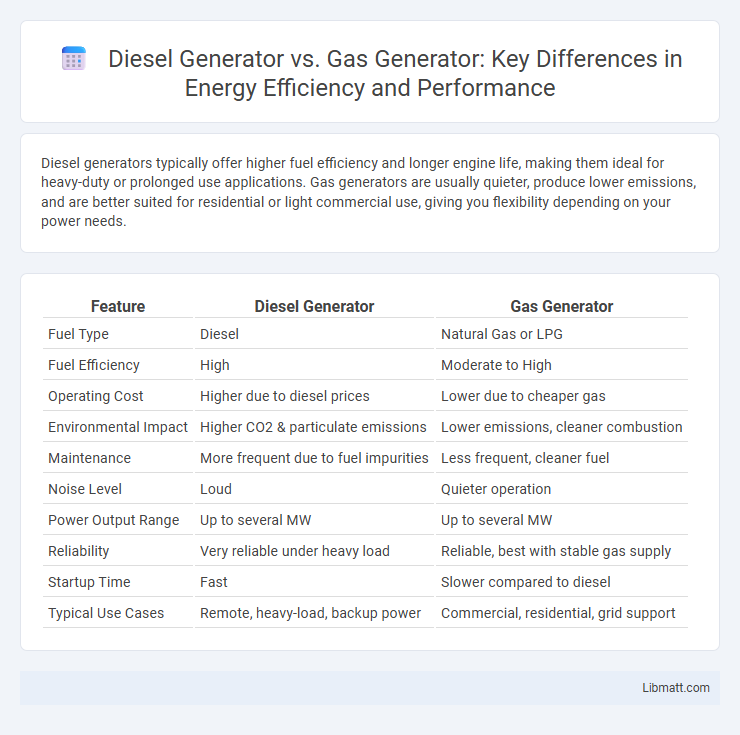
Diesel generators typically offer higher fuel efficiency and longer engine life, making them ideal for heavy-duty or prolonged use applications. Gas generators are usually quieter, produce lower emissions, and are better suited for residential or light commercial use, giving you flexibility depending on your power needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Diesel Generator | Gas Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Diesel | Natural Gas or LPG |
| Fuel Efficiency | High | Moderate to High |
| Operating Cost | Higher due to diesel prices | Lower due to cheaper gas |
| Environmental Impact | Higher CO2 & particulate emissions | Lower emissions, cleaner combustion |
| Maintenance | More frequent due to fuel impurities | Less frequent, cleaner fuel |
| Noise Level | Loud | Quieter operation |
| Power Output Range | Up to several MW | Up to several MW |
| Reliability | Very reliable under heavy load | Reliable, best with stable gas supply |
| Startup Time | Fast | Slower compared to diesel |
| Typical Use Cases | Remote, heavy-load, backup power | Commercial, residential, grid support |
Introduction to Diesel and Gas Generators
Diesel generators operate using compression ignition engines fueled by diesel, offering high fuel efficiency and durability for heavy-duty applications. Gas generators run on natural gas or propane, providing cleaner emissions and quieter operation suitable for residential and light commercial use. Your choice depends on factors like fuel availability, cost, environmental impact, and power requirements.
How Diesel Generators Work
Diesel generators operate by igniting diesel fuel through compression, which produces mechanical energy to turn the generator's rotor and generate electricity. Unlike gas generators that use spark ignition, diesel engines rely on the heat of compressed air to ignite the fuel, resulting in higher fuel efficiency and durability. Understanding how diesel generators work helps you choose the right power solution for long-lasting and heavy-duty applications.
How Gas Generators Operate
Gas generators operate by combusting natural gas or propane within an internal combustion engine to convert chemical energy into mechanical energy, which then drives an alternator to produce electricity. Their engines are designed for cleaner burning and lower emissions compared to diesel generators, making them suitable for residential and light commercial use. The fuel delivery system in gas generators ensures a consistent and controlled air-fuel mixture, optimizing engine efficiency and performance under varying load conditions.
Efficiency Comparison: Diesel vs Gas Generators
Diesel generators typically offer higher fuel efficiency than gas generators, converting more energy per gallon of fuel, resulting in lower operational costs over time. Your choice impacts fuel consumption rates, with diesel engines often performing better under heavy loads and longer runtime conditions. Gas generators, while generally cleaner and quieter, may have lower efficiency, especially in high-demand applications, making diesel a preferable option for sustained energy needs.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Maintenance
Diesel generators typically demand a higher initial investment compared to gas generators due to their robust construction and fuel storage requirements. However, diesel engines often benefit from lower fuel costs and longer engine life, which can reduce overall maintenance expenses. Your choice should weigh the upfront costs against potential savings in fuel and maintenance, especially if you anticipate frequent or long-term usage.
Fuel Availability and Storage Considerations
Diesel generators benefit from widely available fuel that is easy to store for long periods without significant degradation, making them ideal for remote locations or emergency backup power. Gas generators, often running on natural gas or propane, require a steady supply connection or pressurized tanks, limiting storage flexibility but offering cleaner combustion. Your choice depends on fuel accessibility and storage conditions relevant to your specific energy needs and site logistics.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
Diesel generators produce higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter, and carbon dioxide (CO2), contributing significantly to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions compared to gas generators. Gas generators, particularly those using natural gas, emit lower levels of harmful pollutants and carbon emissions, making them a cleaner option for power generation. Your choice of generator impacts local air quality and carbon footprint, with gas generators offering a more environmentally friendly solution.
Longevity and Durability of Generators
Diesel generators are known for their exceptional longevity and durability, often outlasting gas generators due to their robust engine construction and ability to handle heavy loads over extended periods. Gas generators typically require more frequent maintenance and have shorter lifespans because of their sensitivity to fuel quality and engine wear. Choosing a diesel generator ensures your power solution remains reliable and cost-effective for long-term use in demanding environments.
Applications: Choosing the Right Generator for Your Needs
Diesel generators are ideal for industrial, construction, and backup power applications due to their durability and fuel efficiency under heavy loads. Gas generators suit residential use and small businesses, offering quieter operation and lower emissions. Selecting the right generator depends on power demands, fuel availability, and environmental considerations.
Pros and Cons: Diesel Generators vs Gas Generators
Diesel generators offer higher fuel efficiency and greater durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty and long-term applications, but they tend to be noisier and produce more emissions. Gas generators are cleaner and quieter, providing easier maintenance and lower initial costs, yet they generally have shorter lifespans and higher fuel expenses. Selecting between diesel and gas generators depends on factors like operational demands, environmental regulations, and budget constraints.
Diesel Generator vs Gas Generator Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com