Day-ahead trading involves buying and selling electricity contracts for delivery on the next day, allowing market participants to plan and hedge their positions with greater price certainty. Intraday trading enables you to adjust your energy portfolio in real-time, responding to unexpected changes in supply and demand to optimize profitability and manage risk effectively.
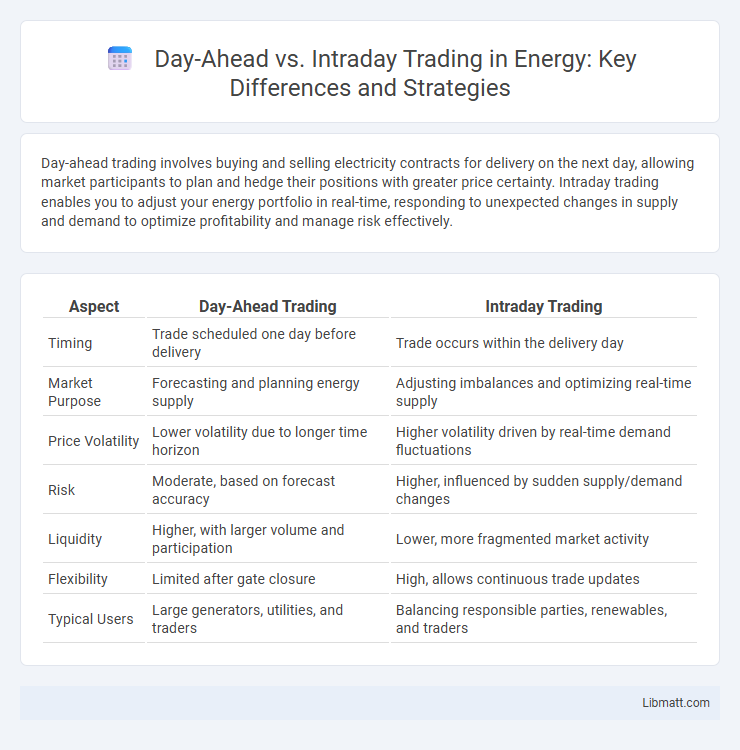
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Day-Ahead Trading | Intraday Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Trade scheduled one day before delivery | Trade occurs within the delivery day |
| Market Purpose | Forecasting and planning energy supply | Adjusting imbalances and optimizing real-time supply |
| Price Volatility | Lower volatility due to longer time horizon | Higher volatility driven by real-time demand fluctuations |
| Risk | Moderate, based on forecast accuracy | Higher, influenced by sudden supply/demand changes |
| Liquidity | Higher, with larger volume and participation | Lower, more fragmented market activity |
| Flexibility | Limited after gate closure | High, allows continuous trade updates |
| Typical Users | Large generators, utilities, and traders | Balancing responsible parties, renewables, and traders |
Introduction to Day-Ahead and Intraday Trading
Day-Ahead trading involves purchasing and selling electricity contracts one day before the actual delivery, allowing market participants to optimize their schedules based on forecasted demand and supply. Intraday trading occurs within the same day, offering flexibility to adjust positions in response to real-time market fluctuations, grid constraints, and unexpected changes in renewable generation. Both trading mechanisms play crucial roles in balancing supply and demand, enhancing market efficiency, and supporting grid stability in electricity markets.
Definition and Core Concepts
Day-ahead trading involves purchasing or selling electricity contracts one day before the actual delivery, allowing market participants to secure prices based on forecasted demand and supply. Intraday trading occurs within the same day, providing flexibility to adjust positions as real-time market conditions, such as unexpected demand fluctuations or renewable energy output changes, become clearer. Understanding these core concepts helps you optimize energy procurement strategies by balancing price certainty and adaptability.
How Day-Ahead Markets Operate
Day-Ahead Markets operate by allowing participants to submit bids and offers for electricity delivery for each hour of the next day, facilitating price discovery and grid scheduling 24 to 36 hours in advance. Market operators clear these bids to balance supply and demand, setting prices and generation schedules before real-time operations commence. This forward scheduling helps ensure system reliability while providing market participants price signals to optimize their production and consumption plans.
Key Features of Intraday Trading
Intraday trading involves buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day, enabling traders to capitalize on short-term price movements and market volatility. Key features include high liquidity, rapid execution, use of technical analysis, and the necessity for constant market monitoring due to the short holding periods. Unlike day-ahead trading, intraday trading requires quick decision-making and risk management tools such as stop-loss orders to mitigate potential losses.
Main Differences Between Day-Ahead and Intraday Trading
Day-ahead trading involves purchasing electricity contracts one day before the actual delivery, allowing market participants to plan and hedge against price volatility with fixed schedules. Intraday trading occurs within the same day, offering flexibility to adjust positions closer to real-time based on updated demand forecasts or unexpected supply changes. The primary difference lies in timing: day-ahead markets provide price certainty with advance planning, while intraday markets enable dynamic responses to short-term market fluctuations.
Advantages of Day-Ahead Trading
Day-ahead trading offers significant advantages such as improved price predictability by locking in electricity prices 24 hours before delivery, reducing exposure to real-time market volatility. This trading strategy enhances grid stability by allowing better demand forecasting and resource planning, minimizing imbalances and associated penalties. Market participants benefit from increased liquidity and transparent pricing, enabling more efficient risk management and optimized asset utilization.
Benefits of Intraday Trading
Intraday trading offers the benefit of rapid capital turnover, allowing you to capitalize on short-term market fluctuations within a single trading day. It provides increased flexibility, enabling traders to adjust positions promptly in response to real-time market data and volatility. This trading style reduces overnight risk by closing all positions before the market closes, minimizing exposure to after-hours events.
Challenges and Risks in Both Markets
Day-Ahead trading involves forecasting electricity prices and demand one day ahead, which poses challenges due to market volatility and forecast inaccuracies, potentially leading to financial losses. Intraday trading requires real-time adjustments to positions, exposing traders to higher price fluctuations and liquidity risks as demand and supply conditions continually change. Your ability to manage rapid decision-making and adapt to market signals is crucial to mitigate risks in both trading environments.
Choosing the Right Trading Strategy
Selecting the appropriate trading strategy between day-ahead and intraday trading depends on market volatility, risk tolerance, and liquidity requirements. Day-ahead trading optimizes schedules with fixed prices set one day before delivery, ideal for managing predictable energy consumption or production. Intraday trading allows real-time adjustments in response to fluctuating prices and demand, offering greater flexibility for traders seeking to capitalize on short-term market changes.
Future Trends in Electricity Market Trading
Future trends in electricity market trading emphasize increased integration of renewable energy sources and advanced forecasting technologies to enhance the accuracy of Day-Ahead and Intraday trading strategies. You will see growing adoption of automated trading platforms leveraging real-time data and machine learning algorithms to optimize energy bids and reduce market risks. Enhanced grid flexibility and demand response mechanisms will further transform the balance between Day-Ahead commitments and Intraday adjustments, leading to more efficient and dynamic electricity markets.
Day-Ahead vs Intraday Trading Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com