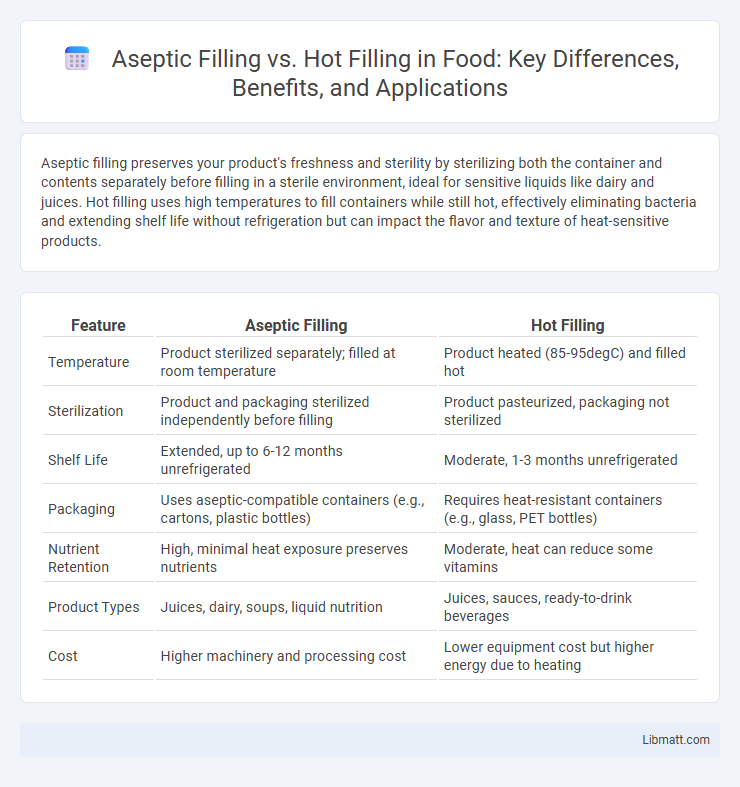
Aseptic filling preserves your product's freshness and sterility by sterilizing both the container and contents separately before filling in a sterile environment, ideal for sensitive liquids like dairy and juices. Hot filling uses high temperatures to fill containers while still hot, effectively eliminating bacteria and extending shelf life without refrigeration but can impact the flavor and texture of heat-sensitive products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aseptic Filling | Hot Filling |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Product sterilized separately; filled at room temperature | Product heated (85-95degC) and filled hot |
| Sterilization | Product and packaging sterilized independently before filling | Product pasteurized, packaging not sterilized |
| Shelf Life | Extended, up to 6-12 months unrefrigerated | Moderate, 1-3 months unrefrigerated |
| Packaging | Uses aseptic-compatible containers (e.g., cartons, plastic bottles) | Requires heat-resistant containers (e.g., glass, PET bottles) |
| Nutrient Retention | High, minimal heat exposure preserves nutrients | Moderate, heat can reduce some vitamins |
| Product Types | Juices, dairy, soups, liquid nutrition | Juices, sauces, ready-to-drink beverages |
| Cost | Higher machinery and processing cost | Lower equipment cost but higher energy due to heating |
Introduction to Beverage Filling Technologies
Aseptic filling preserves beverage quality by sterilizing both the container and the product separately, enabling extended shelf life without refrigeration. Hot filling involves heating the beverage to high temperatures before filling, effectively killing microbes but requiring heat-resistant containers. Your choice between these technologies depends on factors like product type, packaging materials, and desired shelf stability.
What is Aseptic Filling?
Aseptic filling is a sterile process where both the product and packaging materials are separately sterilized before being combined in a contaminant-free environment, ensuring extended shelf life without preservatives. This method is commonly used in dairy, juice, and pharmaceutical industries to maintain product quality and safety. Your choice of aseptic filling can significantly reduce microbial contamination risks compared to hot filling, preserving freshness and nutritional value.
What is Hot Filling?
Hot filling is a food and beverage packaging process where products are heated to a high temperature, usually around 85-95degC (185-203degF), to kill microorganisms and then immediately filled into sterilized containers. This method ensures product sterilization and extends shelf life without requiring preservatives or refrigeration. Your choice between hot filling and aseptic filling depends on factors like product type, packaging materials, and desired shelf stability.
Key Process Differences
Aseptic filling involves sterilizing both the container and the product separately before filling in a sterile environment, ensuring extended shelf life without preservatives. Hot filling heats the product to high temperatures and immediately fills it into warm, sanitized containers, relying on heat to sterilize during the process. Your choice depends on product sensitivity to heat and desired shelf stability.
Equipment Requirements Comparison
Aseptic filling requires specialized sterilization equipment, including steam sterilizers and sterile air filtration systems, to maintain contamination-free environments. Hot filling equipment demands heat-resistant containers and machinery capable of handling high temperatures during the filling process. Your choice depends on the balance between maintaining product sterility and accommodating thermal processing capabilities.
Product Compatibility and Limitations
Aseptic filling offers superior compatibility with heat-sensitive products like dairy, juices, and pharmaceuticals, preserving nutritional value and flavor by sterilizing both product and packaging separately. Hot filling suits products that can withstand high temperatures, such as juices and sauces, but may degrade quality or alter taste in heat-sensitive items. Your choice depends on the product's thermal stability and shelf-life requirements, ensuring optimal preservation and safety.
Packaging Material Considerations
Aseptic filling requires packaging materials with excellent barrier properties, such as multi-layered cartons or PET bottles coated with oxygen and light barriers, to maintain product sterility without refrigeration. Hot filling uses heat-resistant materials like glass or specially designed PET that can withstand elevated temperatures during the filling process while ensuring durability and product safety. The choice between these packaging materials directly impacts shelf life, product quality, and manufacturing efficiency in food and beverage production.
Shelf Life and Product Quality
Aseptic filling extends shelf life by sterilizing both product and packaging separately, preventing microbial contamination and preserving nutritional value and flavor. Hot filling involves filling the container with heated product, which can reduce microbial load but may cause slight nutrient degradation and flavor changes. Shelf life is typically longer with aseptic filling due to superior asepsis, while hot filling maintains product quality through heat resistance but may limit certain delicate ingredients.
Cost and Operational Efficiency
Aseptic filling generally involves higher initial capital investment and more complex equipment compared to hot filling, leading to increased upfront costs but lower energy consumption due to ambient temperature processing. Hot filling requires continuous heating and sterilization, resulting in higher operational costs from energy use and potential wear on machinery. While aseptic filling offers greater operational efficiency through extended shelf life without preservatives, hot filling can reduce packaging material costs by enabling simpler container requirements.
Choosing the Right Filling Method
Choosing the right filling method depends on product type, shelf life requirements, and production scale. Aseptic filling ensures extended shelf life by sterilizing both product and packaging separately, ideal for sensitive products like dairy and juices without preservatives. Hot filling suits acidic products and simpler processes but may impact flavor and packaging options due to heat exposure.
Aseptic Filling vs Hot Filling Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com