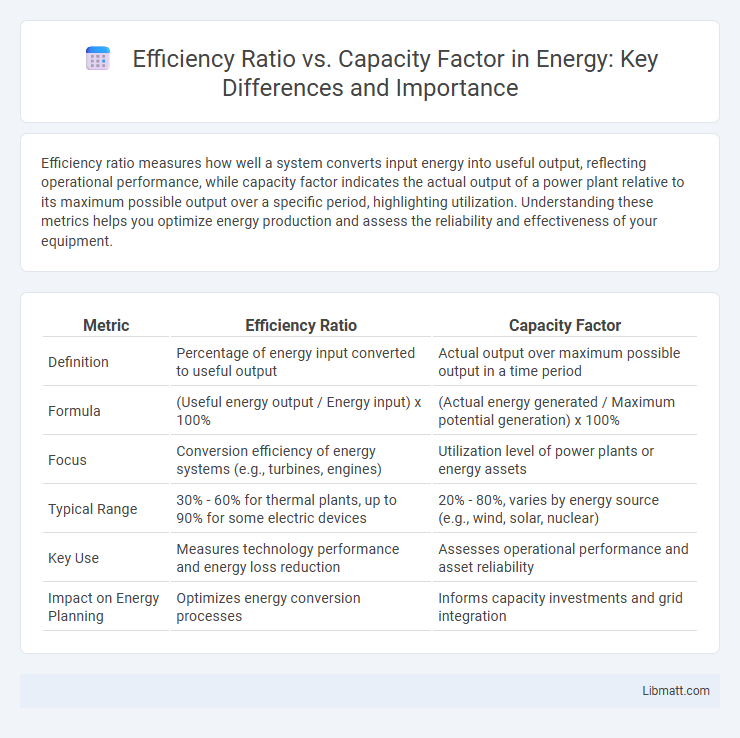
Efficiency ratio measures how well a system converts input energy into useful output, reflecting operational performance, while capacity factor indicates the actual output of a power plant relative to its maximum possible output over a specific period, highlighting utilization. Understanding these metrics helps you optimize energy production and assess the reliability and effectiveness of your equipment.
Table of Comparison
| Metric | Efficiency Ratio | Capacity Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Percentage of energy input converted to useful output | Actual output over maximum possible output in a time period |
| Formula | (Useful energy output / Energy input) x 100% | (Actual energy generated / Maximum potential generation) x 100% |
| Focus | Conversion efficiency of energy systems (e.g., turbines, engines) | Utilization level of power plants or energy assets |
| Typical Range | 30% - 60% for thermal plants, up to 90% for some electric devices | 20% - 80%, varies by energy source (e.g., wind, solar, nuclear) |
| Key Use | Measures technology performance and energy loss reduction | Assesses operational performance and asset reliability |
| Impact on Energy Planning | Optimizes energy conversion processes | Informs capacity investments and grid integration |
Introduction to Efficiency Ratio and Capacity Factor
Efficiency ratio measures the actual output of a system relative to its maximum possible output under ideal conditions, reflecting how well resources are utilized. Capacity factor represents the ratio of actual energy produced by a power plant to the maximum possible energy it could generate over a specific period, indicating operational reliability and consistency. Understanding these metrics helps you evaluate performance and optimize energy production in renewable and conventional power systems.
Defining Efficiency Ratio in Energy Systems
Efficiency ratio in energy systems measures the proportion of useful output energy to the total input energy, reflecting how well a system converts fuel or power into usable electricity or work. It is commonly expressed as a percentage, with higher values indicating less energy lost during conversion processes. Unlike capacity factor, which quantifies actual energy production relative to maximum possible output over time, efficiency ratio specifically evaluates energy conversion effectiveness within a generation unit or system.
What is Capacity Factor?
Capacity factor measures the actual energy output of a power plant compared to its maximum possible output over a specific period, reflecting its operational performance and reliability. Unlike the efficiency ratio, which evaluates how effectively input energy is converted into useful output, capacity factor accounts for downtime, maintenance, and variability in power generation sources such as wind or solar. Understanding your plant's capacity factor helps optimize energy production and plan maintenance schedules to maximize overall performance.
Key Differences Between Efficiency Ratio and Capacity Factor
Efficiency ratio measures the output energy relative to the input energy, reflecting how well a system converts fuel or resources into usable power. Capacity factor indicates the actual output of a power plant over a period compared to its maximum possible output if operated at full capacity nonstop. Key differences include that efficiency ratio emphasizes energy conversion quality and fuel utilization, while capacity factor assesses operational performance and utilization rates of generation assets.
Importance of Efficiency Ratio in Power Plants
Efficiency ratio measures how effectively a power plant converts fuel into electricity, directly influencing operational costs and environmental impact. Capacity factor indicates the actual output over a period compared to maximum potential, but efficiency ratio ensures optimal fuel usage and reduces waste. Understanding your power plant's efficiency ratio is crucial for maximizing performance and achieving sustainable energy production.
The Role of Capacity Factor in Performance Assessment
Capacity factor measures the actual output of a power plant relative to its maximum possible output over a specific period, providing a realistic indicator of operational performance. This metric offers crucial insights into how effectively a facility utilizes its capacity, directly impacting financial and energy production assessments. Understanding your plant's capacity factor enables more accurate evaluation of performance and aids in optimizing energy generation strategies.
Calculating Efficiency Ratio: Formulas and Examples
Efficiency ratio is calculated by dividing the useful output energy or power by the total input energy or power, expressed as a percentage to indicate how effectively a system converts energy. For example, if a power plant generates 800 MW from an input of 1,000 MW, its efficiency ratio is (800 / 1,000) x 100 = 80%. This metric differs from capacity factor, which measures actual output over maximum possible output over time, making efficiency ratio a direct indicator of energy conversion performance.
How to Determine Capacity Factor in Real-World Scenarios
Capacity factor is calculated by dividing the actual energy output of a power plant over a specific period by the maximum possible energy output if the plant operated at full capacity continuously. To determine capacity factor in real-world scenarios, accurate measurement of energy generated through meters combined with detailed records of operational hours and maintenance downtime is essential. Comparing this data with the plant's rated capacity enables a precise evaluation of performance and efficiency beyond simple efficiency ratios.
Applications: Efficiency Ratio vs Capacity Factor Across Industries
Efficiency ratio measures the output efficiency relative to inputs, commonly applied in financial sectors to evaluate asset utilization and operational performance. Capacity factor is prevalent in energy industries, indicating actual energy produced versus potential output over time, critical for assessing power plant performance and reliability. Both metrics support optimization decisions: efficiency ratios enhance process improvements, while capacity factors guide resource allocation and maintenance scheduling across manufacturing, utilities, and renewable energy sectors.
Summary: Selecting the Right Metric for Energy Analysis
Efficiency ratio measures the proportion of useful energy output to total energy input, reflecting the performance of energy conversion systems, while capacity factor quantifies the actual output of a power plant relative to its maximum possible output over time. Choosing between efficiency ratio and capacity factor depends on the analysis goal; efficiency ratio suits evaluating system operational effectiveness, whereas capacity factor is ideal for assessing utilization and reliability of energy assets. Accurate energy analysis requires selecting the metric that aligns with project objectives, operational characteristics, and performance benchmarks to optimize energy management and investment decisions.
Efficiency ratio vs Capacity factor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com