Peak demand refers to the highest level of electricity consumption during specific periods, usually when energy usage spikes, while base demand represents the consistent, minimum level of energy required throughout the day. Understanding the difference helps you optimize energy consumption and reduce costs by managing load during peak times and ensuring efficient use during base demand periods.
Table of Comparison
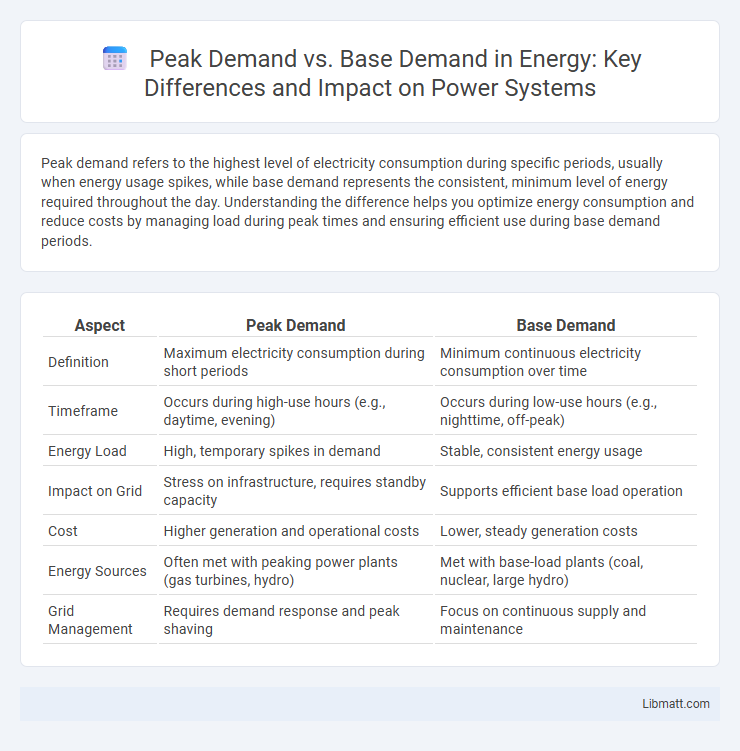
| Aspect | Peak Demand | Base Demand |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maximum electricity consumption during short periods | Minimum continuous electricity consumption over time |
| Timeframe | Occurs during high-use hours (e.g., daytime, evening) | Occurs during low-use hours (e.g., nighttime, off-peak) |
| Energy Load | High, temporary spikes in demand | Stable, consistent energy usage |
| Impact on Grid | Stress on infrastructure, requires standby capacity | Supports efficient base load operation |
| Cost | Higher generation and operational costs | Lower, steady generation costs |
| Energy Sources | Often met with peaking power plants (gas turbines, hydro) | Met with base-load plants (coal, nuclear, large hydro) |
| Grid Management | Requires demand response and peak shaving | Focus on continuous supply and maintenance |
Understanding Peak Demand and Base Demand
Peak demand refers to the highest level of electricity consumption recorded during a specific period, often driven by factors such as extreme weather or business operating hours. Base demand, in contrast, represents the consistent minimum level of electricity usage required to meet essential and continuous needs throughout the day. Understanding these demands is critical for effective energy management, enabling utilities to optimize generation capacity and maintain grid stability.
Key Differences Between Peak and Base Demand
Peak demand represents the highest level of electricity consumption occurring during specific periods, typically when residential and commercial activities surge, whereas base demand refers to the consistent minimum level of power usage maintained 24/7. Peak demand requires utilities to deploy additional power generation resources or purchase energy at premium rates, impacting overall system reliability and costs. Understanding these key differences helps you optimize energy management strategies, reduce expenses, and enhance grid stability.
Importance of Monitoring Energy Demand Patterns
Monitoring energy demand patterns by distinguishing peak demand from base demand is crucial for optimizing power grid efficiency and reducing operational costs. Accurate analysis of peak demand helps in minimizing the risk of outages and guides infrastructure investments for capacity expansion. Understanding base demand variations enables utilities to enhance energy storage solutions and implement demand response strategies effectively.
Factors Influencing Peak Demand Levels
Peak demand levels are influenced by factors such as temperature extremes, industrial activity, and consumer behavior patterns. High temperatures often drive increased use of air conditioning systems, while cold spells can raise heating demand, both contributing to peak loads. Economic growth and changes in residential habits also significantly impact fluctuations between peak demand and base demand periods.
Base Demand: Definition and Characteristics
Base demand refers to the consistent and minimum level of electricity consumption maintained over a specific period, typically reflecting essential residential, commercial, and industrial activities. This demand is characterized by its relatively stable and predictable nature, occurring during off-peak hours when energy usage fluctuates minimally. Utilities rely on base demand forecasts to optimize power generation, ensure grid stability, and manage energy resources efficiently.
Impact of Peak Demand on Energy Costs
Peak demand significantly increases energy costs due to the need for utilities to activate expensive, less efficient power plants to meet sudden surges in electricity usage. These plants, often relying on fossil fuels, operate at higher marginal costs compared to base load power sources like nuclear or hydroelectric, leading to elevated prices during peak periods. Managing and reducing peak demand through demand response programs and energy storage solutions can effectively lower overall energy expenses for both providers and consumers.
Strategies to Manage and Reduce Peak Demand
Implementing demand response programs and utilizing smart grid technology allows you to shift or reduce electricity usage during peak demand periods, lowering overall strain on the grid. Energy storage systems, such as batteries, store excess energy during base demand times and release it when peak demand occurs, enhancing grid stability and cost efficiency. Encouraging energy efficiency measures and time-of-use pricing incentivizes consumers to optimize consumption patterns, effectively managing peak and base demand fluctuations.
Role of Smart Technologies in Demand Management
Smart technologies play a crucial role in managing peak demand by enabling real-time monitoring and automated adjustments to your energy usage. Advanced systems like smart meters and demand response programs help shift loads away from peak periods, reducing stress on the grid and lowering electricity costs. Integrating IoT devices and AI-driven analytics optimizes base demand, ensuring efficient energy consumption throughout the day.
Environmental Implications of Demand Fluctuations
Peak demand periods strain energy grids, often requiring the activation of less efficient, high-emission power plants, which contribute significantly to increased greenhouse gas emissions. Base demand, supported primarily by stable and renewable energy sources, results in lower environmental impact due to consistent energy production and reduced reliance on fossil fuels. Effective demand management reduces the environmental footprint by smoothing fluctuations, optimizing energy resource utilization, and minimizing the frequency of peak-dependent, polluting energy generation.
Future Trends in Energy Demand Management
Future trends in energy demand management emphasize balancing peak demand spikes with stable base demand through smart grid technologies and advanced energy storage solutions. You can expect increasing integration of renewable energy sources combined with AI-driven demand response systems to optimize consumption patterns and reduce costs. Efforts to decentralize power generation and enhance real-time data analytics will drive more efficient and sustainable energy usage.
Peak Demand vs Base Demand Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com