A Supergrid is a large-scale electricity network designed to transmit renewable energy across vast distances using high-voltage direct current (HVDC) lines, enhancing global energy exchange and grid stability. Your choice between a Smart Grid, which focuses on intelligent energy management and bidirectional communication within local networks, and a Supergrid depends on whether you prioritize localized efficiency or expansive renewable energy distribution.
Table of Comparison
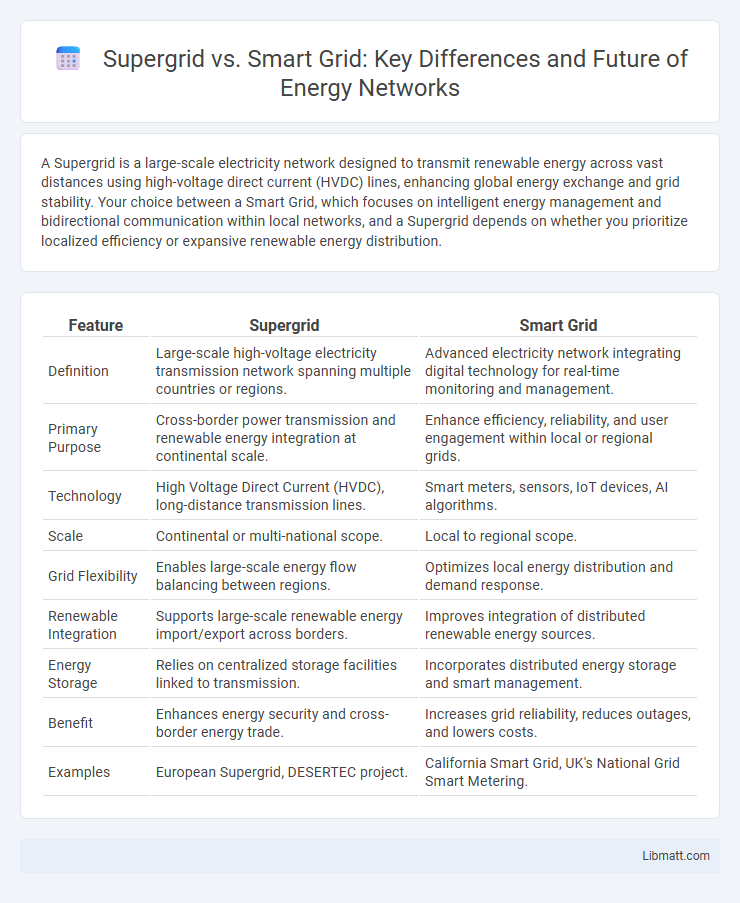
| Feature | Supergrid | Smart Grid |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large-scale high-voltage electricity transmission network spanning multiple countries or regions. | Advanced electricity network integrating digital technology for real-time monitoring and management. |
| Primary Purpose | Cross-border power transmission and renewable energy integration at continental scale. | Enhance efficiency, reliability, and user engagement within local or regional grids. |
| Technology | High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC), long-distance transmission lines. | Smart meters, sensors, IoT devices, AI algorithms. |
| Scale | Continental or multi-national scope. | Local to regional scope. |
| Grid Flexibility | Enables large-scale energy flow balancing between regions. | Optimizes local energy distribution and demand response. |
| Renewable Integration | Supports large-scale renewable energy import/export across borders. | Improves integration of distributed renewable energy sources. |
| Energy Storage | Relies on centralized storage facilities linked to transmission. | Incorporates distributed energy storage and smart management. |
| Benefit | Enhances energy security and cross-border energy trade. | Increases grid reliability, reduces outages, and lowers costs. |
| Examples | European Supergrid, DESERTEC project. | California Smart Grid, UK's National Grid Smart Metering. |
Introduction to Supergrid and Smart Grid
Supergrid refers to a large-scale, high-capacity electricity transmission network designed to connect multiple regions or countries, facilitating long-distance power exchange and integration of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar. Smart Grid involves the use of digital communication technologies, sensors, and automation to optimize electricity distribution, enhance grid reliability, and enable real-time monitoring and demand response within localized power networks. Both systems aim to modernize energy infrastructure but differ in scale and technological focus: Supergrid emphasizes cross-regional energy transmission, while Smart Grid prioritizes intelligent management of localized electricity flow.
Defining Supergrid: Overview and Key Features
A Supergrid is an extensive, high-capacity electricity network designed to connect multiple countries or regions, enabling large-scale transmission of renewable energy across vast distances with minimal losses. Key features include ultra-high voltage direct current (UHVDC) technology, enhanced grid stability, and the integration of diverse energy sources to optimize supply and demand balancing on a continental scale. Your energy infrastructure benefits from the Supergrid's ability to support massive renewable integration and cross-border energy trade, distinguishing it from localized Smart Grid systems focused on optimizing distribution and consumption within smaller areas.
Understanding the Smart Grid: Core Concepts
The smart grid integrates advanced digital communication and control technologies to enhance the reliability, efficiency, and sustainability of electricity distribution. It employs sensors, smart meters, and automated control systems to optimize energy flow and enable real-time monitoring across the network. Unlike the supergrid, which emphasizes large-scale transmission infrastructure connecting regional grids, the smart grid focuses on localized, intelligent management of energy resources and consumer usage patterns.
Main Differences between Supergrid and Smart Grid
The main differences between a Supergrid and a Smart Grid lie in their scale and function: a Supergrid is a large-scale, high-capacity transmission network designed to transport electricity over long distances, often across countries or continents, while a Smart Grid focuses on enhancing the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of local electricity distribution using digital communication and automation technologies. Supergrids primarily facilitate bulk power transfer, especially integrating renewable energy sources like offshore wind farms, whereas Smart Grids optimize your energy usage through real-time monitoring, demand response, and decentralized generation. Understanding these distinctions helps in assessing how each grid technology can support your energy needs and future infrastructure developments.
Technological Innovations in Supergrid and Smart Grid
Supergrids leverage high-voltage direct current (HVDC) technology and advanced power electronics to enable long-distance, large-scale renewable energy transmission with minimal losses, enhancing grid stability and interconnectivity across regions. Smart Grids utilize real-time data analytics, IoT sensors, and automated control systems to optimize energy distribution, enhance demand response, and improve outage management within localized networks. Both grids integrate cutting-edge innovations, but while Supergrids emphasize large-scale energy transfer infrastructure, Smart Grids focus on decentralization, digital communication, and adaptive grid management.
Benefits of Supergrid Implementation
Supergrid implementation enhances energy security by enabling large-scale integration of renewable sources across regional boundaries, reducing dependency on fossil fuels. It facilitates efficient long-distance electricity transmission with minimal losses, optimizing resource distribution and balancing supply and demand on a continental scale. The supergrid's ability to connect diverse grids improves grid resilience and supports decarbonization goals through increased use of clean energy.
Advantages of Smart Grid Solutions
Smart Grid solutions offer enhanced energy efficiency by enabling real-time monitoring and adaptive control of electricity distribution, reducing outages and energy waste. Your energy management becomes more reliable and flexible, integrating renewable sources and supporting demand response programs to optimize consumption. Enhanced security features and advanced analytics in Smart Grids contribute to improved grid resilience compared to traditional Supergrid systems.
Challenges and Limitations: Supergrid vs Smart Grid
Supergrids face challenges such as high initial infrastructure costs, complex cross-border regulations, and vulnerability to large-scale failures due to their centralized nature. Smart grids, while more flexible and resilient, encounter limitations including cybersecurity risks, integration difficulties with legacy systems, and the need for widespread consumer adoption of smart devices. Your energy management strategy should consider these factors to balance scalability, security, and reliability effectively.
Role in Renewable Energy Integration
Supergrids enable the large-scale transmission of renewable energy across vast distances, efficiently connecting remote wind and solar farms to major consumption centers. Smart Grids optimize local energy distribution by using real-time data and automation to balance supply and demand, incorporate distributed renewable sources, and enhance grid reliability. Together, Supergrid and Smart Grid technologies are crucial for maximizing renewable energy integration and reducing carbon emissions on a regional and national scale.
Future Prospects: Supergrid and Smart Grid Development
Supergrid development promises a future of expansive, cross-border energy transmission that enhances renewable energy integration and grid resilience on a continental scale. Smart grid technologies focus on optimizing your local energy consumption through real-time data, decentralized generation, and improved demand response. Together, these innovations drive a more sustainable, efficient, and interconnected energy system for future power networks.
Supergrid vs Smart Grid Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com