Cold press juicing preserves more nutrients and enzymes by slowly crushing fruits and vegetables without heat, resulting in a nutrient-dense juice with a longer shelf life. Centrifugal juicing, while faster and more convenient, uses high-speed blades that generate heat, which can reduce nutrient quality and cause oxidation in your juice.
Table of Comparison
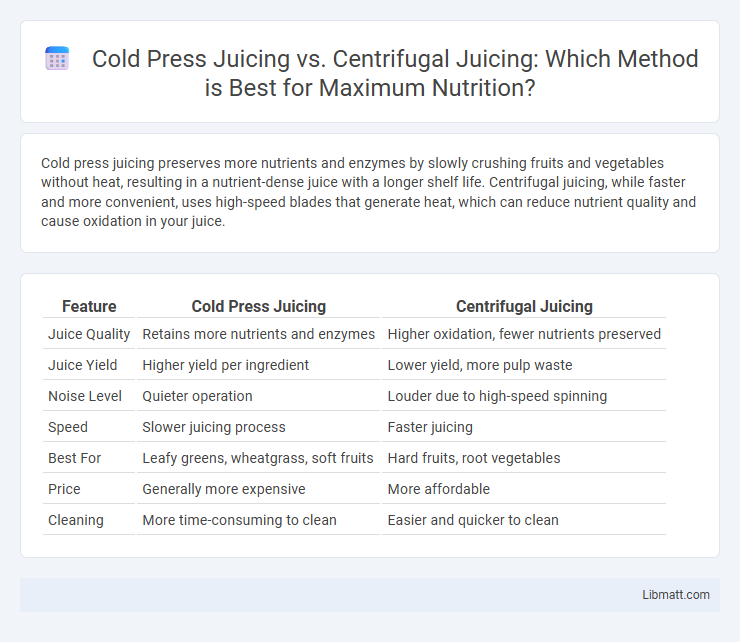
| Feature | Cold Press Juicing | Centrifugal Juicing |
|---|---|---|
| Juice Quality | Retains more nutrients and enzymes | Higher oxidation, fewer nutrients preserved |
| Juice Yield | Higher yield per ingredient | Lower yield, more pulp waste |
| Noise Level | Quieter operation | Louder due to high-speed spinning |
| Speed | Slower juicing process | Faster juicing |
| Best For | Leafy greens, wheatgrass, soft fruits | Hard fruits, root vegetables |
| Price | Generally more expensive | More affordable |
| Cleaning | More time-consuming to clean | Easier and quicker to clean |
Introduction to Juicing Methods
Cold press juicing uses a slow, hydraulic press to extract juice, preserving more nutrients and enzymes by minimizing heat and oxidation. Centrifugal juicing employs a high-speed spinning blade to shred fruits and vegetables, offering faster processing but generating heat that can reduce nutrient content. Understanding these juicing methods helps consumers choose between nutrient retention and speed based on their health goals and lifestyle.
What Is Cold Press Juicing?
Cold press juicing, also known as masticating juicing, uses a slow, crushing, and pressing method to extract juice from fruits and vegetables, preserving maximum nutrients and enzymes. This method operates at low temperatures, minimizing oxidation and retaining vibrant color, flavor, and nutritional content compared to centrifugal juicing. Cold press juicers are ideal for leafy greens and wheatgrass, producing higher yields and nutrient-dense juice with a longer shelf life.
What Is Centrifugal Juicing?
Centrifugal juicing uses high-speed spinning blades to shred fruits and vegetables, extracting juice quickly by separating it from the pulp through centrifugal force. This method generates more heat and oxidizes the juice faster, which can reduce nutrient retention compared to cold press juicing. Understanding how centrifugal juicing works helps you choose the best juicer based on your priorities for juice freshness and nutrient content.
Nutrient Retention Comparison
Cold press juicing preserves a higher concentration of vitamins, enzymes, and antioxidants by using slow, hydraulic pressure that minimizes heat and oxidation. Centrifugal juicing operates at high speeds, generating heat that can degrade sensitive nutrients like vitamin C and folate, resulting in lower nutrient retention. Studies show cold press juice retains up to 40-60% more nutrients compared to centrifugal methods, making it superior for maximizing nutritional benefits.
Juice Quality and Taste Differences
Cold press juicing preserves more nutrients and enzymes due to its slow, gentle extraction process, resulting in richer flavor and higher juice quality compared to centrifugal juicing. Centrifugal juicers use high-speed spinning blades that generate heat and oxidation, often leading to a lower nutrient content and a slightly diluted, less vibrant taste. Consumers seeking maximum juice freshness and nutritional value typically prefer cold press juicers for their superior taste and health benefits.
Oxidation and Shelf Life
Cold press juicing minimizes oxidation by using a slow, crushing process that preserves nutrients and enzymes, resulting in juice with a longer shelf life of up to 72 hours when refrigerated. Centrifugal juicing operates at high speeds, generating heat and introducing more air, which accelerates oxidation and reduces shelf life to around 24 hours. The reduced oxidation in cold press juice maintains higher vitamin content and freshness compared to the quicker degradation found in centrifugal juice.
Juicing Speed and Efficiency
Cold press juicing operates at a slower speed, using a hydraulic press that gently extracts juice while preserving nutrients and minimizing oxidation. Centrifugal juicing is faster, employing high-speed spinning blades to quickly shred fruits and vegetables, but can generate heat that may reduce nutrient content. Efficiency varies as centrifugal juicers handle harder produce more rapidly, whereas cold press machines excel in maximizing juice yield and quality, especially from leafy greens and soft fruits.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Cold press juicers generally require more time for cleaning due to their multiple parts and slow extraction process, but their components are often dishwasher safe, making maintenance manageable. Centrifugal juicers feature fewer parts and simpler designs, resulting in quicker cleaning times, though pulp can get stuck in small crevices requiring careful attention. You should consider your willingness to invest time in cleaning when choosing between cold press and centrifugal juicers for daily use.
Cost and Investment Considerations
Cold press juicers generally require a higher initial investment, often ranging from $200 to $600, due to their slow, efficient extraction method that preserves nutrients. Centrifugal juicers are usually more affordable, with prices between $50 and $200, making them a budget-friendly option for quick juice preparation. Your choice should consider not only the upfront cost but also the long-term value based on juice quality and machine durability.
Which Juicer Is Best For You?
Cold press juicers extract juice by slowly crushing fruits and vegetables, preserving more nutrients and yielding higher-quality juice ideal for health-conscious individuals. Centrifugal juicers operate quickly by shredding produce at high speeds, providing convenience and efficiency for users who need fast juicing without prioritizing maximum nutrient retention. Your choice depends on whether you value nutrient preservation and juice quality or speed and ease of use in your daily routine.
Cold Press Juicing vs Centrifugal Juicing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com