Fast charging rapidly replenishes your device's battery, minimizing downtime, while slow charging extends battery lifespan by reducing heat and stress on battery cells. Choosing between fast and slow charging depends on whether speed or battery health is your priority.
Table of Comparison
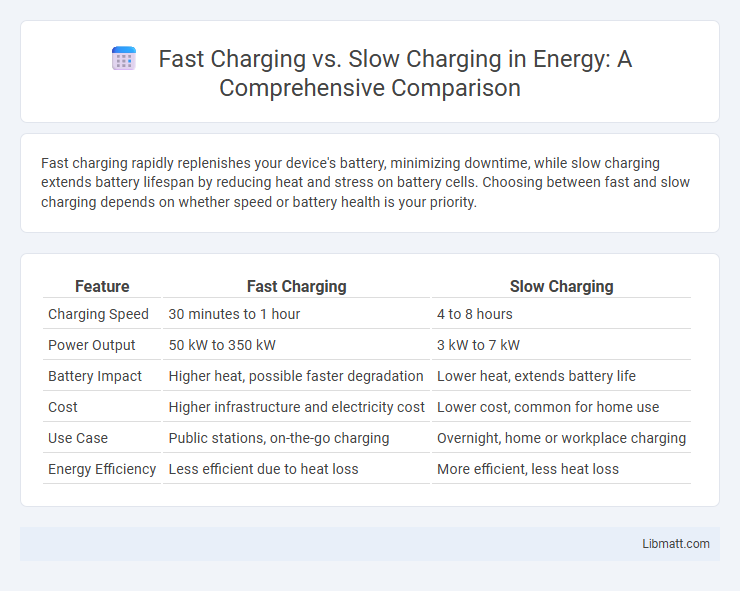
| Feature | Fast Charging | Slow Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Speed | 30 minutes to 1 hour | 4 to 8 hours |
| Power Output | 50 kW to 350 kW | 3 kW to 7 kW |
| Battery Impact | Higher heat, possible faster degradation | Lower heat, extends battery life |
| Cost | Higher infrastructure and electricity cost | Lower cost, common for home use |
| Use Case | Public stations, on-the-go charging | Overnight, home or workplace charging |
| Energy Efficiency | Less efficient due to heat loss | More efficient, less heat loss |
Introduction to Charging Speeds
Fast charging significantly reduces the time needed to power your device by delivering higher wattage compared to slow charging, which provides a steady, lower current over an extended period. Slow charging preserves battery health by minimizing heat generation and reducing wear on battery cells, making it ideal for overnight charging. Understanding charging speeds helps you balance convenience and battery longevity depending on your daily usage patterns.
What is Fast Charging?
Fast charging is a technology designed to significantly reduce the time required to recharge your device by delivering higher electrical current compared to standard slow charging methods. It uses advanced power management systems and compatible chargers to safely increase the voltage and amperage, allowing batteries to reach a higher percentage of charge in a shorter period. Smartphones, electric vehicles, and portable electronics benefit from fast charging to quickly restore battery life while maintaining long-term battery health.
What is Slow Charging?
Slow charging refers to the process of replenishing an electric vehicle's battery at a lower power level, typically using AC chargers with power outputs ranging from 3 to 7 kW. This method extends battery life by reducing heat generation and stress on battery cells, making it ideal for overnight charging at home. Understanding slow charging helps you optimize your EV's longevity and manage energy consumption effectively.
Key Differences Between Fast and Slow Charging
Fast charging delivers higher power levels, typically above 18 watts, allowing devices to reach 50% battery in 30 minutes or less, while slow charging usually operates below 10 watts, taking several hours for a full charge. Fast chargers generate more heat and may impact battery longevity if used excessively, whereas slow charging is gentler and can extend overall battery lifespan. Your choice between fast and slow charging depends on the need for quick power replenishment versus maintaining long-term battery health.
Impact on Battery Health
Fast charging generates more heat and stress on the battery's cells, which can accelerate capacity degradation and reduce overall battery lifespan over time. Slow charging maintains lower temperatures and imposes less strain on the battery, preserving its health and maximizing longevity. To optimize your device's battery health, prefer slow charging whenever possible, especially for daily or overnight charges.
Charging Efficiency and Time Comparison
Fast charging delivers a high power output, significantly reducing charging time by up to 80% compared to slow charging, which typically operates at lower wattages around 5-10W. Efficiency in fast charging can vary due to heat generation and battery management systems, sometimes leading to slightly reduced energy efficiency compared to slow charging that maintains a steady, lower temperature and minimizes battery stress. Slow charging offers better battery longevity by reducing thermal strain and energy loss, while fast charging prioritizes speed, making it ideal for quick top-ups despite minor trade-offs in overall charging efficiency.
Cost Implications of Fast vs Slow Charging
Fast charging typically incurs higher electricity costs due to increased energy demand and infrastructure expenses, while slow charging utilizes off-peak electricity rates, reducing overall costs. The installation of fast chargers requires significant investment in high-capacity hardware and grid upgrades, whereas slow chargers have lower setup and maintenance costs. Businesses and consumers must weigh the premium on convenience against long-term electricity and infrastructure expenditures when choosing between fast and slow charging.
Environmental Considerations
Fast charging consumes more energy and generates higher heat, which can reduce battery lifespan and increase electronic waste over time. Slow charging minimizes thermal stress and energy loss, promoting longer battery health and reducing the frequency of replacements. Choosing slow charging can lower overall environmental impact by conserving energy and extending device usability.
Best Use Cases for Each Charging Method
Fast charging is ideal for situations where you need to quickly replenish your device's battery, such as during short breaks or when you're on the go, providing up to 80% charge in about 30 minutes. Slow charging is best suited for overnight or extended charging periods, as it helps preserve battery health and extends overall lifespan by reducing heat and stress on the battery cells. Your choice depends on balancing convenience and battery longevity based on your daily charging habits and device usage.
Future Trends in Charging Technology
Fast charging technology is rapidly evolving with innovations like ultra-fast chargers delivering up to 350 kW, significantly reducing charging times for electric vehicles (EVs). Research into solid-state batteries and wireless charging is expected to enhance both charging speed and safety, making slow charging more convenient and efficient in residential settings. Your future EV experience will benefit from these advancements, balancing rapid energy replenishment with battery health optimization.
Fast charging vs Slow charging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com