments or areas with fluctuating sunlight.
What Are Crystalline Solar Panels?
Crystalline solar panels consist of silicon crystals that are either monocrystalline or polycrystalline, providing higher efficiency rates of around 15-20% due to their well-ordered atomic structure. The manufacturing process involves cutting large silicon wafers into thin slices, which leads to improved electrical conductivity and durability. These panels are widely used in residential and commercial solar installations where space efficiency and long-term performance are critical factors.
Efficiency Comparison: Amorphous vs Crystalline
Crystalline solar panels, including monocrystalline and polycrystalline types, typically offer higher efficiency rates ranging from 15% to 22%, owing to their well-ordered silicon crystal structures that enhance electron flow. Amorphous solar panels, characterized by their non-crystalline silicon layers, generally have lower efficiencies between 6% and 10%, but perform better in low-light conditions and high temperatures. The efficiency gap makes crystalline panels more suitable for space-constrained installations aiming for maximum power output, while amorphous panels are favored for cost-effective, flexible applications where efficiency is less critical.
Cost Differences Between Amorphous and Crystalline Panels
Amorphous solar panels typically have lower manufacturing costs due to simpler production processes and less silicon usage, making them more affordable upfront compared to crystalline panels. Crystalline panels, including monocrystalline and polycrystalline types, generally offer higher efficiency but come with higher material and fabrication expenses, contributing to increased overall costs. Despite the initial cost benefit of amorphous panels, their lower efficiency often results in higher long-term costs per watt generated compared to crystalline panels.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Crystalline solar panels, both monocrystalline and polycrystalline, typically offer higher durability and longer lifespans of 25 to 30 years due to their solid silicon structure and robust encapsulation materials. Amorphous solar panels, based on thin-film technology, generally have shorter lifespans ranging from 10 to 15 years and are more prone to degradation caused by environmental factors such as UV exposure and temperature fluctuations. The superior durability of crystalline panels results in more stable energy output over time, making them a preferred choice for long-term solar energy investment.
Performance in Low Light Conditions
Amorphous solar panels excel in low light conditions due to their ability to absorb a broader spectrum of light, maintaining higher energy output on cloudy days or during dawn and dusk. Crystalline panels, while more efficient under direct sunlight, experience a significant drop in performance when light intensity decreases. Your choice between amorphous and crystalline solar panels should consider these differences to maximize energy production based on your local weather and lighting conditions.
Installation Flexibility and Applications
Amorphous solar panels offer superior installation flexibility due to their lightweight, thin-film design, allowing seamless integration on curved surfaces, rooftops with varied angles, and portable devices. Crystalline solar panels, with higher rigidity and efficiency, are best suited for standard flat roof installations, ground-mounted solar farms, and large-scale commercial applications requiring robust structural support. The choice between these solar panel types depends on the installation environment and application-specific requirements for performance and design adaptability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Amorphous solar panels have a lower energy payback time due to less energy-intensive manufacturing processes, resulting in reduced carbon emissions and a smaller environmental footprint compared to crystalline panels. Crystalline solar panels, despite higher initial energy costs, offer longer lifespans and higher efficiency, contributing to greater long-term sustainability by maximizing energy output per unit area. Recycling technologies for crystalline silicon modules are more advanced, promoting circular economy practices and reducing hazardous waste impact, while amorphous panels offer benefits in flexible applications that minimize material use.
Which Solar Panel Type Is Right for You?
Amorphous solar panels offer flexibility and better performance in low-light conditions, making them ideal for shaded or irregularly shaped installations, while crystalline solar panels provide higher efficiency and durability, suitable for maximizing energy output in limited space. Consider your budget, available installation area, and energy goals when choosing between the two types, as crystalline panels generally cost more but deliver greater long-term savings through efficiency. Evaluating factors like climate, shading, and system size helps determine if the cost-effective amorphous or high-efficiency crystalline panel aligns best with your solar energy needs.
Amorphous vs Crystalline Solar Panel Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com