On-grid systems connect your energy setup directly to the utility grid, allowing you to use solar power while drawing electricity when needed and selling excess back to the grid. Off-grid systems operate independently, storing energy in batteries for use during outages or in remote locations without grid access.
Table of Comparison
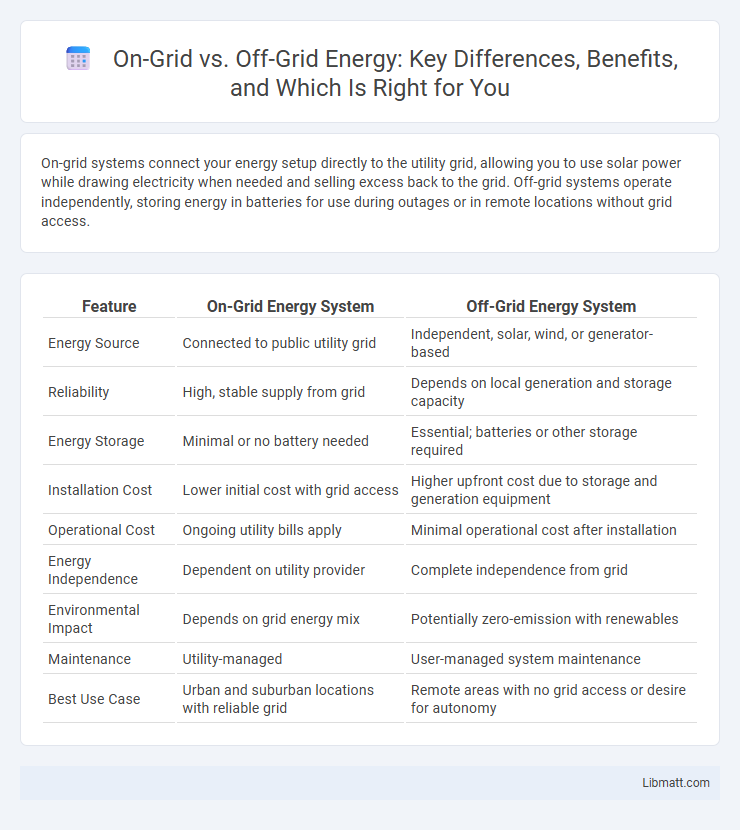
| Feature | On-Grid Energy System | Off-Grid Energy System |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Connected to public utility grid | Independent, solar, wind, or generator-based |
| Reliability | High, stable supply from grid | Depends on local generation and storage capacity |
| Energy Storage | Minimal or no battery needed | Essential; batteries or other storage required |
| Installation Cost | Lower initial cost with grid access | Higher upfront cost due to storage and generation equipment |
| Operational Cost | Ongoing utility bills apply | Minimal operational cost after installation |
| Energy Independence | Dependent on utility provider | Complete independence from grid |
| Environmental Impact | Depends on grid energy mix | Potentially zero-emission with renewables |
| Maintenance | Utility-managed | User-managed system maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Urban and suburban locations with reliable grid | Remote areas with no grid access or desire for autonomy |
Introduction to On-Grid and Off-Grid Systems
On-grid systems connect your solar power setup directly to the public electricity grid, allowing you to draw energy when needed and sell excess power back to the utility. Off-grid systems operate independently, relying on batteries or alternative storage to provide power without linking to the main grid, ideal for remote locations. Choosing between on-grid and off-grid depends on your energy independence goals, location, and access to reliable grid infrastructure.
How On-Grid Solar Systems Work
On-grid solar systems operate by connecting your solar panels directly to the public electricity grid, allowing you to use solar energy during the day and draw power from the grid when solar production is low. Excess electricity generated by your panels is fed back into the grid, often earning you credits through net metering programs. This seamless integration maximizes energy efficiency and reduces your reliance on traditional utility power.
How Off-Grid Solar Systems Work
Off-grid solar systems operate independently from the utility grid by capturing sunlight through solar panels, converting it into electricity via an inverter, and storing energy in batteries for later use. These systems rely on battery storage to provide power during nighttime or cloudy days, ensuring continuous electricity supply without grid connection. Proper design includes solar panels, charge controllers, inverters, and battery banks to manage energy production, storage, and consumption efficiently.
Key Differences Between On-Grid and Off-Grid
On-grid solar systems connect directly to the utility grid, allowing you to draw power when your panels aren't producing enough and to sell excess power back, optimizing energy efficiency and cost savings. Off-grid systems operate independently from the grid, relying on batteries to store energy, making them ideal for remote locations but requiring careful management of energy usage and storage capacity. The key differences lie in their dependency on the grid, energy storage needs, installation costs, and suitability for your specific power requirements.
Cost Comparison: On-Grid vs Off-Grid
On-grid solar systems typically have lower upfront costs due to simpler installation and the ability to sell excess power back to the grid, reducing your overall electricity expenses. In contrast, off-grid systems require significant investment in batteries and backup components, increasing initial costs and ongoing maintenance. Evaluating your energy needs and budget is crucial to determine the most cost-effective solution for your home or business.
Energy Storage Solutions and Battery Needs
On-grid energy storage solutions typically rely on the grid as a backup, reducing the need for large battery banks, whereas off-grid systems demand substantial battery capacity to ensure uninterrupted power. Lithium-ion batteries are preferred for both setups due to high energy density and longer life cycles, but off-grid installations often require deeper cycle capabilities and greater storage capacity. Hybrid inverters and smart energy management systems optimize battery use in on-grid setups by balancing grid interaction and stored energy discharge.
Reliability and Power Backup Considerations
On-grid systems depend on the utility grid, providing reliable electricity as long as the grid is active but lack power backup during outages, making them less suitable for areas with frequent blackouts. Off-grid systems offer complete independence with energy storage solutions like batteries, ensuring continuous power supply even in remote locations, but require careful management to maintain reliability. Your choice hinges on prioritizing uninterrupted power availability versus grid connectivity and backup needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
On-grid solar systems contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and enabling energy sharing with the grid, which lowers overall carbon emissions. Off-grid systems promote self-sufficiency and minimize environmental impact by using renewable energy storage, though they may require batteries with ecological considerations for disposal and recycling. Both approaches advance sustainable energy use, but on-grid systems typically offer greater efficiency and integration with renewable energy infrastructure.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Selecting between on-grid and off-grid solar systems depends on your energy requirements, location, and budget. On-grid systems, connected to the utility grid, offer cost-effective energy solutions with net metering benefits, ideal for areas with reliable grid access. Off-grid systems provide energy independence through battery storage, suitable for remote locations or backup power needs where grid connection is unavailable or unreliable.
Future Trends in On-Grid and Off-Grid Technology
Future trends in on-grid technology emphasize advanced smart grid integration, increased use of AI for energy management, and enhanced storage solutions to optimize energy distribution. Off-grid technology is rapidly evolving with improvements in battery efficiency, solar panel affordability, and hybrid systems that combine renewable energy sources for greater self-sufficiency. Both on-grid and off-grid innovations focus on sustainability, resilience, and enabling decentralized energy access to meet growing global demands.
On-grid vs Off-grid Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com