Pasteurized cheese offers enhanced safety by eliminating harmful bacteria through heat treatment, making it a reliable choice for sensitive groups, while raw milk cheese provides complex, rich flavors and unique textures derived from natural microflora, appealing to connoisseurs seeking authentic taste experiences. Understanding the differences can help you select the cheese that best suits your health considerations and flavor preferences.
Table of Comparison
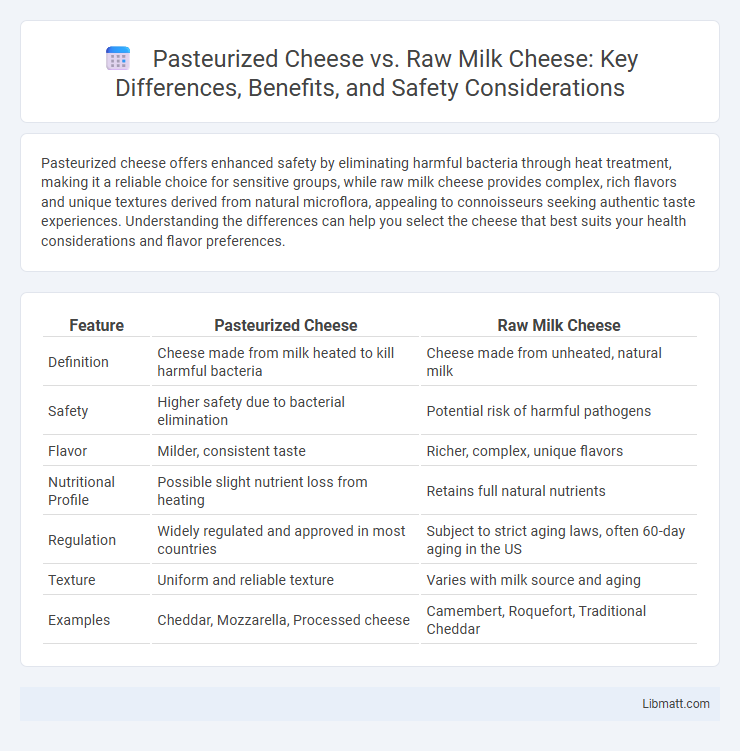
| Feature | Pasteurized Cheese | Raw Milk Cheese |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cheese made from milk heated to kill harmful bacteria | Cheese made from unheated, natural milk |
| Safety | Higher safety due to bacterial elimination | Potential risk of harmful pathogens |
| Flavor | Milder, consistent taste | Richer, complex, unique flavors |
| Nutritional Profile | Possible slight nutrient loss from heating | Retains full natural nutrients |
| Regulation | Widely regulated and approved in most countries | Subject to strict aging laws, often 60-day aging in the US |
| Texture | Uniform and reliable texture | Varies with milk source and aging |
| Examples | Cheddar, Mozzarella, Processed cheese | Camembert, Roquefort, Traditional Cheddar |
Introduction to Cheese Types
Pasteurized cheese is made from milk that has been heat-treated to kill harmful bacteria, ensuring safety and longer shelf life, while raw milk cheese is crafted from unheated milk, preserving natural enzymes and complex flavors. Raw milk cheese often has a richer taste profile and unique textures due to the presence of native microflora, whereas pasteurized cheese offers consistency and reduced risk of pathogens. Understanding these differences helps you choose cheese that aligns with your taste preferences and health considerations.
What is Pasteurized Cheese?
Pasteurized cheese is made from milk that has been heat-treated to eliminate harmful bacteria, enhancing food safety and extending shelf life. The pasteurization process typically involves heating milk to at least 161degF (72degC) for 15 seconds, effectively reducing pathogens without significantly altering the cheese's flavor or texture. This type of cheese is widely favored in commercial production due to regulatory standards and consumer safety concerns.
What is Raw Milk Cheese?
Raw milk cheese is made from milk that has not undergone pasteurization, preserving its natural enzymes and microorganisms. This cheese offers complex flavors and textures influenced by the unique microflora of the milk and the aging process. Your choice between raw milk and pasteurized cheese impacts taste, safety, and legal availability, with raw milk cheese often favored by connoisseurs seeking traditional and artisanal qualities.
Key Differences Between Pasteurized and Raw Milk Cheese
Pasteurized cheese is made from milk heated to a specific temperature to kill harmful bacteria, ensuring safety and longer shelf life, while raw milk cheese is produced from unheated milk, preserving natural enzymes and complex flavors. Raw milk cheese often contains a richer texture and more nuanced taste profiles due to native microflora, but it carries a higher risk of foodborne pathogens compared to pasteurized cheese. Regulatory standards vary globally, with some countries imposing strict aging requirements on raw milk cheeses to reduce health risks.
Safety and Health Considerations
Pasteurized cheese reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses by eliminating harmful bacteria such as Listeria, Salmonella, and E. coli, making it a safer option for pregnant women, young children, and immunocompromised individuals. Raw milk cheese contains beneficial probiotics and enzymes that can enhance gut health, but it carries a higher risk of contamination if not properly aged and handled. Regulatory agencies often require minimum aging periods for raw milk cheese to ensure pathogenic bacteria are minimized, balancing safety with potential health benefits.
Flavor and Texture Profiles
Pasteurized cheese offers a consistent, milder flavor and a smooth, uniform texture due to heat treatment that reduces bacteria and enzymes. Raw milk cheese provides a complex, robust flavor and varied texture, with richer aromas and a more pronounced character resulting from natural microbial activity. Your choice between the two depends on whether you prefer reliable mildness or a bold, nuanced tasting experience.
Nutritional Comparison
Pasteurized cheese undergoes heat treatment that reduces certain heat-sensitive vitamins and enzymes, potentially lowering its nutritional complexity compared to raw milk cheese. Raw milk cheese retains a broader spectrum of natural probiotics, vitamins B and C, and beneficial enzymes that contribute to enhanced digestibility and immune support. Nutritional differences hinge on the balance between safety from pathogens in pasteurized cheese and the preservation of bioactive compounds in raw milk cheese.
Legal Regulations and Availability
Legal regulations surrounding pasteurized cheese mandate strict pasteurization processes to eliminate harmful bacteria, ensuring widespread availability in supermarkets and commercial outlets. Raw milk cheese regulations vary significantly by country and state, with some jurisdictions imposing aging requirements of at least 60 days before sale to reduce microbial risks, resulting in limited and often specialty market availability. Availability of raw milk cheeses is generally restricted to artisanal producers and specialty cheese shops due to regulatory hurdles and safety concerns.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Consumer preferences show a growing interest in raw milk cheese due to its perceived richer flavor and artisanal qualities, appealing to food enthusiasts seeking authentic taste experiences. Pasteurized cheese remains popular for safety concerns, especially among families and healthcare institutions prioritizing low risk of pathogens. Current trends indicate an increase in specialty cheese markets where raw milk varieties are featured prominently, reflecting a niche yet expanding segment driven by gourmet demand and cultural heritage appreciation.
Making an Informed Choice
Choosing between pasteurized cheese and raw milk cheese requires understanding their production differences and health implications. Pasteurized cheese undergoes heat treatment to eliminate harmful bacteria, ensuring safety, while raw milk cheese retains natural enzymes and complex flavors, offering a richer taste profile but with potential health risks. Your informed choice depends on prioritizing safety standards or seeking traditional cheesemaking authenticity.
Pasteurized Cheese vs Raw Milk Cheese Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com