Top oil temperature indicates the overall thermal condition of the transformer's oil, while winding temperature specifically reflects the heat in the windings where electrical losses generate the most heat. Monitoring your transformer's winding temperature is crucial for assessing insulation integrity and preventing overheating that can lead to failures.
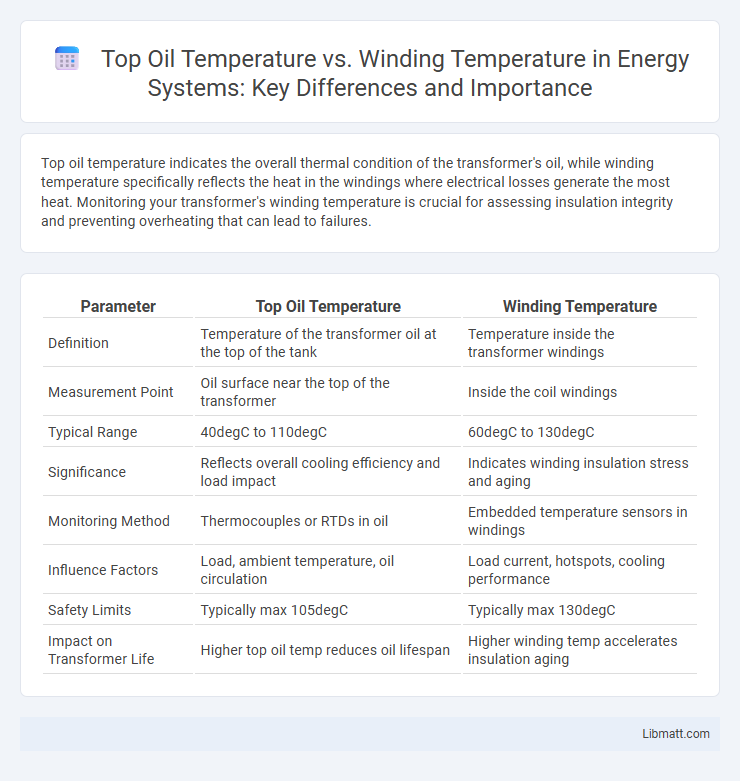
Table of Comparison
| Parameter | Top Oil Temperature | Winding Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature of the transformer oil at the top of the tank | Temperature inside the transformer windings |
| Measurement Point | Oil surface near the top of the transformer | Inside the coil windings |
| Typical Range | 40degC to 110degC | 60degC to 130degC |
| Significance | Reflects overall cooling efficiency and load impact | Indicates winding insulation stress and aging |
| Monitoring Method | Thermocouples or RTDs in oil | Embedded temperature sensors in windings |
| Influence Factors | Load, ambient temperature, oil circulation | Load current, hotspots, cooling performance |
| Safety Limits | Typically max 105degC | Typically max 130degC |
| Impact on Transformer Life | Higher top oil temp reduces oil lifespan | Higher winding temp accelerates insulation aging |
Introduction: Understanding Transformer Temperature Metrics
Top oil temperature reflects the highest oil temperature within a transformer tank, serving as a key indicator of overall thermal performance and cooling efficiency. Winding temperature specifically measures the hottest point in the transformer windings, directly correlating with insulation aging and transformer lifespan. Monitoring both temperatures is critical for assessing transformer health and preventing overheating-related failures.
Defining Top Oil Temperature
Top oil temperature is the temperature of the oil that circulates within a transformer's tank and acts as the primary cooling medium, directly affecting the overall thermal condition of the transformer. It is a critical parameter monitored to prevent overheating and ensure the longevity of the insulation system by indirectly reflecting the internal winding temperature. Your transformer's performance and reliability depend on maintaining an optimal top oil temperature to safeguard winding integrity and prevent thermal degradation.
What is Winding Temperature?
Winding temperature refers to the heat generated within the coils of electrical windings due to electrical resistance and current flow in transformers or motors. This temperature directly impacts the insulation life and operational reliability of the equipment. Monitoring your winding temperature helps prevent overheating, ensuring optimal performance and extending the lifespan of the device compared to just measuring the top oil temperature.
Measurement Methods for Top Oil and Winding Temperatures
Top oil temperature is typically measured using thermowell sensors immersed in the transformer oil, providing an accurate reading of oil thermal conditions. Winding temperature is commonly monitored using embedded resistance temperature detectors (RTDs) or fiber optic sensors directly attached to the transformer windings for precise thermal assessment. Accurate measurement of these temperatures is crucial for maintaining your transformer's operational efficiency and preventing overheating-related failures.
Importance of Monitoring Transformer Temperatures
Monitoring top oil temperature and winding temperature in transformers is crucial for ensuring operational reliability and preventing failures. Elevated top oil temperature indicates overall thermal stress, while winding temperature directly reflects internal hotspot conditions that can degrade insulation. Accurate and continuous temperature monitoring optimizes transformer lifespan, reduces outage risk, and supports efficient maintenance strategies.
Factors Affecting Top Oil Temperature
Top oil temperature is influenced by factors such as load current, ambient temperature, cooling system efficiency, and transformer design, directly affecting the thermal balance of your equipment. Winding temperature rises primarily due to current density and insulation properties, but top oil temperature sets the overall heat environment impacting winding heat dissipation. Monitoring top oil temperature is crucial for preventing accelerated insulation aging and ensuring reliable transformer performance.
Factors Influencing Winding Temperature
Winding temperature is primarily influenced by factors such as load current, ambient temperature, and cooling efficiency, which directly affect the heat generated within transformer coils. Top oil temperature reflects the overall thermal condition of the transformer oil insulating system but responds more slowly to changes compared to winding temperature. Monitoring your transformer's winding temperature under varying load conditions ensures optimal performance and prevents insulation degradation.
Comparative Analysis: Top Oil vs Winding Temperature
Top oil temperature measures the average heat within transformer oil, reflecting the overall cooling efficiency, while winding temperature indicates the hottest point in the transformer windings, crucial for managing insulation aging. Monitoring winding temperature provides a more accurate assessment of transformer health and operational limits compared to top oil temperature alone. Your transformer's reliability depends heavily on understanding this comparative data to prevent overheating and extend equipment lifespan.
Impact on Transformer Lifespan and Performance
Top oil temperature and winding temperature critically influence transformer lifespan and performance by directly affecting insulation aging and thermal degradation. Elevated winding temperature accelerates insulation breakdown, reducing operational life, while excessive top oil temperature indicates insufficient cooling, leading to overheating and efficiency loss. Maintaining optimal temperature ranges through real-time monitoring ensures reliable transformer operation and prolongs service life.
Best Practices for Temperature Monitoring and Management
Top oil temperature and winding temperature are critical parameters in transformer monitoring, with top oil temperature indicating the overall thermal state and winding temperature reflecting the internal heat stress on the coils. Best practices for temperature monitoring include using accurate sensors like RTDs for winding temperature and thermocouples for top oil temperature, combined with real-time data acquisition systems to detect abnormal rises early. Your temperature management strategy should involve setting alarm thresholds, implementing effective cooling methods, and scheduling maintenance based on temperature trends to ensure reliability and extend transformer lifespan.
Top oil temperature vs Winding temperature Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com