Ring Main System offers enhanced reliability by allowing power to be supplied from multiple directions, minimizing outages during faults, whereas Radial Power System delivers power in a single path, making it simpler but more prone to complete power loss if a fault occurs. Understanding your power needs helps determine whether the redundancy of a Ring Main or the straightforward design of a Radial system best suits your electrical network.
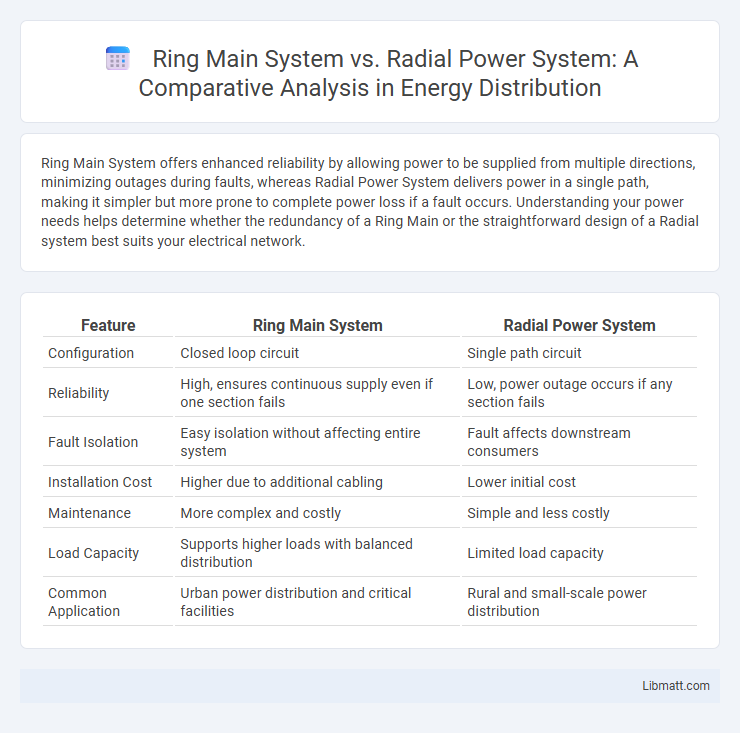
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ring Main System | Radial Power System |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration | Closed loop circuit | Single path circuit |
| Reliability | High, ensures continuous supply even if one section fails | Low, power outage occurs if any section fails |
| Fault Isolation | Easy isolation without affecting entire system | Fault affects downstream consumers |
| Installation Cost | Higher due to additional cabling | Lower initial cost |
| Maintenance | More complex and costly | Simple and less costly |
| Load Capacity | Supports higher loads with balanced distribution | Limited load capacity |
| Common Application | Urban power distribution and critical facilities | Rural and small-scale power distribution |
Introduction to Power Distribution Systems
Power distribution systems play a crucial role in delivering electrical energy efficiently and reliably from substations to end-users, with Ring Main System (RMS) and Radial Power System being two primary configurations. The Ring Main System forms a closed loop, allowing multiple paths for power flow, which enhances reliability and fault tolerance by enabling alternative routes if a fault occurs. In contrast, the Radial Power System supplies power through a single path to each load, making it simpler and cost-effective but less reliable due to the lack of alternative paths during faults or maintenance.
Overview of Ring Main System
The Ring Main System is an electrical distribution network that forms a closed loop, ensuring continuous power supply even if one section experiences a fault. This configuration enhances reliability and reduces outage duration by allowing power to flow from multiple directions. Your facility benefits from improved voltage stability and easier fault isolation compared to the Radial Power System.
Overview of Radial Power System
A Radial Power System delivers electricity through a single transmission line from the source to the load, making it simple and cost-effective for small to medium-sized networks. Your power reliability can be compromised since any fault in the single line causes a complete outage downstream, requiring manual intervention to restore service. Despite its limitations, the Radial Power System remains widely used due to ease of design, installation, and maintenance compared to more complex systems like the Ring Main System.
Key Design Differences
Ring Main System features a looped network allowing power to flow in multiple directions, enhancing reliability and fault isolation. Radial Power System consists of a single path for electricity flow, making it simpler but more vulnerable to outages when faults occur. Your choice depends on the need for redundancy, with Ring Main Systems offering higher operational flexibility compared to Radial Systems.
Advantages of Ring Main System
The Ring Main System offers enhanced reliability and continuity of power supply by creating a closed loop, allowing electricity to flow in multiple directions and ensuring minimal disruption during faults. It improves system flexibility and load distribution, reducing the risk of overload and enabling easier maintenance without complete shutdowns. This system's design supports faster fault detection and isolation, which enhances overall network stability and efficiency compared to the Radial Power System.
Advantages of Radial Power System
Radial Power Systems provide a simple and cost-effective solution for power distribution, ideal for small networks with low load density. Their straightforward design allows for easy fault detection and isolation, minimizing downtime and maintenance complexity. Due to fewer components and simpler infrastructure, radial systems typically exhibit lower initial installation costs compared to ring main systems.
Disadvantages and Limitations
Ring Main Systems face disadvantages such as higher installation complexity and increased initial costs due to the need for more cables and equipment. Fault isolation can be challenging, potentially affecting multiple consumers if proper sectionalizing devices are not used. Radial Power Systems carry limitations including reduced reliability since a fault in one segment causes interruptions downstream, and longer outage durations due to simpler but less redundant networks impacting your power supply resilience.
Reliability and Fault Management
The Ring Main System offers higher reliability by providing multiple power paths, enabling continuous supply even if one section experiences a fault. Fault management is more efficient in ring systems due to quick isolation and rerouting of power, minimizing outage duration. In contrast, Radial Power Systems have limited fault tolerance, as a fault in the feeder causes interruption to all downstream loads, lengthening restoration times.
Cost and Maintenance Comparison
A Ring Main System offers cost efficiency through improved reliability and reduced downtime, leading to lower long-term maintenance expenses compared to a Radial Power System. Radial systems generally have lower initial installation costs but incur higher maintenance costs due to increased fault vulnerability and longer outage durations. For your power distribution needs, choosing a Ring Main System can minimize both operational costs and maintenance efforts over time.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Selecting between a Ring Main System and a Radial Power System depends on the specific power distribution requirements and reliability needs of your facility. Ring Main Systems offer enhanced reliability and fault tolerance by providing multiple pathways for power flow, making them ideal for critical applications with high uptime demands. Radial Power Systems, being simpler and cost-effective, are suitable for less complex installations where budget constraints and lower redundancy are acceptable.
Ring Main System vs Radial Power System Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com